File - Ms. Weigel's Agriculture Class

Unit 4
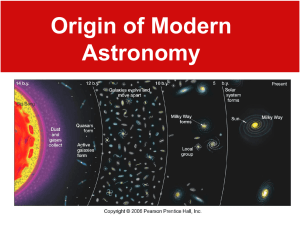
Earth’s place in the universe
Agriculture Earth Science
Ms. Weigel
Student Objectives
1.
Describe the contributions of ancient Greeks to astronomy
2.
Compare and contrast the geocentric and heliocentric models of the solar system
3.
Explain the contributions to astronomy of
Copernicus, Brahe, Kepler, Galileo and Newton
The observable universe
https://youtu.be/HiN6Ag5-DrU
Class discussion: How do you think the earth fits in the universe?
Vocabulary Terms
1.
Astronomy
2.
Geocentric
3.
Heliocentric
4.
Retrograde motion
5.
Ellipse
6.
Astronomical Unit (AU)
Ancient Greeks
Astronomy is the science that studies the universe.
Astronomy deals wit properties of objects in space and their laws.
• The “golden age of early astronomy (600 B.C. –
A.D. 150)
• They developed basics of geometry and trigonometry
• Using math, they measured the sizes and distances of the sun and the moon
Aristotle
• 384 – 322 B.C.
• Concluded that earth is round because it always casts a curved shadow on the moon when it passes between moon & sun.
His belief that the earth was round was abandoned during the middle ages
Eratosthenes
• 276-194 B.C.
• The first successful attempt to establish the size of
Earth
• Observed angles of noonday sun in two Egyptian cities north and south of each other – Syene
&Alexandria
• Finding angles were 7 degrees different or 1/50 he decided the circumference of Earth must be 50 times the distance of the cities
• His view – earth 39,400 kilometers
• Modern- 40,075 kilometers
Hipparchus
• Second century B.C.
• Greatest of the early Greek astronomers best know for his Star Catalog
• Determined the location of almost 850 stars
• Divided them into 6 groups depending on brightness
• Measured length of the year
• Developed a method for predicting lunar eclipses
Geocentric Model
• The Greeks believed the geocentric view.
They thought that Earth was a sphere that stayed motionless at the center of the universe
A) In the geocentric model , the mon, sun, and the known planets- Mercury, Venus, Mars and
Jupiter- orbit earth
B) This model, however was not correct
Heliocentric Model
• Aristarchus (312-230B.C.) was the first Greek to believe in a sun-centered universe
• In the heliocentric model , Earth and the other planets orbit the sun.
• He used geometry to calculate relative distances form earth to the sun and from the earth to the moon.
Geocentric Vs. Heliocentric
• Though there was evidence to support the heliocentric mode, the Earthcentered view dominated Western thought for nearly 2000 years.
Ptolemaic System
Claudius Ptolemy
• 13 Volume published work in A.D. 141 which showed a model of the universe that was called the Ptolemaic System
• Ptolemy theory accounted for the movements of the planets
Ptolemy and Retrograde Motion
• The model showed the planets moving in a circular motion around motionless Earth
• The background of stars seemed odd to him
• Periodically each planet appears to stop, reverse direction for time then resume eastward motion
• The apparent wester ward drift is called retrograde motion.
• Negative part of the theory- he said it was Earth
Centered
The Birth of Modern Astronomy
• The development of modern astronomy involved a break from pervious philosophical and religious views.
• Scientist began to discover the universe governed by natural laws.
Nicolaus Copernicus
• 1473-1543 from Poland
• The first great astronomer to emerge after the middle ages
• Concluded that Earth is a plenet. He proposed a model of the solar system with the sun at the center
Tycho Brahe
• 1546-160-Danish nobility born
3 yrs after the death of Copernicus
• Brahe designed and built instruments such as the angle measuring device
▫ He had king Frederick II build an observatory in
Copenhagen even though there was no telescope yet
• His observations, especially of Mars, were far more precise than any made previously
Johannes Kepler
• 1571-1630
• Discovered three laws of planetary motion
1.
The path of earth planet around the sun is an ellipse with the sun at one focus
2.
Each planet revolves so that an imaginary line connecting it to the sun sweeps over equal areas in equal time intervals
3.
The square of the length of time it takes a planet to orbit the sun is proportional to the cube of it’s mean distance to the sun
Kepler
• The orbital period of revolution is measured in
Earth years. The planets distance is expressed in
AU.
• The astronomical Unit (AU) is the average distance between Earth and the Sun. About 150 million kilometers
Galileo Galilei
• 1564-1642 was the greatest Italian scientist of the renaissance
• Most important contributions were his descriptions of the behavior of moving objects
• Using the telescope Galileo was able to view the universe in a new way
• Galileo made 5 discoveries
The discovery of four satellites, or moons orbiting Jupiter.
• This proved that the old idea of Earth being the only center of motion in the universe was wrong
The discovery that the planets are circular disks, not just points of light as was previously thought.
• Showed that planets must be earth like
The discovery that Venus has phases just like the moon
• Venus orbits it’s light source- the sun
• Galileo saw that Venus appears smallest when it is in full phase and farthest from the earth
The Discovery that the moon’s surface was not smooth.
• He saw mountains, craters and plains.
• He thought the plains might be bodies of water
The discovery that the sun had sunspots
• Tracked movement of spots and estimated rotational period of the sun as under one month
Sir Isaac Newton
• 1642-1727- born in the year of Galileo’s death
• Proposed moving object will continue to move at a constant speed or in a straight line – known as inertia.
• Newton was the first to
Formulate and test the law of universal gravitation.
Universal Gravitation
• According to Newton, every body in the universe attracts every other body with a force that is directly proportional to their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their center mass
• The law also states that the greater the mass of the object, the greater is it’s gravitation force.
• Example: the moon causing ocean tides on earth
Critical Thinking
Applying concepts
What role did the telescope play in Galileo’s contributions to science
Discovery Channel Video
Space exploration
• Historical Field Trip