The Byzantine Empire and Russia
advertisement

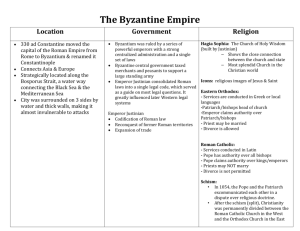
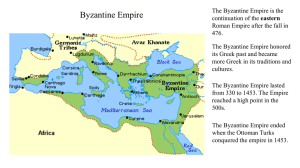
The Byzantine Empire What was the Byzantine Empire? • The predominantly Greek-speaking continuation of the Roman Empire during the Middle Ages. • Initially the eastern half of the Roman Empire, it survived the collapse of the Western Roman Empire and continued to thrive • Its capital city was Constantinople, originally known as Byzantium. • Existed for an additional thousand years until it fell to the Ottoman Turks in 1453. • During most of its existence, the empire was the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. Justinian • Crowned Emperor of the Byzantine Empire in 527 A.D • Hoped to reunite the Eastern & Western Roman Empires • Made the Eastern Orthodox Church the Official Church of the Byzantine Empire • Justinian’s Code • Justinian put Roman laws into a book called “The Body Of Civil Laws” • Able advisers • Theodora – Justinian's wife • Convinced him to change laws: • Divorce laws for more legal power for women • Allowed a woman to own property in the same amount as dowry • Belisarius – leader of the army • Crushed Nika revolt • Won back lands from Germania Strengths of the Empire • Leaders were clever diplomats • Military • • Well trained Greek fire on naval ships • Strong, centralized government • Constantinople was a center of trade • Large tax revenues The Christian Church • Iconoclastic Controversy • • • • Some Byzantines kept icons (pictures or statues of Jesus, Mary, etc.) Iconoclasts - believed keeping icons was wrong Emperor Leo III ordered all relics be destroyed The Pope called a meeting of church officials • Declared icons to be ok • Contributed to the Great Schism (split in the church) • Roman Catholic Church in Rome • Eastern Orthodox in Constantinople Byzantine Culture • Cyril and Methodius were Christians that helped spread the gospel • Created an alphabet for the Slavs • Cyrillic language • Art • Mosaic – picture or design made from small pieces of enamel or glass • Architecture • Hagia Sophia – “holy wisdom” The Decline of the Empire • Conflicts with outside powers • • Persians, Slavs, Turks, Muslims, Germans Even disagreements with Western Empire caused conflicts • Seljuq Turks captured Asia Minor • Sunni dynasty in Persia, preceded Safavids • Ottoman Turks conquered Constantinople Legacy: • Impacted Russia • • • Religion: Eastern Orthodox Language Art/Architecture Achievements: • Built the Hagia Sofia • Spread Christianity • Justinian’s Code of Laws • Continued Roman culture and ideals after the fall of the Western Roman Empire