Cabbage Lab: Testing pH Values

Cabbage Lab: Testing pH Values
Purpose:
To use a natural indicator to test pH values of various substances
To use pH values to classify substances as an acid or a base
To determine the relative concentrations of unknown bases by titration
Procedure:
1.
Put on safety glasses and apron.
2.
Copy Table 1 into a notebook and for each substance listed, hypothesize if it is acid, base, or near neutral and record in Table 1.
3.
These substances will irritate the skin upon contact. In case of accidental contact, rinse generously with water.
4.
Place 3-5 drops of the cabbage juice indicator in one well of a clean well plate.
5.
Being careful not to overflow the well, add 3-5 drops of the first substance to be tested.
6.
After a few moments, record the color of the liquid in Table 1.
7.
Use Table 2 to determine the corresponding pH and record in Table 1.
8.
Use the pH value to classify the substance as an acid, base, or near neutral and record in
Table 1.
9.
Repeat steps 3-7 for the remaining substances and any possible additional substances.
Be sure to record the data in Table 1.
10.
Carefully rinse the liquids from the well plate into the sink.
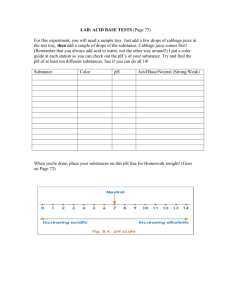
TABLE 1. pH Hypotheses and Data
Substance
Vinegar
Detergent
Water
Lemon Juice
Windex w/
Ammonia
Drano
Soda Pop
Hydrochloric
Acid (HCl)
Additional
Substances??
Acid/Base
Prediction
Observed Color pH of Observed
Color
Acid or Base?
TABLE 2. Color Key to pH Values pH
2-3
3-4
4-6
6-8
Cabbage Juice Color (natural indicator)
Red
Pink
Purple
Blue-Green
8-12
12-14
pH Scale
Green
Yellow
I___________________________________I_________________________________________I
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Most Acidic Most Basic
Analyze & Conclude:
1.
Which chemical had the lowest pH value (most acidic)?
2.
Which chemical had the highest pH value (most basic)?
3.
Explain what a strong acid is and tell if all acids are equally dangerous.
4.
Explain what a strong base is and tell if all bases are equally dangerous.
5.
Predict what would happen if an acid and a base were mixed together. (Assume both chemicals are in equal amounts and concentrations).
Titration Option: (Time allowing)
1.
In a clean well plate, add exactly 5 drops of unknown base A to a clean well.
2.
Add exactly 1 drop of phenolphthalein to the same well. The solution should turn pink.
3.
Add 1 M HCl one drop at a time and count the number of drops needed to turn the solution clear. You may use a toothpick to mix the liquids. Record the number of drops in Table 3, below.
4.
Repeat steps 1-3 for unknown bases B, C, and D. Be sure to record the data below.
5.
Repeat steps 1-4 and record data in the Trial 2 and Trail 3 rows.
6.
Carefully rinse the liquids from the well plate into the sink.
7.
Calculate the average of the three trials and record in Table 3.
8.
Using the data in Table 3, list the base letters in order of increasing concentration.
TABLE 3. Titration Data
Drops HCl Trial 1
Drops HCl Trial 2
Drops HCl Trial 3
Average Drops
Increasing
Concentration
Base A Base B Base C Base D
To turn in for the Lab report:
Cabbage Lab:
Data Table 1 and complete sentence answers to the Analyze and Conclude questions.
Titration Option:
Data Table 3 and the response to step #7 listing the base letters in order of increasing concentration.