Schmidt_LP2_GroupPamp._DP

Factors that affect development before conception
There are two main factors that affect your development before you are even conceived. These factors are your mother and father. You are made up of generations and generations of selection. Before you and even before your parents, your grandparents made selections that led to the conception of your parents. This can back as far as man has walked the earth.
Natural selection is known as the evolutionary process by which individuals of a species that are best adapted are the ones that survive and reproduce. This idea was introduced by Darwin and is commonly known as survival of the fittest. This idea was taken to the next step in evolutionary psychology . Evolutionary psychology puts emphasis on the idea that adaptation, reproduction, and “survival of the fittest” shape behavior. Increasing reproductive success and passing genes on is what this view favors. This view implies that women seek mates that have attractive traits to be their partners; thinning out those who have less attractive traits. Your mother and father were more likely in favor of each other traits, maybe even subconsciously eliminating those who were less appealing to mate with. Natural selection overtime has effected your development prior to conception because nature is naturally making the species better and better therefore making you better. (Santrock, 2011)
Who you are is mapped out on a blue print that is the size of a single cell. All of the trillions of cells that make you who you are contain that blue print or “genetic code”. What determines your layout of DNA is inherited species from species not just from your parents. Your floor plan is made up from generations of selection. (Santrock, 2011)
Your parents set the stage for your genes . Each parent gives you chromosomes usually resulting in you having 23 pairs; your mother gives you half of the set and your fathers give you the other half. Inside of the chromosomes lies your deoxyribonucleic acid or more commonly referred to as DNA . Your DNA is a complex molecule that contains your genetic information.
(Santrock, 2011, p. 58) Your genes are units of DNA that reproduce and manufacture the proteins that maintain life. (Santrock, 2011)
Picture options:
Genetic and Chromosomal Foundations of development
Mitosis , meiosis , and fertilization are the steps in which your genes get passed down to you.
The first step, mitosis, is when a nucleus in the cell duplicates itself to form a new cell which has the same DNA as the original cell. The second is called meiosis and is different for men and women because it is a special cell division that forms eggs and sperm. In men meiosis takes place in the testes and in women in takes place in the ovaries. With both sexes the end result is duplicated chromosomes that have been divided two times to form four cells resulting with sperm and egg to have 23 unpaired chromosomes . Finally there is fertilization where sperm and egg come together to form a single cell. This cell is called a zygote where the 23 pairs of chromosomes pair up to form one set.
When a zygote splits after fertilization the result is identical twins who share the same genetic make-up. Fraternal twins are not from one zygote but two separate eggs being fertilized .
Identical twins are different from one another even though they have the same DNA . Although they have the same genotype which is a person’s genetic heritage they have a different phenotype which is how ones genotype is expressed in observed and measurable characteristics. (Santrock, 2011)
There are several principles that explain why genotypes create different phenotypes . The
Dominant-Recessive Genes Principle explains how one gene is dominant and overrides the other recessive gene . If both genes are recessive than that gene has a chance influence a trait.
Sex-Linked Genes explains how most mutated genes are recessive and depending on your sex can affect you differently. X-linked inheritance is when a muted gene is carried on the X chromosome . Males only have one X chromosome so they would be more likely to carry an xlinked disease because they do not have a copy to counter the gene . Genetic Imprinting is when one gene “silences” the other and the expression of a gene has different effects depending if you received the gene from your mother or father. (Santrock, 2011, p. 61)
Polygenic Inheritance is a complex genetic transmission where your genes interact with different genes and are also influenced by environment. (Santrock, 2011)
Abnormalities sometimes happen in the genetic process whether it is harmful genes or whole genes that do not separate correctly during meiosis . Chromosomal abnormalities happen when a male’s sperm or females ovum do not have a set of 23 chromosomes . Down syndrome is the most common association of a chromosome abnormality . An individual who has an extra set of chromosome 21 has a chromosomally transmitted form of mental retardation known as Down syndrome . (Santrock, 2011)
There are also sex-linked chromosomal abnormalities where an individual is either born with an extra Y or X chromosome or a female without an X chromosome . A genetic disorder called
Klinefelter syndrome is where a male is born with an extra X chromosome resulting in undeveloped testes, become tall, and sometimes have enlarged breasts. Another genetic
disorder called Fragile X syndrome is where the X chromosome has an abnormality where it becomes constricted and often breaks off. An individual with Fragile X syndrome could have mental deficiency, learning disabilities, short attention span or mental retardation. Fragile X syndrome usually occurs in males probably because females have the extra X chromosome to contradict the effects. (Santrock, 2011)
A genetic disorder that takes place in females where there is a missing X chromosome or a second X chromosome that is partially deleted is called Turner syndrome . Females with
Turner syndrome tend to be shorter, have a webbed neck, may be infertile, and have difficulty in mathematics. Males can have a genetic disorder called XYY syndrome where they have an extra Y chromosome . (Santrock, 2011)
Harmful genes are the cause for over 7,000 genetic disorders. One of these genetic disorders is
Phenylketonuria or PKU where an individual cannot metabolize amino acids properly. It is easily detected and can be treated but if it is not it can lead to mental retardation and hyperactivity. Sickle-cell anemia is another genetic disorder that impairs the body’s red blood cells. A recessive gene causes red blood cells to be shaped different not allowing them to receive the right amount of oxygen. This causes anemia and early death to the individuals.
Diabetes is also a genetic disorder where your body does not make enough insulin leading to abnormal metabolism of sugar. (Santrock, 2011)
Picture options:
Hazards to prenatal development
Even in within the protection of the womb there can be hazards to a fetus. Teratogen is any agent that causes a birth defect or negatively alters cognitive and behavioral outcomes.
(Santrock, 2011, p. 86) Almost every fetus is at risk for at least one teratogen because there are so many; this makes it difficult to determine which teratogen causes which problem.
Teratology is the field of study that studies the causes for birth defects. The field of study that focuses on the cognitive and behavioral half of teratogens is called behavioral teratology.
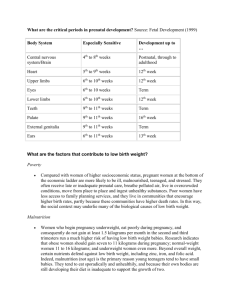
There are three factors that affect the severity and type of defect; dose , genetic susceptibility , and time of exposure . The first factor is dose which means the greater the dose of an agent the greater the effect. An example of an agent would be any type of drug. The second is genetic susceptibility which means that the type or severity of the abnormality caused by the teratogen is directly correlated to the genotype of the pregnant mother and the genotype of the fetus. Each period of development for a fetus will have different outcomes for teratogens .
For example the embryonic period is more vulnerable than fetal period . (Santrock, 2011)
Pregnant women are given and take prescription and nonprescription drugs in the United States that have effects on the fetus. Antibiotics, some antidepressants, some hormones, and
Accutane can function as teratogens . Pregnant women who take antidepressants Diet pills and high dosages of aspirin are examples of nonprescription drugs that can function as a teratogen .
(Santrock, 2011)
Psychoactive drugs such as caffeine, alcohol, nicotine, cocaine, methamphetamine, marijuana, and heroin can be teratogens . Caffeine is recommended to not consumed or consumed sparingly because women who consumed 200 milligrams or more a day were likely to have a miscarriage. Drinking alcohol while pregnant can lead to fetal alcohol spectrum disorder
(FASD) which is a cluster or abnormalities that offspring of pregnant women that drank can have. Some of these abnormalities include facial deformities, defective limbs, face and heart.
Children with FASD can have learning problems, below average intelligence, or mental retardation. Nicotine can have negative effects such as preterm births, low birth weights, fetal and neonatal deaths, respiratory problems, sudden infant death syndrome, and cardiovascular problems. Illicit drugs like cocaine can cause reduced birth weight, length, and head circumference. It can also cause neurological, medical, and cognitive defects. Pregnant women who use methamphetamine put their babies at risk for high infant mortality, low birth weight, and developmental and behavioral problems. Marijuana use of pregnant women can lead to lower intelligence in children. Use of heroin in pregnant women can lead to children to go through withdrawal symptoms like tremors, irritability, abnormal crying, disturbed sleep, and impaired motor control. (Santrock, 2011)
When the mother and fathers blood types are incompatible is another teratogen . If a fetus and mothers blood types end up being incompatible the mother’s immune system could produce antibodies that would attack the fetus and this could result in miscarriage, stillbirth, anemia, jaundice, heart defects, brain damage, or death soon after birth. First born babies are less likely to be at risk but with each birth risk increases. Mothers can be given a vaccine so their immune system does not attack the fetus. Babies can also be given blood transfusions before or right after birth that are affected by this. (Santrock, 2011)
Radiation, toxic waste, and other chemical pollutants are all examples of environmental hazards to the fetus. (Santrock, 2011) These things should not just be a concern for the pregnant mother but for any male thinking about becoming a father. Exposure to lead, radiation, some pesticides, and petrochemicals can cause abnormalities in sperm. These abnormalities can lead to miscarriages or diseases such as childhood cancer. (Santrock, 2011)
There are also teratogens within the womb. Maternal diseases and infections, if they cross the placenta or during birth, can cause birth defects. Syphilis can cause eye lesions and skin lesions. Genital herpes can give newborns this virus when they are delivered. If a mother has
AIDS her offspring could be affected by gestation across the placenta, during delivery, or postpartum during breast feeding. If a mother has HIV her baby could be born with HIV, be infected and show symptoms, or not be infected at all. If a mother has gestational diabetes the infants are at risk for having it. (Santrock, 2011)
Pregnant women can create teratogens for a fetus. A fetus depends completely on their mother for nutrition. A pregnant woman’s nutrition and diet are very important to a developing fetus.
Being overweight can lead to infertility, hypertensive disorders, diabetes, and a cesarean section delivery. In terms of the fetus it can lead to macrosomia, intrauterine fetal death, still birth, and admission to the NICU or neonatal intensive care unit. To make yourself low risk including folic acid in your diet whether it is alone or in a multivitamin will increase your chances for a healthier pregnancy. Eating fish can be healthy but because of the mercury levels in their environment it could be dangerous for your fetus. (Santrock, 2011)
Age is more than just a number when it is referring to the age you become pregnant. There are two harmful maternal ages; adolescence and 35 years and older. Morality rates for adolescent mothers infants are double that of infants born to mothers in their twenties. Down syndrome is a greater risk for children born to women who are 35 years or older. (Santrock, 2011)
Intense fears, stress, anxieties, and other emotions or negative moods are teratogens . They can indirectly cause the mother to use drugs or have poor prenatal care. High anxiety and stress can also directly affect the offspring by causing them to have a high risk for emotional and cognitive problems, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and language delay. Depression can also cause slower prenatal growth rates and preterm birth. (Santrock, 2011)
Picture options:
Cultural differences in pregnancy, delivery, and prenatal development
Your ethnicity and cultural differences make you who are. Pregnancy is no exception in being different depending on your culture. In the Korean culture women are submissive to their husbands and their husbands’ family due to their cultural hierarchy. Giving birth to a boy is highly desired in this culture, surrogate mothers may be found just to accomplish having a boy.
In the Korean culture the mother-inlaw makes the decisions and it is the mother’s job only to focus on positive things to ensure good features and shape for the baby. Korean women are not allowed to consume “broken” foods (cookies, crackers, duck, and tofu) or hot foods because it would lead to a weak child. Looking at dead flowers or dead animals is also not permitted because this is thought to lead to negative features for the baby. It is common to go to a fortune teller to find out the sex, due date, and appropriate name for the baby. (University of Hawaii,
2005)
In Japan Midwives is a large part of the delivery process. They attended to the pregnant mothers until the baby is ready to be born, and assist the doctor and mother during delivery.
(Megan, 2011) The Mayans of Mexico expect the father of the child to be in the delivery room during birth. It is such a high expectation that stillbirths are blamed on the father not being there.
The mother of the pregnant woman is also expected there, and the first birth usually takes place in her home. If there are difficulties during labor other Mayan women who have given birth before will come to the home to assist in the birth. A midwife is also present whose only prerequisite is being a well respected member of the society. (Jordan, 1992)In Turkey no male is allowed in the delivery area. It is thought to be shameful for any male, including the husband, to see a womans genital. It is the norm for a Turkish woman to give to birth in the mother-in-
laws home where a government midwife is present in case of difficulties. (Delaney, 2000) These traditions are very unlike America where mothers typically give birth in hospitals where the father, nurses, and medically trained obstetrician are present. (Jordan, 1992) The position in which a mother gives birth also varies. In the United States women usually give birth laying down on a bed with their legs separated, pushing the baby the out and assisted by the doctor. In
Turkey a women sits in a washtub on a stool using gravity to help push the baby out. (Delaney,
2000)
In the country of Israel alone there are cultural differences between Arab women and Jewish mothers during delivery. Arab women are more likely to have more people in the room, have higher expressions of pain, and have more of difference people in the room. Jewish mothers are more likely to have epidurals than Arab mothers. (Rassin, Klug, Nathanzon, Kan, & Silner,
2009) In Korea it is typical that the mother-in-law be a part of the entire labor. It is not allowed for the mother to show any signs of pain during delivery. Their culture tells them these are signs of shame and weakness. (University of Hawaii, 2005)
Depending on your culture you could be more likely for different hazards in your prenatal development . PKU is associated with your ethnicity and is more commonly found in Caucasian babies than any other race. Sickle-cell disease is recessive, but is more likely to diagnose to
West African and African American babies. It is so popular in West Africa that almost half the babies have this trait. People from the Mediterranean, Caribbean, India, Arab, and Latin
America are also more likely to have sickle-cell traits or disease. Jewish couples of Eastern
European heritage have about 1 in every 3,000 babies suffer from the recessive disorder Tay-
Sachs disease. In African countries HIV/AIDS is a wide spread problem. In South Africa alone
30% of pregnant women have the HIV virus . (Pearson Highered)
Picture options:
References
Delaney, C. (2000). Making Babies in a Turkish Village. In C. Delaney, A World of Babies: Imagined
Childcare Guides of Seven Societies (pp. 117-144). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Jordan, B. (1992). Birth in Four Cultures. Prospect Heights, IL: Waveland Press.
Megan. (2011, March 8). 10 Differences in Pregnancy and Parenting in Japan and the US from the
Viewpoint of a Natural Mama. Retrieved September 13, 2012, from ichigo means strawberry : http://ichigomeansstrawberry.blogspot.com/2011/03/10-differences-in-pregnancy-and.html
Pearson Highered. (n.d.). Prenatal Development. Retrieved September 14, 2012, from Pearson Highered: http://www.pearsonhighered.com/assets/hip/us/hip_us_pearsonhighered/samplechapter/0205256023
Rassin, M., Klug, E., Nathanzon, H., Kan, A., & Silner, D. (2009). Cultural differences in child delivery: comparisons between Jewish and Arab women in Israel. Internation Nursing Review , 123-130.
Santrock, J. W. (2011). Life-Span Development 13.e. New York: McGraw-Hill.
University of Hawaii. (2005, October 7). Korean Childbirth Traditions. Retrieved September 14, 2012, from Transcultural Index: http://www.hawcc.hawaii.edu/nursing/RNKorean_04.html