Bluetooth
advertisement

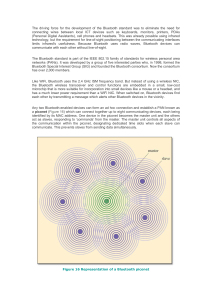
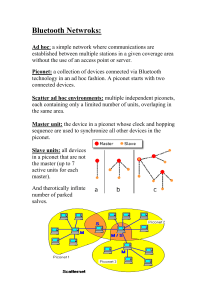
Bluetooth By Sonny Leung Jennifer Portillo Thomas Razo Samson Vuong Introduction • What is Bluetooth? • What does it do? • History of Bluetooth Introduction (cont’d) • Is Bluetooth here to stay? • What should we expect from Bluetooth in the future? What Bluetooth Delivers to the end-user • Connects a wide range of computing and telecommunication devices • Expand communication capabilities • Devices can communicate with each other with wireless connectivity User Application • Car manufactures Industry • E-Mail / Internet / Intranet Access • Headsets • Bluetooth will facilitate Local Area Networks Bluetooth in Action In the house Source: http//:www.motorola.com In the Office ... Home Security On the Road Source: http//:www.motorola.com On your Car Source: http//:www.motorola.com Bluetooth Specifications • Things that you must have: – Transceivers and Receivers that can send and receive data because they use Radio Waves. – MAC Address (Physical Address) • Burnt on the NIC card by the manufacturer. – PIN Number • To identify the user using the device. – A Piconet – A FHHS protocol What is a Piconet? • A Piconet session is a communication link that must be created between devices for devices to communicate with each other. • This is done when the MAC address and the PIN number match. Piconet (cont.) • If two devices come onto contact with each other( 32 feet) the user will be prompted to initiate a communication session • Users then can either deny or accept the request to initiate a session • Only devices approved by the user can take part in the session • Data will appear as noise to unauthorized devices (A great security feature). FHHS • Bluetooth devices use a protocol called (FHHS) Frequency-Hopping Spread Spectrum . • Uses packet-switching to send data. • Bluetooth sends packets of data on a range of frequencies. • In each session one device is a master and the others are slaves. • The master device decides at which frequency data will travel. FHHS • Transceivers “hop” among 79 different frequencies in the 2.4 GHz baud at a rate of 1600 frequency hops per second. • The master device tells the slaves at what frequency data will be sent. • This technique allows devices to communicate with each other more securely. FHHS Example Source: http://www.xircom.com Bluetooth Security • Modes – Security Mode 1 • No Security – Security Mode 2 • Service Level Enforced Security • Implemented after channel is established – Security Mode 3 • Link Level Enforced Security • Implemented before channel is established Devices • “Trusted” – No Restrictions • “Untrusted” – Restrictions, Access is limited Service Levels • Authorization and Authentication • Authentication Only • Open to all Devices Link Level • Bluetooth Device Address • Private Link Key • Private Encryption Key • Random Number Bluetooth Secure Enough? • Not enough for confidential and top secret information now but . . . • Security will Improve – Improve exisiting security – Implement new security Wrap up • Growing Technology • Automation For More Information Please Visit The Following Sites • www.motorola.com • www.xircom.com • www.palowireless.com • www.bluetooth.com