Bluetooth Netwroks:
Bluetooth Netwroks:
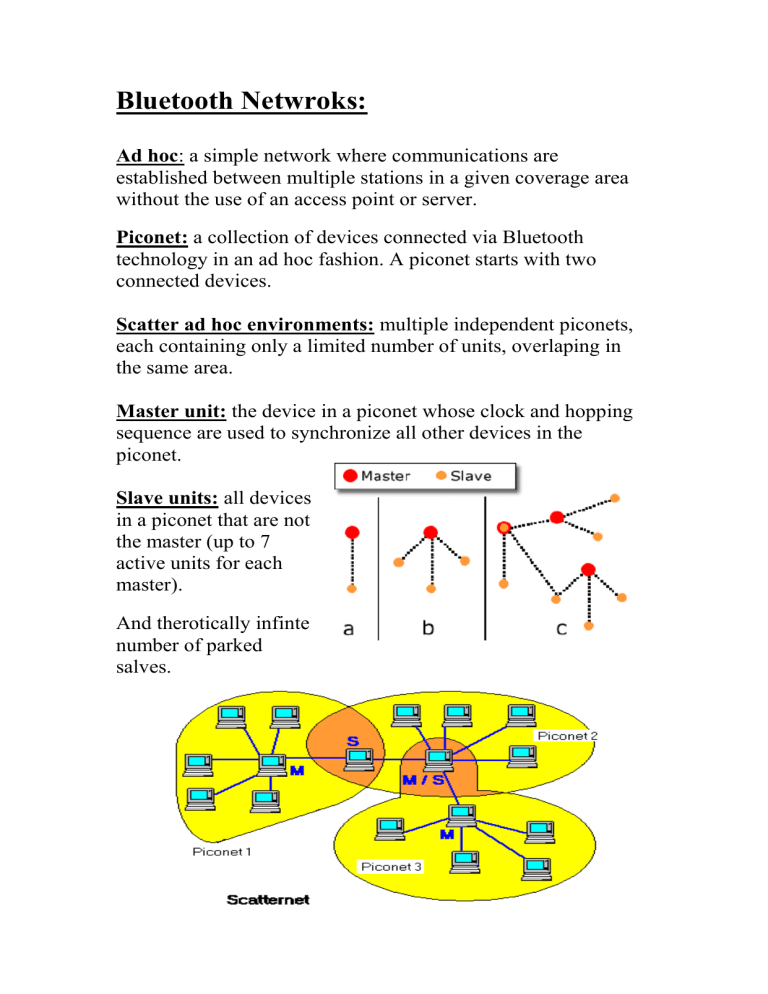
Ad hoc : a simple network where communications are established between multiple stations in a given coverage area without the use of an access point or server.
Piconet: a collection of devices connected via Bluetooth technology in an ad hoc fashion. A piconet starts with two connected devices.
Scatter ad hoc environments: multiple independent piconets, each containing only a limited number of units, overlaping in the same area.
Master unit: the device in a piconet whose clock and hopping sequence are used to synchronize all other devices in the piconet.
Slave units: all devices in a piconet that are not the master (up to 7 active units for each master).
And therotically infinte number of parked salves.
Connections establishment:
STANDBY: unconnected unit (before any connections in a piconet are created ) periodically "listens" for messages every 1.28 seconds on a set of 32 hop frequencies .
A connection is made by a PAGE message being sent if the address is already known, or by an INQUIRY message followed by a subsequent
PAGE message if the address is unknown.
HOLD: A power saving mode can be used for connected units in a piconet if no data needs to be transmitted.
SNIFF: (devices that are synchronized to a piconet, and which have temporarily entered power-saving modes, a slave device listens to the piconet at reduced rate.
PARK: (devices in a piconet which are synchronized but do not have a
MAC addresses), a device is still synchronized to the piconet but does not participate in the traffic. Parked devices have given up their MAC address and only occasionally listen to the traffic of the master to re-synchronize and check on broadcast messages. It can thus receive broadcasts, but not addressed messages while parked.
Bluetooth Protocols:
The Link Manager (LM)
: discovers other LM’s and communicates with them via the Link Manager Protocol (LMP) to perform its service provider role and to use the services of the underlying Link Controller.
Carries control information exchanged between the link managers of the master and the slave(s).
Link Layer Control & Adaptation (L2CAP):
A simple data link protocol on top of the baseband connection- oriented & connectionless protocol multiplexing segmentation
& reassembly QoS flow specification per connection (channel) group abstraction.
Service Discovery Protocol (SDP):
Defines an inquiry/response protocol for discovering servicesSearching for and browsing services.
Defines a service record format Information about services provided by attributes; Attributes composed of an ID (name) and a value(IDs may be universally unique identifiers (UUIDs)).
RFCOMM:
emulates a serial-port to support a large base of legacy
(serial-port-based) applications.
allows multiple “ports” over a single physical channel between two devices.
Telephony Control Protocol Spec (TCS):
call control (setup & release)
group management for gateway serving multiple devices
Legacy protocol reuse
reuse existing protocols, e.g., IrDA’s OBEX, or WAP for interacting with applications on phones
Bluetooth Architecture:
Hardware Architecture:
The Bluetooth Specification does not define what should be hardware and/or software.
The Bluetooth hardware consists of an analog radio part and a digital part - the Host Controller.
Radio: The Spread spectrum radio frequency transceiver.
Which transmits and/or receives signals from the digital processor unit.
Link Controller (LC): a hardware digital signal processing part called the a CPU core and interfaces to the host environment. it performs base band processing and physical layer protocols such as ARQ-protocol and FEC coding. The function of the
Link Controller includes Asynchronous transfers, Synchronous transfers, Audio coding and Encryption.
Software Architecture:
In order to make different hardware implementations compatible, Bluetooth devices use the Host Controller Interface.
Host Controller Interface (HCI): provides a common interface between the Bluetooth host and a Bluetooth module Interfaces in spec 1.0: USB; UART; RS-232
The software architecture of the bluetooth is an implemenattion of the bluetooth upper layer protocols.