biotin and folacin 413
advertisement

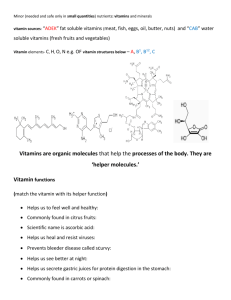
Vitamins are essential organic compounds that the animal organism is not capable of forming itself, although it requires them in small amounts for metabolism. Most vitamins are precursors of coenzymes precursors of hormones or act a antioxidants Color atlas of biochemistry Vitamin requirements vary from species to species and are influenced by age, sex, and physiological conditions such as pregnancy, breast-feeding, physical exercise, and nutrition. Vitamins are classified as: The lipid-soluble vitamins include vitamins A, D, E, and K the water-soluble vitamin include vitamins B1(thiamin) ,B2 (riboflavin),folic acid (folcine), H(biotin). Color atlas of biochemistry present in liver, egg yolk, and other foods. synthesized by the intestinal flora. Harper’s Illustrated Biochemistry In the body, biotin is covalently attached via a lysine side chain to enzyme that catalyze carboxylation reactions. Biotin-dependent carboxylases include pyruvate carboxylase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase . CO2 binds, using up ATP, to one of the two N atoms of biotin . Play an important role in fat, amino acid,and carbohydrate metabolism. Color atlas of biochemistry • Biotin deficiency is extremely rare. • Some potential causes of biotin deficiency are: intravenous feeding . eating raw egg whites on a regular basis. carboxylase deficiency. Supplementing with biotin appears • helpful for the treatment of this deficiency. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/natural/patient-biotin.html Impaired fat and carbohydrate metabolism alopecia and a characteristic scaly, erythematous dermatitis Harper’s Illustrated Biochemistry, www.pubmed.com Folacin *Folic acid, folate,vit.B9 *water-soluble vitamin Source Biochemical role - Essential role in Metabolism -Red blood cells, white blood cells, or cells of the intestinal mucous membrane pharmacotherapy • Biochemical role Folacin (polyglutamate form ) monoglutamate Small intestine cobalamin-dependent reaction tetrahydrofolate pharmacotherapy Biochemical role tetrahydrofolate carrier choline purine methionine pyrimidine Biochemical role - decrease the incidence of neural tube defects without masking occult vitamin B12 deficiency. Deficiency of folacin Causes: Inadequate dietary intake malnutrition malabsorption increased utilization Martindale Risk factors: * Pregnancy or lactation *malignancy *liver disease *alcoholism *chronic hemolytic anemia *Elevated homocysteine level in the blood http:/www.springboard4health.com Symptoms: *Sore mouth *Diarrhea *Irritability and forgetfulness Handbook of nonprescription drugs Diseases *Megaloblastic Anemia -Affects cells that are dividing rapidly - they have a large requirement for thymidine for DNA synthesis. - affects the bone marrow http:/www.springboard4health.com Diseases *environmental carcinogens. * promotes the breakage of chromosomes at fragile sties. *prohibit normal differentiation and replication