The Russian Revolution - AP European History at University High
advertisement

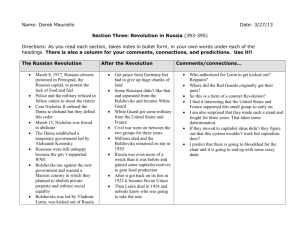
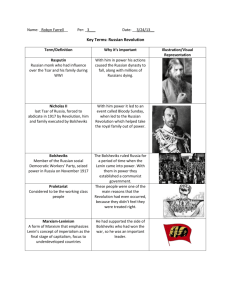
The Russian Revolution U5/Ch. 25 AP European History Ms. Tully - UHS Contributing Factors • Tsarist autocracy – Nicholas II • Bloody Sunday & Revolution of 1905 No real reform • Tsarina Alexandra & Rasputin • WWI Severe Russian losses The March (February) Revolution • Food shortages Riots & Strikes • Russian soldiers sided w/ demonstrators • Duma dissolved Ignored tsar, declared prov. gov. on March 12th • Nicholas II abdicated March 15th • Creation of soviets councils of workers • Army Order No. 1 Issued by Petrograd Soviet Lenin & The Bolsheviks • Radical wing of Marxist Social Democratic Party (split with Mensheviks) • Vladimir Ilyich Ulianov Lenin (1870-1924) • April Theses • July Days Bolsheviks accused of attempting revolution The November (October) Revolution • Bolsheviks gained majority in Petrograd & Moscow Soviets Leon Trotsky chairman of Petrograd Soviet • Nov. 6th Bolsheviks took control of Petrograd • Council of People’s Commissars New gov’t w/ Lenin in charge • Program of nationalization & consolidating power • Creation of Cheka secret police • Social & political reforms Alexandra Kollontai • Bolsheviks Communist Party • Treaty of Brest-Litovsk March 3, 1918 The Russian Civil War • Opposition to Bolshevik regime White Army • Red Army New Bolshevik army led by Trotsky • War Communism nationalization of banks & industry • Red Terror Power of the Cheka • Execution of royal family July 1917 • Red victory 1921 • High cost of war approx. 27 Russian casualties