File - Mr.P Biology B at EKFC
advertisement

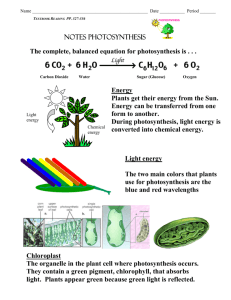
As you enter, PLEASE Answer the following questions on a lined piece of paper: What are Mr. P’s five rules for the classroom. Which rule do you think you will have the most difficulty with? What can you do to avoid any issues? Add your own rules to Mr. P’s list. Create your rules for Mr. P to follow At least 3. Cel.ly Learning Targets Used so you can track your progress in learning the CONTENT. Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration are difficult, you will want to keep track of how much you have learned. Then, you can seek help in the areas that you need to work on. Content Learning Target Check-Sheet Photosynthesis Learning Target Number Learning Target P1 I can identify the organisms that can utilize photosynthesis. P2 I can identify the organelle in which photosynthesis occurs as well as its components. P3 I can identify the origin of all energy on Earth. P4 I can define a pigment and name the two pigments involved in photosynthesis. P5 I can explain how these pigments determine the color of the photosynthetic organism. P6 I can describe the light dependent reactions. P7 I can describe the structure of ATP. P8 I can describe the light independent reactions. P9 I can identify and explain the equation for photosynthesis. P10 I can specifically predict the effects of removing specific ingredients from photosynthesis. Mastered (Check) Evidence PHOTOSYNTHESIS What do you know about Photosynthesis? P1: Which organisms go through Photosynthesis? P1: Which organisms go through Photosynthesis? I’ve Got a Problem P9: Equation for Photosynthesis 6 H2O + 6 CO2 + Light C6H12O6 + 6 O2 Water + Carbon Dioxide + Light Sugar + Oxygen P2: Where does this occur? P2: Where does this occur? P2: Where does this occur? Chromatography Lab Chromatography Lab Follow Up •What pigments did you observe in the spinach leaf? The coleus leaf? •How are the two leaves different? •When you look outside in the Fall you see many vibrant colors like red, yellow, orange, and yellow. Where do you think these colors were during the summer? •How can they suddenly appear in autumn? •Why are leaves green? As you enter, PLEASE Get out your homework from last night (Don’t turn it in to the box yet). Get out your notes from Wednesday. P4, P5: Why are plants green? P4, P5: Are plants green? P4, P5: Why do we see color? Why do you see rainbows? P4, P5: The Nature of Light White light from the sun is composed of a range of wavelengths (colors). P4, P5: The Nature of Light Different colors are actually different wavelengths; violet is the shortest wavelength (and most energy) and red is the longest (and least energy) P4, P5: What is Color? Wavelength Color 400 Violet 425 Violet 450 Blue 475 Blue 500 Blue/ Green 525 Green 550 Green 575 Green/ Yellow 600 Yellow 625 Orange 650 Orange/ Red 675 Red 700 Red As you enter PLEASE: Turn in the homework from Friday (if you haven’t turned it in already. Answer the following on a lined piece of paper: What do pigments do for plants? What are the colors that make up the visible spectrum (the same colors that make up a rainbow)? What Why? What color does chlorophyll make plants? colors do the carotenoids make plants? Why? When do we see these colors? P4: Pigments Pigments are molecules that absorb different wavelengths of light. P4, P5: Chlorophyll and Light Chlorophyll is the main photosynthetic pigment. Plants are green because of the presence of this pigment; the pigment REFLECTS green light and absorbs all others. What about in fall? P4, P5: Carotenoids In the fall, chlorophyll is broken down and the carotenoids are exposed. Practice with Pigments Why are plants green in the spring/ summer? They absorb blue and red light, and reflect green light. B. They absorb blue and green light, and reflect yellow, orange, and red light. C. They absorb green light, and reflect blue light. D. They absorb yellow, orange, and red light, and reflect blue and green light. A. Practice with Pigments Why aren’t plants green in the fall? They absorb blue and red light, and reflect green light. B. They absorb blue and green light, and reflect yellow, orange, and red light. C. They absorb green light, and reflect blue light. D. They absorb yellow, orange, and red light, and reflect blue and green light. A. Practice with Pigments Why aren’t plants green in the fall? Chlorophyll is expressed at a high level. B. The carotenoids aren’t expressed. C. Chlorophyll has broken down and the carotenoids are expressed the most. D. They are never green. A. Pigment Practice A. B. C. D. At what two wavelengths does chlorophyll “b” absorb light the best? 425nm & 675nm 500nm & 600nm 425nm & 630nm 475nm & 630nm Pigment Practice What color of light does chlorophyll “a” not use at all (reflect)? A. B. C. D. Orange Violet Green Red Groups Get into groups of NO MORE THAN 3. This will be your group for all of Photosynthesis/ and Cellular Respiration. Be sure to get with people that you can be successful with. The Flipped Classroom What is a flipped classroom? What is the point? How are we going to flip the class? First Flipped Class Lesson Watch ATP video on Youtube Look it up or access it through weebly Create your own notes Get with your group and be sure that you have everything that you need. As you enter, PLEASE Get out your notes. You may discuss your notes with your group to fix any inconsistencies or modify your notes in any way. THIS IS NOT A TIME TO COPY YOUR PARTNERS NOTES. P7: ATP Data Collection Did it work? Critique your experiment and 1 other groups. Why do you think it did or didn’t work. Be sure to use your knowledge about photosynthesis. How would you change the experiment to fix this? Photosynthesis Project Due: Wednesday at the end of class. Create a poster that will demonstrate the light-dependent and independent reactions of photosynthesis. Must include the following: (chloroplast, chlorophyll, thylakoid, stroma, light-dependent reactions, light, electrons, electron transport chain, NADP+, NADPH, protons, ADP + P, ATP, water, oxygen, light-independent reactions, carbon dioxide, and glucose) You may use your notes, your book, and/ or the internet. All people in the group must be able to explain the process. P6: Light-Dependent Reactions Light strikes chlorophyll and excites an electron to a higher energy state. (P3) The sun provides all energy found in the environment. Electrons are excited. These electrons are moved to the electron transport chain where they produce NADPH from NADP+. P6: Light-Dependent Reactions These electrons must be replaced. H2O is split into H and O. The electrons from H replace the excited electrons. O combines to make O2. This is the waste of photosynthesis. P6: Light-Dependent Reactions The H are used by the ATP synthase to combine a phosphate with ADP to make ATP. P8: Light-Independent Reactions Known as the Calvin Cycle Phosphates are broken off of ATP and electrons are removed from NADPH which provides the energy to turn CO2 to glucose (C6H12O6) It takes six cycles to do this As you enter, PLEASE Get out your notes. Finish collecting your data from the Photosynthesis experiment. Develop a conclusion. Was your hypothesis correct? Use data and your knowledge of photosynthesis to prove your conclusion. Turn in one lab document per group. Light-Dependent Video P9: Equation for Photosynthesis 6 H2O + 6 CO2 + Light C6H12O6 + 6 O2 Water + Carbon Dioxide + Light Sugar + Oxygen As you enter, PLEASE: Get out your poster and any notes from Photosynthesis. STUDY FOR THE QUIZ. I will give you instructions on what you need to do as soon as class starts.