Unit Three Part I Student Notes
advertisement

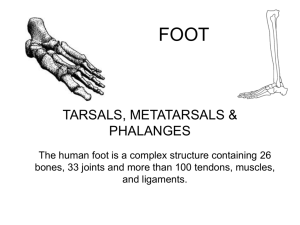
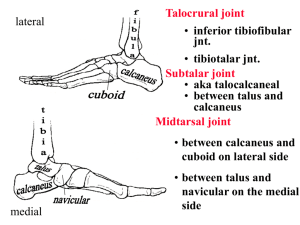
Unit 3/ Chapter 18: The Foot Part I ANATOMY OF THE FOOT Bones Toes- ____________________________ (14) o Wider base for ______________________ o Propelling the body o 2 sesmoid bones Metatarsal Bones (5 bones) o Between the tarsals and phalanges o Semimovable- gives elasticity to the foot o _______________________________ is the main weight bearing bone of the foot Tarsal Bones (7 Bones) o Calcaneus- ______________________ bones Supports the talus and Achilles attach o ___________________ - most superior tarsal bone Gives lateral and dorsi/ plantar flexion o ______________________ (Medial side) Anterior to the talus Cuboid (lateral side) Articualtes with the calcaneus and the 4TH and 5TH metatarsal o Cuneiforms (3 bones) Medial aspect Between the navicular and the 3 metatarsals QUESTION How many phalanges are there on one foot? ______________________________________________________________________________ How many metatarsal bones? ______________________________________________________________________________ Name the 7 tarsals? ______________________________________________________________________________ Arches of the Foot Roles: o _____________________ the body weight o Absorbing ___________________________ o Providing space for blood vessels, nerves, and muscles 4 Arches o __________________________ Arch: Shaped by the distal heads of the metetarsals Stretches from the 1ST to the 5TH o _______________________________: Extends across the transverse tarsal bones Half dome o Medial Longitudinal: Along the _____________________________________ Plantar Calcaneonavicualr ligament (spring) returns arch to normal position after pressure o Lateral Longitudinal: Along the lateral border Much lower and less flexible Plantar Fascia Thick, white band of fibrous tissue from the medial calcaneus to the proximal heads of the metatarsals Supports the foot against downward forces Extension of the “calf” muscles Draw & Label the 4 Arches Articulations (Joints) _________________________________: o Flexion and extension o Reinforcing medial and lateral collateral ligaments as well as plantar and dorsal ligaments Metatarsophalengeal: o Flexions, extension, adduction and abduction o Collateral ligaments as well as plantar and dorsal Intermetatarsal: _____________________________ o Between the metatarsals Tarsometatarsal Joint: (_________________________) o Between the tarsals and the heads of the metatarsals Subtalar: ____________________________________________ o Inversion, Eversion, Pronation and Supination Midtarsal (Chopart’s): Calcaneocubiod and talonavicular Label the Articulations Stabilizing Ligaments Subtalar Ligaments o Interosseus talocalcaneal and the anterior, posterior, lateral and medial talocalcaneal Plantar Calcaneonavicular o __________________________ for the medial arch Midtarsal Joint o Dorsal talonavicualr, bifurcate, Dorsal calcaneocuboid, Long plantar ligament Anterior Tarsal Joints o Cuneonavicular, cuboideonavicualr, intercuniform and cuneocuboid Muscles and Movement Dorsiflexion: (________________________________________) o Tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucus longus and peroneus tertius Plantar Flexion: (_________________________________________) o Gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris, perioneus longus/ brevis, tibilais posterior, flexor hallucis longus and flexor digitorum longus Inversion, Adduction & Supination o Medial movements of the foot o Muscles pass behind and in front of the medial malleolus o Behind Malleolus: tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, and flexor hallucis longus (__________________________________________) o Front of Malleolus: Tibialis anterior and extensor hallucis longus Eversion, Abduction & Pronation o ______________________________________ of the ankle o Muscles pass behind and in front of the lateral malleolus o Behind the malleolus: Peroneus longus and peroneus brevis o In front of the malleolus: Peroneus tertius and extensor digitorum longus Movement of the Phalanges (Flexion, extension, abduction and adduction) o Flexion of the 2nd through 5 th : Flexor ___________________ longus and brevis Flexion of Great Toe: Flexor _______________________ longus Extension: Extensor digitorum longus and brevis. (2nd- 5th) o Extensor __________________________ longus great toe Nerve and Blood Supply Plantar side nerve: medial and lateral plantar nerves from the tibial nerve Dorsal side nerve: Deep peroneal nerve Blood supply: anterior tibial artery and the posterior tibial artery Functional Anatomy of the Foot and Biomechanics Kinetic Chain- Segments are joined together o When considering foot, ankle, and leg injuries, need to look at kinetic chain Each segment has an effect on ___________________________________ segments Lower-extremity chronic and overuse injuries need to look at biomechanical factors New Vocab Word Stance Phase o From initial contact to toe-off Swing Phase o Period of non-weight bearing Normal Gait Stance Phase o Accounts for ______________% of gait cycle o __________________ kinetic chain o Five periods Initial contact (double limb support) Loading response (double limb support) Mid stance (single limb support) Terminal stance (single limb support) Pre swing Swing Phase o Period of non-weight bearing o Three periods Initial swing Mid swing Terminal swing Running Gait o Loading and mid-stance = more rapid o After toe off – _____________________________________ contact for both feet o Stance phase = ______________% of gait cycle o Shock absorber at heel strike and adapts to uneven surface during stance o At push-off foot serves as rigid lever to provide propulsive force o 80% of distance runners follow heel strike pattern o Sprinters tend to be _______________________ strikers Subtalar Joint Pronation and Supination Excessive or prolonged pronation or supination can contribute to _______________________________________________ Subtalar joint allows foot to make stable contact with ground and get into weight bearing position Excessive motion, compensates for structural deformity Structural Deformities o Forefoot and rearfoot varus are usually associated with over-pronation o Forefoot valgus causes excess supination o May interfere with shock absorption New Vocab Word Excessive Pronation o Produced in Stance phase or prolonged pronation in propulsive phase Excessive Supination o At heel strike, excessive supination in the subtalar joint Prevention of Foot Injuries Forces foot encounters can result in acute traumatic and overuse injuries Injuries best prevented by: o Selecting appropriate footwear o Correcting biomechanical structural deficiencies through orthotics o Paying attention to hygiene Selecting Appropriate Footwear o Pronators: _________________ shoe is recommended o Supinators: Require ________________________ footwear with increased cushioning o Basic form shoe is constructed on (last) dictates stability of shoe Slip last shoe (moccasin style) is very flexible (Supinators) Board last provides firm inflexible base (Pronators) Combination last provides rearfoot stability and forefoot mobility Using Orthotics o Used to correct for _________________________________ problems in the foot o Can be constructed of plastic, rubber, cork, or leather o Can be prefabricated or custom fitted Foot Hygiene o Keeping toenails trimmed correctly o Shaving down excessive calluses o Keeping feet ______________ o Wearing clean and correctly fitting socks and shoes o Keeping feet as dry as possible to prevent development of athlete’s foot