Unit 7 – Industrialization: North and South Economies Develop
advertisement

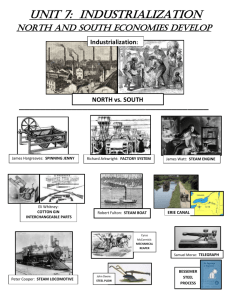
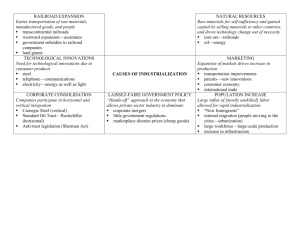
Unit 7 – Industrialization: North and South Economies Develop TEST REVIEW BE SURE TO REVIEW/STUDY: Industrialization: Causes and Effects CHART Innovations CHART and Transportation and Communication Info Sheets Industrialization: Major Factors NOTES (from Shift to Industrialization POWER POINT) Growing Differences PACKET (online) Free Enterprise (aka free markets, capitalism, laissez-faire economy) Developed by Enlightenment thinker: Adam Smith Also known as laissez-faire economy (the government should “leave it (business) alone”)—gov’t stay out of economy/marketplace Americans had developed a system of law and government based on individual rights and wanted that freedom reflected in the market place and economy, as well. (Opposite of mercantilism with great gov’t control of business) Idea that Free and open markets operate naturally and most efficiently leading to better economy for the people/nation Competition in free market leads to businesses producing better products at cheaper prices—benefits the consumer Supply and Demand naturally determines prices in a free market Led to less dependence on foreign products because our economy/industry flourished (did very well) Industrialization Factory system, population shift to cities (urbanization), immigration, inventions, expansion of slavery, slave rebellions, start of reform movements. Factory system contributed to rapid industrialization because making goods in factories was more efficient than making goods by hand; interchangeable parts and the assembly line contributed to this even more Industrialism leads to the growth of cities Increased with innovations like the cotton gin, steam engine*, Bessemer steel process, and mechanical reaper Expansion of canals and railroads most contributed to rapid industrialization in the years before the Civil War Innovations – some highlights listed here, but still need to study your Innovations Chart! Textile Mills in America: Samuel Slater—“Father of American Industrial Revolution”—at first powered by water so built on rivers; later steam power allows mills and factories to be built anywhere; Rhode Island System vs. Lowell System Cotton Gin: Eli Whitney, sped up the cleaning of cotton and led to increased production of raw cotton in the South, increased the demand for fieldworkers => expansion of slavery Interchangeable Parts: Eli Whitney, mass production of identical goods (rifles), replacement parts available, then idea of interchangeable parts is applied to other industries Steam power: *Most responsible for the growth of industry, used in factory steam engines, then steamboats and steam locomotives; increased the demand for factory labor Steel plow: John Deere; “Plow that broke the plains” made farming easier, especially in Great Plains were hard soil made it difficult to farm before—so helped westward expansion Mechanical Reaper: Cyrus McCormick; could harvest more wheat, so could grow more; increased agriculture in South Railroads: Allowed for faster movement of people and products; helped westward expansion; Chinese helped build railroads Bessemer Steel Process: allowed the U.S. to become a top producer of steel, inexpensive way to produce steel and didn’t require the large labor force to do so; helped expand the railroad by mass producing rails, made building skyscrapers possible Erie Canal: Faster movement of people and products, commerce benefited from a means of faster, smoother transportation Telegraph: Samuel Morse; using Morse Code with the telegraph could communicate instantly now; united the nation Many scientific discoveries contributed to increased immigration, urbanization, increased agriculture and expansion of slavery Urbanization People from rural areas moving to cities—for jobs in industry/factories More immigrants from Europe and Asia in the cities—moving to America for jobs in industry/factories More pollution—from industry/factories (burn coal and wood to produce steam) Overcrowding, crime, disease, fires – problems with urbanization Immigrants Immigrants from Europe and Asia settled in cities for job opportunities and… Often settled in the same neighborhoods so they could live with others of the same national origin (think of Little Italy, China Town today) Irish and German immigrants came to East Coast for job opportunities in the factories o Irish Potato Famine led many Irish to come to America o German immigrants brought traditions like kindergarten and the Christmas tree Chinese immigrants came to West Coast (California), helped build the transcontinental railroad Regional Differences North: Highly/densely populated (A LOT of people living in a small area) , urban (cities) economy is centered around factories and manufacturing, its natural harbors promoted the growth of trade and shipbuilding South: Less densely populated (fewer people), rural economy is centered around agriculture and the plantation system, main workforce is made up of slaves