August 17, 2011
advertisement

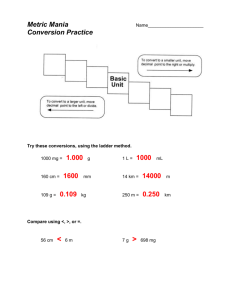
Measurement: Errors, Accuracy, and Precision PHYSICS CHAPTER 1, SECTION 2 August 17, 2011 HW: Physics to Go (PTG)-pg. 32, #6-9 Do Now (NB pg. 6) WDYS & WDYT TB pg 22 Success Criteria Calibrate the length of a stride Measure a distance by pacing it off and by using a meter stick Identify sources of error in measurement Evaluate estimates of measurements as reasonable or unreasonable Complete various metric conversions Agenda: Do Now 1.2 Measurement: Errors, Accuracy, and Precision Physics Talk Metric Mania Homework: PTG, pg. 32, #6-9 Investigate pg. 23-24 In your notebooks: READ ENTIRE INVESTIGATE Turn all questions (1-8) with pencils next to them into statements in your notebook Do 1-8 in your notebooks Example: For 2a you will put the statement in your notebook as:” The number of strides is__________.” For 3a you will put in your notebook “The measurement is___________.” For 4a you will put in your notebook” The calculations are___________.” Materials After turning all of the text (where pencil is at #s 1-8)from the book into statements. Check off with Mr. LePera and pick up a meter stick Mr. LePera has taped off the distance for you in the hallway. Keep in mind…..Disruptions in the hallway will cause your group to do the work inside the classroom, and outside classroom privileges will be revoked!!! Do your lab in the hallway and finish in the classroom. HW: Finish PTG #6-9 Do Now (below data for 1.2 in notebook): What is the difference between a systematic error and a random (human) error? In your groups answer #9 on TB pg. 24 in your notebooks, be prepared to share out Physics Talk What are Random Errors? Produced by measuring tools and human mistakes Cannot be corrected by calculations Can never be eliminated Physics Talk What are Systematic Errors? Can be avoided Corrected by calculations Example: If I accidentally measured in inches, when I was supposed to measure in centimeters, I could convert to get the right numbers Physics Talk What is accuracy? How close to an accepted What is precision? Frequency of results Always hit close to the value Example: Shooting on goal in soccer same spot Example: Always missing wide right when shooting the ball in soccer Metric Conversions Metric Conversions Ladder Method Ladder Method T. Trimpe 2008 http://sciencespot.net/ T. Trimpe 2008 http://sciencespot.net/ August 17, 2011 HW:PTG pg. 32 #6-9 Do Now: In your notebook (below notes) answer the following: WDYTN? TB Pg. 30 Reflecting on the Section Challenge: TB pg. 31 How will what you learned in 1.2 help you with your chapter challenge (pg. 3) Success Criteria Calibrate the length of a stride Measure a distance by pacing it off and by using a meter stick Identify sources of error in measurement Evaluate estimates of measurements as reasonable or unreasonable Complete various metric conversions Agenda: Collect Metric Mania Do Now Success Criteria PTG pg. 32 #6-9 Quiz 1.2