chemistry-notes-chapters-22-1
advertisement

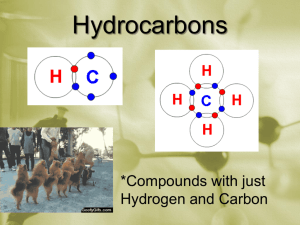
Chemistry Notes Chapters 22 Organic Chemistry Name __________________________ Section 1 Pg 762 1. Organic compounds – have what main element? _______________. 2. Hydrocarbons have what 2 main elements? __________________ and _________________. 3. Carbon is very easy to make compounds with because it is in column number _____________ so it has ____________ valence electrons and can make ______________ bonds. BE ABLE TO RECOGNIZE AND DRAW BALL AND STICK DIAGRAMS AND ELECTRON DOT DIAGRAMS OF THE COMPOUNDS WE DO!!!! Pg 763-65 Pg 764 4. Alkanes are hydrocarbons that have all ___________ bonds between the carbons and are as full of bonds as they can be (this is called being _________________ Pg 772). KNOW THE PREFIXES OF THE ALKANES BASED ON THE NUMBERS OF CARBON IN EACH (come up with a sentence to remember order) AND BE ABLE TO DRAW THEIR STRUCTURAL FORMULA AND WRITE THEIR MOLECULAR FORMULAS!!!!! PG 765-66 Molecular formula of alkanes: CnH2n+2 ex: ethane C2H6 , propane C3H8 , butane ____________ Draw structural formula of propane : HOMEWORK: Methane – Ethane – Propane – Butane – Pentane – Hexane – Heptane – Octane – Nonane – Decane – Look up the uses of each of these. (be able to match on test) Section 2 Pg 772 5. Alkenes have at least one ____________ bond between _______ carbons and are considered ________________ since they could break that double bond and take on more elements. Pg 773 6. Alkynes have at least one ___________ bond between ___________ carbons and are also considered ________________. LOOK AT STRUCTURAL FORMULAS PG 766, 772, 773. NOTICE CARBON CAN ONLY HAVE _______________ BONDS DUE TO HAVING _____________ VALENCE ELECTRONS!!!!!!!!! DRAW BUTENE: BUTENE MOLECULAR FORMULA: _______________ ALKENES CnH2n Why isn’t there such a thing as methene? _____________________________________________ Pg 809 Adding Hydrogen to double bond to force it to single bond is called ___________________ reaction (trans fats, saturated fat, margarine, peanut butter, etc). DRAW BUTYNE: BUTYNE MOLECULAR FORMULA: ________________ ALKYNES CnH2n-2 Section 4 Pg 779 7. Cyclic Hydrocarbons – in a _________ instead of a straight line chain Pg 780 8. _____________ – _________ sided ring shaped aromatic (aromas such as spices & moth balls) DRAW BENZENE STRUCTURAL FORMULA BENZENE MOLECULAR FORMULA __________________ Section 5 Pg 782 9. Petroleum and natural gas are two fossil fuels formed from _____________________________ ________________________________. 10. What are the alkanes in natural gas by percent? Chemistry Notes Chapter 22 Page 2 Name _______________________________ 11. Methane is a good major component of natural gas because it burns ____________________. 12. What are the two components of liquid petroleum gas? 13. What is necessary for combustion of a hydrocarbon? 14. What kind of combustion is it called when there is not enough of #13? 15. What color is the flame in complete and incomplete combustion? Complete is _____________ Incomplete is ________________ 16. The two products of incomplete combustion are a black carbon powder called _________________ and a toxic gas called ________________________________. NOTICE IN THE PICTURE BOTTOM PG 782 THAT NATURAL GAS IS IN A POCKET ABOVE PETROLEUM. NATURAL GAS IS OFTEN NOT A LIQUID. PRESSURE FROM THIS GAS PUSHING DOWN ON TOP OF PETROLEUM FORCES PETROLEUM UP OIL WELL JUST LIKE AIR PRESSURE FORCES DRINK UP A STRAW. Pg 783 17. Petroleum contains ____________ which causes sulfuric acid rain and _____________ which causes nitric acid rain. 18. Petroleum is separated into ___________% gasoline, as well as kerosene and diesel through a heating process at a refinery called D_______________________ that separates the parts of petroleum based on _____________ point. See picture Pg 783 19. The residue left over after petroleum is separated into fuels is made into products that can be used for street paving such as ______________ and __________________. Pg 785 20. Coal is a fossil fuel made from ____________________________________________________. 21. Types of coal: (in order of formation from least ____________ to high ______________) a. Peat – ___________ material, ___________ water content, ____________ fuel b. Lignite – ____________% carbon content, still high ____________ content c. Bituminous – ____________% carbon content, called ________ coal d. Anthracite – exceeds _____% carbon content, called _______ coal, _________ fuel source, found in eastern ______________, formed under ____________ pressure (the more carbon the more _____________ Pg 785) 22. The United States is a good source of coal because the coal is only ______ meters underground instead of __________ meters underground in other countries. Chemistry Notes Chapter 23 Substituted Hydrocarbons Name ________________________ Section 1-3 Pg 798 1. A substituted hydrocarbon is one in which a hydrogen has been replaced with a _____________ group. Pg 799 Examples of Substituted Hydrocarbons: (be able to name, describe and give example on test) Halocarbon – Pg 800, hydrogen replaced with a ______________ from column _____________ on the periodic table. Ex: CCl4 ___________________(old toxic dry cleaning fluid) C2Cl4 _____________________(current dry cleaning fluid) Alcohol – H replaced with _________ (hydroxyl) Ex: ethanol (drinking alcohol), isopropyl alcohol (rubbing alcohol) Pg 805-6 , mouthwash, antifreeze, cosmetics Soluble in water up to _______ carbons, after that too much carbon makes it _________________ Pg 806 Denatured alcohol – toxic because it contains ______________ Pg 807 Formed by _______________ reaction that adds _____________ to alkane Pg 808 Ether – H replaced with ___________ Ex: anesthesia Pg 810 Aldehyde- H replaced __________ Pg 812 Ex: formaldehyde preservative Pg 813, and flavorings Ketone – H replaced with ___________ Pg 812 Ex: acetone (nail polish remover), and odors Carboxylic acid – H replaced with ____________ (carboxyl) Ex: ethanoic acid (acetic acid/vinegar),Pg 815-16 (acetum in Latin= vinegar, Luke 23:36 soldiers gave Jesus acetum) Esters – H replaced with ___________ Ex: _______________ and ________________ Pg 821, made by mixing ___________ and carboxylic acid Pg 819, ________________ gives low boiling pt Section 4 on back Section 4 Pg 822 2. Polymer – 3. Monomer – Examples of Polymers: (all made from OIL) (be able to name and describe on test) Polyethylene (chain of ethenes, plastics) Teflon (nonstick pans) Dacron (surgical fibers) Neoprene (synthetic rubber wetsuits) Mylar (balloons) Kevlar(bullet proof vests) Nylon and Polyester Sodium Polyacrylate (diaper filler, plant moisture holding crystals) Tyvek (rip proof mailing envelopes, moisture barrier in walls of house) HOMEWORK 1– 2– 3– 4– 5– 6– 7– Find out the names AND uses of the following numbers of plastics: (be able to match on test)