First Prenatal Visit
advertisement

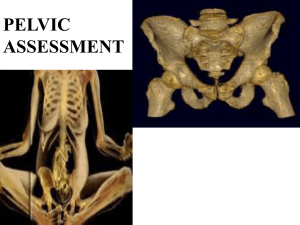
Preconception Care Promotion of health before pregnancy Identify areas that might unfavorably affect pregnancy. Risk Factors for adverse pregnancy outcomes • • • • • • Smoking Alcohol Folic Acid Obesity Drugs Medical conditions Nursing Management • Assessment History • Health promotion activities and education Prenatal Care Essential for ensuring the overall health of newborns and their mothers. Ideally, begins during the mother’s childhood. Includes balanced nutrition, adequate immunizations, positive attitudes and education. • Choosing a health care provider – clinic – HMO – nurse midwife – obstetrician – family practitioner Preconceptual Visit • Before becoming pregnant to obtain accurate reproductive life planning. First Prenatal Visit • Establish a baseline • Treat any health problems First Prenatal Visit Interview • provide privacy • when scheduling the appointment caution the woman that it may be a long session • establish your role • provide face to face interview Components of Health History: • Establish rapport • Gain data on physical and psychosocial health First Prenatal Visit • Obtain basis for anticipatory guidance for the pregnancy • Demographic data • Chief concerns • Family profile • History of past illnesses • History of family illnesses • Day history/social profile • Gynecologic history • Review of systems Obstetric History Terms • Viability: – 24 weeks: earliest age fetal survival • Abortion: – Pregnancy terminated before viability (spontaneous or elective) • Term: – Infants born > 37 weeks • Preterm – Infants born 24-36 weeks • Living First Prenatal Visit Support Person’s Role: • Partners, children, best friends come to prenatal visits. • Also allow time for privacy at each visit. Physical Examination: • woman should undress, put on a patient gown, and empty her bladder. • Obtain urine specimen (clean catch) – bacteriuria, protein, glucose, ketones • VS, height, weight baseline Physical Examination Assessment of systems: • general appearance and mental status • head and scalp • eyes • nose • ears • sinuses • mouth, teeth and throat • neck • lymph nodes • breasts • heart • lungs • back • rectum • extremities and skin Measurement of Fundal Height/FH Palpate the fundus at 12 weeks • measure the fundal height • plot on graph • auscultate fetal heart with doppler at 10 to 12 weeks • palpate fetal outline at 28th week Pelvic Examination: • Reveals health information on internal and external reproductive organs. • Equipment - speculum, brush/broom for cervical scrapings, slide/medium for PAP, culture tube, gloves, lubricant, 2-3 cotton tipped applicators, light and stool. • Support is needed during this exam Pelvic Examination External Genitalia • Check for signs of infection, inflammation, irritation, redness, ulceration, discharge or herpes. • Check Skene and Bartholin glands for infection. • Check for rectocele or cystocele. Pelvic Examination Internal Genitalia • Cervix - purple if pregnant, check for lesions, ulcerations, or discharge. • Nulligravida - a woman who is not or never has been pregnant. Cervical os is round and small. • In a woman with previous pregnancy the os will be more slitlike. Pap Smear • Sample from cervical os or vaginal pool. Pelvic Examination Vaginal Inspection • Culture for gonorrhea, chlamydia or group B strep • Dark blue to purple color. Examination of Pelvic Organs • Bimanual exam to assess position, contour, consistency and tenderness of pelvic organs. • Palpate uterus, ovaries and check Hegar’s sign. Rectovaginal Examination • Assess strength and irregularity of posterior vaginal wall. Pelvic Examination • Types of pelvis – Android - male pelvis, the pubic arch forms an acute angle, making the lower dimensions of the pelvis extremely narrow. – Anthropoid - ape like pelvis, the transverse diameter is narrow and the anteroposterior diameter of the inlet is larger than normal. – Gynecoid - normal female pelvis, inlet is well rounded forward and backward, the pubic arch is wide. Ideal for childbirth. – Platypelloid - flattened pelvis, inlet is an oval, smoothly curved, but the anteroposterior diameter is shallow. A fetal head might not be able to rotate to match the curves of the cavity. Pelvic Examination Diagonal conjugate - distance between anterior surface of sacral prominence and anterior surface of inferior margin of symphysis pubis. • Most useful measurement for estimation of pelvic size. • Anteroposterior diameter of the pelvic inlet. • Sacral prominence to symphysis pubis. • Pelvimeter • If measurement is more than 12.5 cm it is adequate (average is 11cm in diameter). Pelvic Examination Ischial tuberosity - measures is the distance between the ischial tuberosities, or the transverse diameter of the outlet. • The narrowest diameter at that level. • Medial and lowermost aspect of the ischial tuberosities at the level of the anus. • Pelvimeter or ruler is used. • 11 cm is adequate because it will allow the widest part of the fetal head, or 9 cm, pass freely through the outlet. Laboratory Assessment Blood studies • CBC, H&H and red cell index (anemia), platelet count, sickle cell trait. • VDRL or RPR • Blood typing (include Rh factor) • AFP at 16 to 18 weeks • Indirect Coombs’ test (Rh antibodies) repeat at 28 weeks. • Antibody titers for rubella and hepatitis Blood Studies • Antibodies for varicella • Obtain consent for HIV screening (ELISA) Western blot (Can start AZT). • 50-g oral 1-hour glucose loading or tolerance test to R/O diabetes if she has a previous history or symptoms of diabetes. Urinalysis • test for albuminuria, glycosuria and pyuria. Laboratory Assessment Tuberculosis Screening • PPD (purified protein derivative) tuberculin test to screen for tuberculosis. • Positive requires a chest X-ray Ultrasonography • Confirms pregnancy length or document healthy fetal growth. Risk Assessment Previous surgery, health history, meds, etc Signs Indicating Complications of Pregnancy • • • • • • • Vaginal Bleeding Persistent Vomiting Chills and Fever Sudden escape of clear fluid from vagina Abdominal or chest pain PIH signs Increase or decrease fetal movement