PowerPoint 3.1 - MAEDA AP Chemistry
advertisement
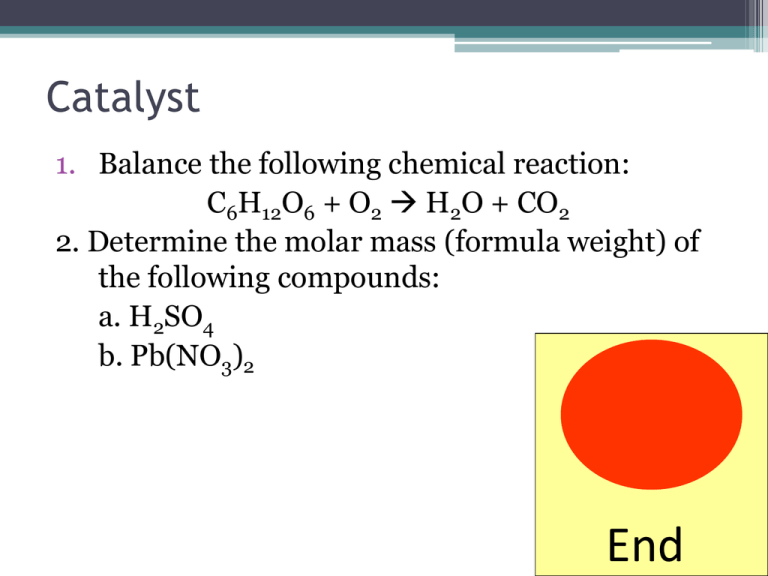
Catalyst 1. Balance the following chemical reaction: C6H12O6 + O2 H2O + CO2 2. Determine the molar mass (formula weight) of the following compounds: a. H2SO4 b. Pb(NO3)2 End Hair Dryer in a Bath Tub Justify – TPS • What chemical properties lead to the explosive reaction of dropping a hair dryer in water? Lecture 3.1 – Electrolytes and Net Ionic Equations Lecture 3.1 – Net Ionic Equations and Electrolytes • LT 3.1 – I can identify a compound as being a strong, weak, or non – electrolyte. • LT 3.2 – I can translate a chemical reaction into a net ionic equation that contains only the ions/molecules that participate in the chemical reaction. Electrolytes vs. Nonelectrolytes • When you dissolve compounds in water, sometimes they dissociate and sometimes they do not. • Electrolyte – Any compound that breaks into ions when in solution and can conduct electricity • Nonelectrolyte – Any compound that does not form ions when in solution and cannot conduct electricity. Ionic Compounds are Electrolytes • When a ionic compound is dissolved in water, it breaks apart into positive and negative ions. • Polar water molecule breaks up the ionic crystal Covalent Compounds are Nonelectrolytes • When a ionic compound is dissolved in water, it cannot be broken apart. • Polar water molecule cannot break apart these compounds because there are no ions Strong vs. Weak Electrolytes • Electrolytes can be characterized as being either strong or week based on the amount they dissociate. • Strong Electrolytes – Compounds that completely dissociate in water. • Weak Electrolytes – Compounds that almost dissociate completely in water Class Example • Is the following compound an electrolyte or a nonelectrolyte • If it is an electrolyte is is strong or weak? KCl Table Talk • Is the following compound an electrolyte or a nonelectrolyte • If it is an electrolyte is is strong or weak? C6H12O6 Net Ionic Equations • Oftentimes we see chemical equations written as this: Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) PbI2 (s) + 2KNO3 Molecular Equation • The electrolytes that are in aqueous solutions can be written as their ions: Pb2+ + 2NO32- + 2K+ +2I- PbI2+ 2K+ +2NO3Complete Ionic Equation Net Ionic Equations • Many of the ions are present on both sides, so they do not participate in the chemical reaction and can be canceled out. Pb2+ + 2NO32- + 2K+ +2I- PbI2+ 2K+ +2NO3- Pb2+ (aq) + 2I- (aq) PbI2 (s) Class Example • Write the net ionic equation for the following reaction: Mg(NO3)2 (aq) + Na2CO3 (aq) MgCO3 (s) + 2 NaNO3 (aq) Table Talk • Write the net ionic equation for the following reaction: SrBr2 (aq) + K2SO4 (aq) SrSO4 (s) + 2 KBr (aq) Investigate and Check Exit Ticket 1. Are the following compounds electrolytes or non-electrolytes? If it is an electrolyte, then is it strong or weak? a. KBr b. CO2 c. CH3COOH (a weak acid) 1. Write the net ionic equation for the following reaction: Na2CO3 (aq) + Co(NO3)2 (aq) 2NaNO3 (aq) + CoCO3 (s) Closing Time • Read sections 4.1 and 4.2 in textbook • Complete Homework 3.1 Net Ionic Equations for class Thursday/Friday • Lab 5 Pre-Lab due at the start of the next class





