Written Methods – Division
advertisement

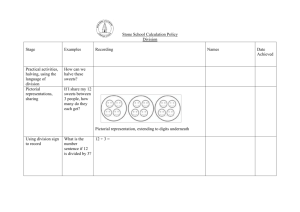
Division Written Methods Written Methods • Throughout their years at school, children should progress from informal jottings and number line methods to formal efficient written methods. • By the end of Year 3, children should be confident using short efficient written methods for all four operations + - x ÷ • Children become secure with these methods with regular practice and should be able to apply skills to problem solving. Grouping/Sharing • Children practice grouping and sharing using practical resources. The language of division is developed. Sharing 30 crayons shared equally between 3 pots 30 ÷ 3 = 10 Grouping/Sharing • Children practice grouping and sharing using practical resources. The language of division is developed. Grouping We have 30 crayons and put 10 in each pot. How many pots do we need? 30 ÷ 10 = 3 Blank Number Line • An empty number line let’s us show division using multiplication tables and facts. We can also show a remainder on a number line. 30 ÷ 5 = 6 1x5 0 Jump in lots of the divisor number (5) 2x5 5 3x5 10 15 31 ÷ 5 = 6 1x5 0 5 2x5 5x5 6x5 20 25 30 Jump in lots of the divisor number (5) 3x5 10 4x5 4x5 15 5x5 6x5 20 25 30 r1 31 Your Turn! • Can you use the partitioning method to solve these multiplications? • 45 ÷ 5 = • 32 ÷ 4 = • 35 ÷ 3 = Bus Stop Method • Formal written layout otherwise known as bus stop methods requires a good knowledge of multiplication facts. Known facts 24÷4=6 3 9 ÷ 3 = 13 6 4 24 13 3 39 How many 4’s in 24? 6 How many 3’s in 3? 1 How many 3’s in 9? 3 Bus Stop Method • Formal written layout otherwise known as bus stop methods requires a good knowledge of multiplication facts. 56÷4= 14 1 4 56 How many 4’s in 5? 1 r1 How many 4’s in 16? 4 5 7 3 ÷ 4 = 13 1 4 3 r1 1 1 4 573 How many 4’s in 5? 1 r1 How many 4’s in 17? 4 r1 How many 4’s in 13? 3 r1 Bus Stop Method Rules of Bus stop method – Set out the sum – How many times will the divisor go into the first number? – How many times will the divisor go into the next number? – Carry remainders to the next number – Remainders at the end – r? 5 4 ÷3 = 3 54 Your Turn! • Can you use the column method to solve these multiplications? •34÷3= •56÷4= •654÷3=