The Fertile Crescent
advertisement
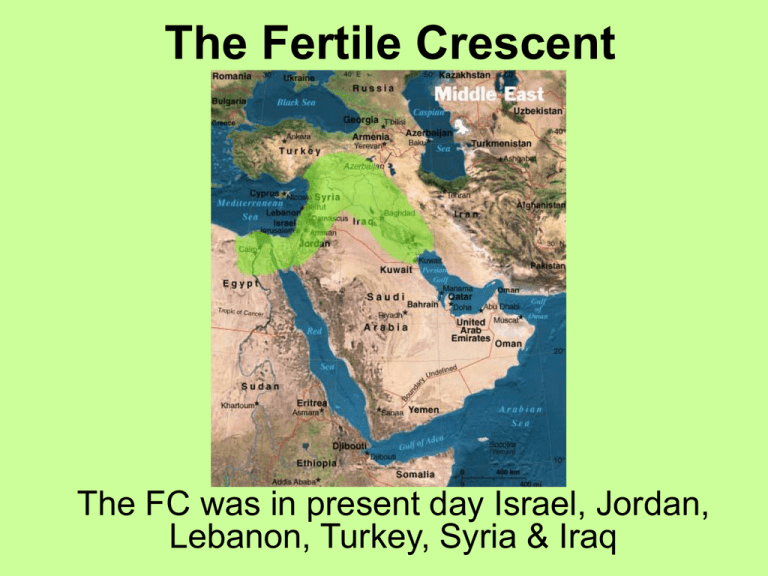
The Fertile Crescent The FC was in present day Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Turkey, Syria & Iraq Mesopotamia - land between two rivers – Tigris – Euphrates • Present Day Iraq • Settled 5000 BC • Flat plain • Need protection from flooding rivers & from invaders – built dams & channels – irrigation Sumerian Civilization (3000 BC) • City State – an independent state consisting of the city & the farms around it • (12) within Sumer valley • common culture, language, religion Religion • Polytheistic – believed in many gods • each City State has a temple – Ziggurat Deities • • • • unpredictable & selfish bring famine, disease, flood, destruction priests & priestesses ask for blessings ceremonies to appease gods • An – god of seasons • Enlil – wind and agriculture • Underworld – no light or air The Story on Enmesh and Enten • Summer Myth in which Enlil, son of the Sumerian supreme God chooses the gifts of Enten (creator of animals over Enmesh creator of villages) • Importance of Neolithic Government • Kings are also priests, responsible for pleasing the deity. • This makes the government a Theocracy – or government controlled by religious leaders Sumerian inventions (develop around the need to trade) – – – – – – – – wheel arch – sturdier buildings potter’s wheel sundial # system (based on 60) lunar calendar 1st bronze Cuneiform – writing • symbols for ideas & objects • hard to learn scribe class studies at eddubas • business, history, literature Empires of Mesopotamia & Hammurabi’s Code Sargon of Akkad– 2350 BC • conquered all c-s of Sumer • 1st Empire – many peoples & previously independent states under one ruler Hammurabi of Babylon • When- 1792- approx. 1750 B.C.E. • Problem – many different laws & customs throughout the land and acts of vengeance were common • Solution- Created a codified law system based on class rank. Harsh punishments Pillar of Law Hammurabi’s Code: “to make justice appear in the land” • 1st “Codified” Law (organized law code) • 1st Written law – engraved on stones throughout the empire • Uniform – all cs had to abide by it Questions • What categories does it deal with? • Is there equality under Hammurabi’s law? • Does it “make justice appear in the land?” • How do Hammurabi’s laws compare with ours in terms of the 1. types of laws, 2. types of punishments, 3. goal of the law?