ITF 220: The Economics of International Financial Policy Shopping
advertisement

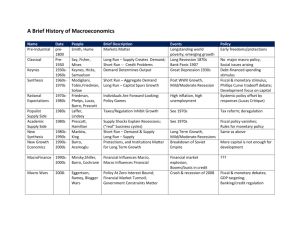
ITF 220: The Economics of International Financial Policy Course Preview, Shopping Day Prof. Jeffrey Frankel January 21, 2016 ITF-220: Economics of International Financial Policy • I.e., Open-economy macroeconomics • Professor: Jeffrey Frankel – Office hours: Mon.& Tues., 3:00-4:00. • Pre-requisites: – Introductory micro-economics – Intermediate macro-economics – Comfort with quantitative thinking, esp. algebra • Prerequisite for ITF 220: standard Intermediate Macroeconomics. For example: API 121 Macro Theory & Policy Spring Filipe Campante 3 Courses at more advanced levels than ITF-220: • API-120 Fall JF Advanced Macro for Open Economy I • API-119 Spring Filipe Campante + JF Advanced Macro for Open Economy II 4 Other useful / relevant courses • Econometrics • Finance – – API-141 – ITF 270 Fall Akash Deep Spring Carmen Reinhart Finance Financial Crises • International trade --at a much less technical level, – ITF-110 Fall Robert Lawrence Political Economy of Trade – ITF-225 Spring Robert Lawrence & Larry Summers Future of Globalization 5 Substitutes for ITF 220 (this course) • but at a more basic level: - ITF-100 F International Capital Markets [not offered, 2015-16 ] • At perhaps a slightly more advanced level: In the Economics Department (FAS), - Ec 1544 Spring Gita Gopinath [not offered 2015-16] • Foundations of International Macroeconomic Policy - Ec 1545 Fall Ken Rogoff International Financial and Macroeconomic Policy 6 Topics covered in ITF220 I) II) III) IV) V) ELASTICITIES & THE TRADE BALANCE THE KEYNESIAN MODEL OF INCOME MONEY AND THE BALANCE OF PAYMENTS GLOBALIZATION OF FINANCIAL MARKETS FISCAL & MONETARY POLICY UNDER INTERNATIONAL CAPITAL MOBILITY VI) INTERDEPENDENCE & COORDINATION VII) SUPPLY, INFLATION & MONETARY UNION VIII) EXPECTATIONS, MONEY & DETERMINATION OF THE EXCHANGE RATE Professor Jeffrey Frankel, Kennedy School, Harvard University Some applied illustrations of international economic questions that we study in ITF220 8 Why was the US trade balance on a downward trend, 1965-2011? with a improvements in 1990-91, 2001, & especially 2008-09? 100000 0 ($ millions) 19 70 19 74 19 78 19 82 19 86 19 90 19 94 19 98 20 02 20 06 20 10 -100000 Measures of external balance: United States ↑ Surplus ↓ Deficit -200000 -300000 Merchandise -400000 G&S TB -500000 CA balance -600000 -700000 -800000 -900000 Why did global trade collapse in the 2008-09 global recession? (much more than usual) 2009 Bussière, Callegari, Ghironi, Sestieri, & N.Yamano, 2013, "Estimating Trade Elasticities: Demand Composition and the Trade Collapse of 2008-2009." Has fiscal austerity helped, as a response to the euro crisis? Source: P.Krugman, 10 May 2012, via R.Portes, May 2013. Why are MacDonald’s hamburgers expensive in Norway & Switzerland? but cheap in India & Ukraine? 12 http://www.economist.com/news/finance-and-economics/21608647-our-flame-grilled-guide-currencies-suggests-dollar-getting-dearer Why has China been losing foreign exchange reserves since mid-2014? June 2014 Dec. 2015 13 Mexican inflation, 1970-2011 Why did Mexico used to suffer a currency crisis every 6 years? Changes in the $ value of the peso, 1970-2011 Hyperinflation: Why did Zimbabwe’s inflation rate reach 2,600% per month in mid-2008? After Fed “taper talk” in May 2013, why did capital flows to Emerging Markets reverse? Powell, Jerome. 2013. “Advanced Economy Monetary Policy and Emerging Market Economies.” Speech at the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco Asia Economic Policy Conference, November . http://www.frbsf.org/economic-research/publications/economic-letter/2014/march/federal-reserve-tapering-emerging-markets/