Requirements of Living Organisms (from external environment)
advertisement

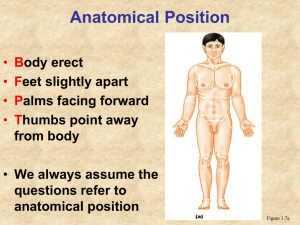
CHAPTER 1 INTRO. TO A&P Intro to A&P • Anatomy – • Physiology – deals with functions & how body parts operate Levels of Organization • Living organisms are composed of different levels of organization: • Atom- particles which make up matter • Organelle• Cell- basic unit of structure and function • Tissue- specialized cells organized into layers or masses that have specific functions. • Organs• Organ systems- groups of organs that function closely together • Organism- Levels of Organization Requirements of Living Organisms 1. Water 2. 3. Oxygen 4. 5. Water • Used in metabolic reactions• Necessary for transport • Body temperature regulation Food • Supplies energy • Supplies raw materials Oxygen • Used to release energy from food in cellular respiration Heat (a product of metabolism) • Determines • Most body heat is produced by the muscular system Pressure (an application of force) Two types: Atmospheric – the force exerted against a surface by the weight of the air above that surface; necessary for breathing • Hydrostatic – Homeostasis • Definition – maintenance of a stable, balanced internal environment • Use homeostatic mechanisms: • Receptors• Control Center- includes a set point, tells what a particular value should be. ( ex. 98.6°F) • Effectors- Negative Feedback • Most use negative feedback – changes that causes responses in the opposite direction; returns the body to normal (set point) • Examples – blood pressure, body temperature, blood glucose level Blood Glucose Level Homeostasis - Positive Feedback • Definition – • Examples – blood clotting, breastfeeding, childbirth Anatomical Terminology • Terms used to describe body position, body planes, etc. Anatomical Position When these terms are used, it is assumed the body is in Anatomical position: • Standing • Facing forward • Palms facing forward Relative Position – describes the location of 1 body part w/respect to another • Superior vs. Inferior • Anterior vs. Posterior • Medial vs. Lateral • Distal vs. Proximal More Anatomical Positions • Contralateral vs. Ipsilateral • Deep vs. Superficial • Peripheral Body Sections – planes along which the body may be cut to observe locations of organs Major Body Cavities – axial portion of body – includes two: 1. Dorsal – has 2 smaller cavities: a. Cranial – includes: - Nasal - Oral - Middle ear - Sinuses b. Vertebral - includes s.c. Major Body Cavities 2. Ventral – has 2 smaller cavities: a.Thoracic – includes: - pleural cavity – Mediastinum – the space separating the two lungs; includes: - pericardial cavity – Diaphragm – separates the thoracic from abdominal cavities b.Abdominopelvic - includes: - abdominal cavity - pelvic cavity - Body Cavities Membranes • 2 types: 1. visceral – covers an organ 2. parietal – • Used in combination w/ terms for body cavities: • Example – visceral pleura parietal peritoneum Characteristics of Life (traits shared by all living things) • Movement • Growth • Reproduction Characteristics of Life • Digestion • Circulation • Excretion Together. these activities constitute an living thing’s metabolism (all the chemical & physical changes that occur) Organ Systems (11 total) • Integumentary system- skin and accessory organs (hair, nails and sweat glands). • Protects underlying tissue, regulates body temp and contains sensory receptors • Skeletal system- Bones, ligaments and cartilage • Provides framework and protective shields for soft tissue. • Production of blood cells • Respiratory system- Lungs, pharynx, larynx and trachea • Exchange gases between air and blood • Reproductive system- Male and female reproductive organs. • Production of new organisms • Endocrine system- Pituitary, thyroid and adrenal glands • Secrete hormones which trigger metabolic function Organ Systems • Muscular system- Provide forces that cause movement. • Nervous System – Brain, spinal cord and nerves • Stimulates muscles to contract and activates glands • Cardiovascular System- Heart, arteries, capillaries and blood. • Transports products throughout body. • Lymphatic System-Lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, thymus and spleen • Filters blood for pathogens and removes fats from digestive tract. Organ Systems • Digestive System- Mouth, teeth, salivary glands, esophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, small and large intestines. • Converts food molecules so they can be absorbed. • Urinary system- Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra • Remove waste from blood and maintain water balance Review • Membranes Review – Relative Positions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. The gall bladder is _______ to the diaphragm. The lungs are ______ to the heart. The esophagus is ______ to the stomach. The wrist is _______ to the shoulder. The uterus is ______ to the ovaries. The ribs are ______ to the vertebrae. The esophagus is ________ to the trachea. The elbow is _____ to the wrist.