Chapter 5

Chapter 5
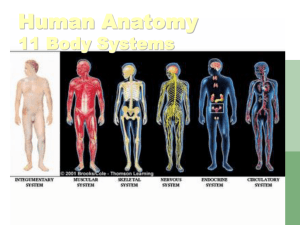
The Human Body
2
Objectives
• There are no 1985 objectives for this chapter.
3
Introduction
• Anatomy
– The study of structures and components of an organism
• Physiology
– The study of the body functions of a living organism
• Pathophysiology
– The study of the body functions of a living organism in an abnormal state
4
The Structure of the Human
Body
(1 of 3)
• Cells
– Most basic component of an organism
• Tissues
– A group of similar cells working together to perform a common function
• Organs
– Different types of tissues working together to perform a particular function
5
The Structure of the Human
Body
(2 of 3)
• Organ systems
– Groups of organs that work together
– May be located together or apart
– Combined, they form an organism
– Carry out vital functions
6
The Structure of the Human
Body
(3 of 3)
• Organ systems include:
– Musculoskeletal, circulatory, respiratory, nervous, gastrointestinal, urinary, reproductive, immune, endocrine, lymphatic, integumentary, and special sensory
• Homeostasis
– Balanced internal environment
– System of checks and balances
7
Anatomic Terminology
(1 of 3)
• Anatomic terminology
– Landmarks for guides of internal structures
• The anatomic position
– Universal position from which all body positions and movements are described
• Anatomic planes
– Flat surfaces that pass through the body
8
The Anatomic Position
9
Anatomic Terminology
(2 of 3)
• Frontal plane
– Anterior and posterior
• Transverse plane
– Cranial and cephalad
• Median plane
– Medial and lateral
• Sagittal plane
• Proximal and distal
• Midline
• Midaxillary line
• Midclavicular line
10
The Midclavicular Line
11
Anatomic Terminology
(3 of 3)
• Directional Terms
– Right and left
– Superior and inferior
– Superficial and deep
– Ventral and dorsal
– Palmar and plantar
– Apex
• Other Directional Terms
– Bilateral
– Contralateral
– Ipsilateral
12
Abdominal Quadrants
• Abdomen
– Two imaginary lines divide this area into four parts
– Inferior tip of sternum to the genital area; iliac crest across the umbilicus
– Right upper quadrant, left upper quadrant, right lower quadrant, left lower quadrant
– Each quadrant contains specific organs
13
The Four Quadrants of the
Abdomen
14
Anatomic Positions
(1 of 4)
• Prone – face down
• Supine – face up
• Lateral recumbent – lying on left side
15
Anatomic Positions
(2 of 4)
• Fowler’s position and semi-Fowler’s position
– Sitting upright at a 90° angle
– Sitting upright at a 45° angle
16
Anatomic Positions
(3 of 4)
• Trendelenburg’s position
– Supine with the head down and lower extremities elevated approximately 12”
– Helps increase blood flow to the brain
17
Anatomic Positions
(4 of 4)
• Shock position
– Also called modified Trendelenburg’s position
– Head and torso are supine
– Lower extremities elevated 6-12”
18
Movements and Positions
(1 of 2)
• Movements
– From simple to complicated, movements can be broken down into a series of components and described with specific terms
• Range of Motion (ROM)
– Full distance that a joint can be moved
– Flexion
• Moving a distal part of an extremity toward the trunk
19
Movements and Positions
(2 of 2)
• ROM
– Extension
– “Hyper”
• Supination and pronation
• Internal and external rotation
• Abduction and adduction
20
Cellular Transport Mechanisms
• Permeability of the cell membrane
– Selective permeability
• Allows some substances to pass, but not others
• Maintains environments
– Electrolytes
• Chemicals dissolved in blood, made of salt or acid substances that become iconic conductors when dissolved in a solvent
21
Diffusion
• Diffusion
– The movement of solutes, which are particles such as salts, dissolved in a solvent
• Concentration gradient
– Difference in concentrations of the substance on either side of the membrane
– Small molecules diffuse more easily than large ones; watery solutions diffuse faster than viscous solutions
22
Osmosis
• Osmosis
– The movement of a solvent, such as water, from an area of low solute concentration to high concentration
• Osmotic pressure
– Measure of the tendency of water to move by osmosis across a membrane
• Crenation
• Lysis
23
Permeability of the Cell
Membrane
• Facilitated diffusion
– The process in which a carrier molecule moves substances in or out of cells from high to low concentration
• Active transport
– The movement of a substance against a concentration or gradient
24
Endocytosis and Exocytosis
• Endocytosis
– Uptake of material through the cell membrane by a membrane-bound droplet that forms within the protoplasm of the cell
– Phagocytosis or “cell eating”
– Pinocytosis or “cell drinking”
• Exocytosis
– The release of secretions from the cells
25
Cellular Metabolism
• Metabolism
– The sum of all the physical and chemical processes that produce and maintain the body
– Two phases:
• Anabolism or “building phase”
• Catabolism or “break down phase”
– Body’s fuel
• Carbohydrates (mostly glucose), fats, and proteins
26
Cellular Respiration
• Respiration
– Process of using glucose, fat, and proteins to generate energy
– Creates energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate
(ATP)
– Takes place within the mitochondria
– Krebs cycle
– Glycolysis
27
Tissues
(1 of 4)
• Epithelial tissue and glands
– Type of tissue that covers all external body surfaces and forms secreting portions of glands
– Lines hollow organs in the body
– Provides a protective barrier
– Functions in absorption of nutrients
– Functions in secretion of body substances
28
Tissues
(2 of 4)
• Connective tissue
– Connects other types of tissue together
– Extracellular matrix
– Adipose tissue
• Contains large amounts of lipids
– Other types of connective tissues
• Aid in formation of blood vessels
• Part of the body’s self-defenses
29
Tissues
(3 of 4)
• Muscle Tissue
– Located within the substance of the body and invariably enclosed by connective tissue
– Classified by structure and function
– Structural
• Striated or nonstriated
– Function
• Voluntary and involuntary
– Cardiac muscle
30
Tissues
(4 of 4)
• Nerve tissue
– Peripheral nerves
• All nerves extending from the brain and spinal cord
• Exiting from between vertebrae to various parts of the body
– Neurons
• Main conducting cells of nerve tissue
– Dendrites
– Axons
– Neuroglia
31
Integumentary System
(1 of 2)
• Integumentary system
– Outer surface of the body
– Skin, nails, hair, and sweat and oil glands
– Largest organ in the body; accounts for 15% of body weight
• Function of the skin
– Protection from the environment
– Regulation of body temperature
– Transmission of information to the brain
32
Integumentary System
(2 of 2)
• Anatomy of the skin
– Epidermis
– Subcutaneous tissue
– Sebaceous glands
– Dermis
– Sweat glands
– Hair follicles
33
Anatomy of the Skin
34
Skeletal System
• Axial skeleton
– Forms the upright part of the body
– Consists of:
• Hyoid, skull, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum
• Appendicular skeleton
– Attached to the axis as appendages
– Consists of:
• Shoulder and pelvic girdles, upper and lower extremities
35
The Skull
(1 of 3)
• Skull
– Consists of 28 bones in three anatomic groups: auditory ossicles, cranium, and face
– Cranial vault
• Encases, protects the brain
• Parietal, temporal, frontal, occipital, sphenoid, and ethmoid bones
• Foramen magnum
36
The Skull
(2 of 3)
• Sutures
– Sagittal suture
– Coronal suture
– Lambdoid suture
• Fontanels
37
The Skull
(3 of 3)
• Mastoid process
• External auditory meatus
• Ossicles
• Styloid process
• Facial nerve
38
The Floor of the Cranial Vault
• Cranial vault
– Divided into three compartments:
• Anterior fossa, middle fossa, and posterior fossa
– Structures of note:
• Crista galli
• Cribiform plate
• Foramina
• Olfactory bulb
• Nasal cavity
• Sella turcica
39
The Base of the Skull
• Base of the skull
– Complex and full of foramina
• Structures of note:
– Occipital condyles
– Palatine bone
– Zygomatic arch
40
The Facial Bones
• Facial bones
– Frontal and ethmoid bones part of the cranial vault and the face
– Composed of 14 bones
– Include:
• Maxillae, mandible, zygoma, palatine, nasal, lacrimal, vomer, and inferior nasal concha bones
– Protect the eyes, nose, and tongue and provide attachment points for muscles involved in mastication
41
Bones of the Orbit
• Orbits
– Cone-shaped fossae
– Enclose and protect the eyes
– Contain blood vessels, nerves, and fat
– Created by the frontal, sphenoid, zygomatic, maxilla, lacrimal, ethmoid, and palatine bones
– Blow to the eye can result in fracture of the orbit floor
(blowout fracture)
42
Bones of the Nose
• Nasal bones
– Composed of several portions of the facial bones
• Structures of note:
– Nasal septum
– Paranasal sinuses
43
The Mandible and
Temporomandibular Joint
• Mandible
– Large movable bone
– Composed of the lower jaw and teeth
• Structures of note:
– Rami
– Mandibular notch
– Temporomandibular joint
44
The Hyoid Bone
• Hyoid
– “Floats”
– Not actually part of the skull
– Supports the tongue and serves as a point of attachment for neck and tongue muscles
45
The Neck
(1 of 2)
• Neck
– Contains several important structures
• C1-C7
• Upper portion of the trachea and esophagus
– Useful landmarks
• Adam’s apple (upper part of the thyroid cartilage)
• Cricoid cartilage
• Cricothyroid membrane
• Cartilaginous rings
46
The Neck
(2 of 2)
• More structures of note:
– Carotid arteries
– Internal jugular veins
– Sternocleidomastoid muscles
– Sternum
– Spines of the cervical vertebrae
• Most prominent is C7
47
The Spine
(1 of 4)
• Vertebral column
– Cervical (7)
– Thoracic (12)
– Lumbar (5)
– Sacrum (5)
– Coccyx (4)
48
The Spine
(2 of 4)
• Atlas (C1)
– Point at which the head rotates
• Axis (C2)
– Dens or odontoid process
• Spinal cord
– Extension of the brain
– Carries messages between the body and brain
– Exits skull through foramen magnum
– Protected by the vertebrae
49
The Spine
(3 of 4)
• The vertebrae
– Anterior portion consists of a solid block called “the body”
– Posterior part called the “bony arch”
– Series of arches form a tunnel that runs the length of the spine called the “spinal canal” which encases and protects the spinal cord
– Vertebrae are connected by ligaments
– Intervertebral discs
50
The Spine
(4 of 4)
51
The Thorax
(1 of 2)
• Thorax
– Contains the heart, lungs, esophagus, and great vessels
– T1-T12
– Clavicle
– Scapula
– Diaphragm
52
The Thorax
(2 of 2)
• Anterior aspects
– Sternum:
• Manubrium, xiphoid process, angle of Louis
– 12 pairs of ribs
• Costal arch
• Floating ribs
• Posterior aspects
– Costovertebral angle (junction of the spine and the tenth ribs)
53
54
Diaphragm/Organs and Vascular
Structures
• Diaphragm
– Muscular dome
– Separates thorax and abdomen
– Involved in respiration
– Anteriorly attaches to costal arch; posteriorly to lumbar vertebrae
• Organs and vascular structures
– Pulmonary artery
– Anatomic landmarks
The Abdomen
• The Abdomen
– Second major body cavity
– Contains organs of digestion and excretion
– Separated by:
• Diaphragm, muscular walls, imaginary plane extending from the pubic symphysis through the sacrum
– Shares organs with the pelvis (depending on posture)
– Quadrants
55
Review of Abdominal Quadrants
56
The Organs of the Abdomen
57
Organs and Vascular Structures
(1 of 2)
• RUQ
– Liver, gallbladder, portion of the colon/small intestine
• LUQ
– Stomach, spleen, portion of the colon/small intestine
• RLQ
– Cecum, appendix
• LLQ
– Descending and sigmoid portions of the colon
• Retroperitoneal
– Kidneys
58
Organs and Vascular Structures
(2 of 2)
59
Anatomic Landmarks
• Landmarks of the abdomen
– Costal arch
– Umbilicus
– Anterior superior iliac spines
– Iliac crest
– Pubic symphysis
• Other structures
– Inguinal ligament
60
The Appendicular Skeleton
(1 of 2)
• Shoulder girdle
– Attaches upper extremity to the body
– Composed of scapula and clavicle
• Shoulder joint
– Acromion process
– Ball and socket joint
– Glenoid fossa
– Motions include: flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation, and circumduction
61
Anterior View of the
Shoulder Girdle
62
Posterior View of the
Shoulder Girdle
63
Anterior View of the
Shoulder Joint
64
The Appendicular Skeleton
(2 of 2)
• Acromioclavicular joint
• Upper extremity
– Forearm, wrist, hand, and fingers
– Humerus
• Forearm and wrist
– Radius and ulna
– Wrist composed of eight bones called carpals
• Hand
– Metacarpals, phalanges
65
The Carpals
66
The Pelvic Girdle
(1 of 2)
• Pelvis
– Where the lower extremities attach to the body
– Ring of bones
• Sacrum, pelvic bones
• Coxal bones: ilium, ischium, and pubis
– Contains three joints
• Two posterior sacroiliac joints, interior midline pubic symphysis
67
The Pelvic Girdle
(2 of 2)
68
The Lower Extremity
• Lower extremity
– Composed of: hip, thigh, knee, leg, ankle, foot, and toes
• Structures of note:
– Femur (longest, strongest bone in the body)
– Femoral head (articulates with pelvic girdle)
– Acetabulum
– Greater trochanter
69
The Leg, Knee, and Ankle
• Leg
– Patella
– Medial malleolus
– Lateral malleolus
• Knee
– Hinge joint
– Contains ligaments within the join
• Ankle
– Phalanges, metatarsals
70
Cartilage, Tendons, and
Ligaments
• Cartilage
– All are connective tissues
– Synovial fluid
• Tendons
– Periosteum
– Connects muscle to bone
• Ligaments
– Tough, white bands of tissue
– Connect bone to bone
71
Bones: Their Growth and
Organization
(1 of 2)
• Bones
– Specialized form of connective tissue
– Protect internal organs
– Storage site for minerals
– Consist of collagen and hydroxyapatite
– Living substances that require blood supply
– Terms:
• Osteoblasts, osteocyte, osteoclasts, lamellae, lacuna, canaliculi
72
Bones: Their Growth and
Organization
(2 of 2)
• Bones
– Classified according to shape
• Long, short, and flat
– Long bones
• Consist of diaphysis, epiphyses, and physis
– Two main types:
• Compact and cancellous
– Growth
• Appositional and endochondral
73
Joints
• Joints
– When two bones contact
– Consist of ends of bones and connective and supporting tissue
– Named by combining names of the two bones
• Joint capsule
• ROM
– Determined by extent ligaments hold together
74
The Ankle Joint
75
The Musculoskeletal System
• Skeletal muscle
– Voluntary, striated
– Under control of the nervous system
• Smooth muscle
– Involuntary
– Responds to stretching, heat, and waste removal
• Cardiac muscle
– Involuntary, rich blood supply, own electrical system
– “automaticity”
76
The Nervous System
(1 of 2)
• Nervous system
– Complex array of structures
– Controls voluntary and involuntary body functions
– Major divisions include:
• Central, peripheral, and autonomic
– Composed of specialized tissue that conducts electrical impulses between the brain and body
77
The Nervous System
(2 of 2)
• Nervous system terminology:
– Synapse
– Presynaptic terminal
– Synaptic cleft
– Postsynaptic cleft
– Neurotransmitters
– Synaptic vesicles
– Nerve fibers
– “Fight or flight” and “Feed or breed”
78
The Central Nervous System
(1 of 2)
• The central nervous system
– Brain and spinal cord
• Cerebrum
– Left and right
– Longitudinal fissure
– Lobes
• Frontal
• Parietal
• Occipital
• Temporal
79
The Central Nervous System
(2 of 2)
80
Cerebral Cortex
• Diencephalon
– Located between brain stem and cerebrum
– Contains thalamus, subthalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus
81
The Brainstem
(1 of 2)
• Brainstem
– Connects spinal cord and brain
– Consists of medulla, pons, and midbrain
– Vital for basic body functions
– Basal ganglia
– Limbic system
– Pons
– Ascending reticular activating system
82
The Brainstem
(2 of 2)
83
The Cerebellum and Meninges
• Cerebellum
– Communicates with other regions of the CNS
– Cerebellar peduncles
– Essential for coordinating muscle movements
• Meninges
– Encloses the CNS
– Dura mater
– Arachnoid
– Pia mater
84
The Spinal Cord
• Spinal cord
– Continuation of the CNS
– Composed of nerve fibers
– Extends to the level of L2
– Cauda equina
– Vertebral canal
– Ascending fibers (afferent tracts)
– Action potentials
– Descending fibers (efferent tracts)
85
The Peripheral Nervous System
• Peripheral nervous system
– Consists of nerves from CNS to peripheral structures
– Ganglia
– Spinal nerves
– Ventral root, dorsal root, dorsal root ganglion
– Intervertebral foramen
– Dermatomes
86
The Plexuses
• Cervical plexus
– Most important nerve is the phrenic nerve
• Brachial plexus
– Divided into rami, trunks, divisions, cords, and branches
– Axillary, radial, musculocutaneous, median, and ulnar
• Lumbosacral Plexus
– Six major nerves: obturator, femoral, tibial, common peroneal, sciatic, deep peroneal, and superficial peroneal
87
The Phrenic Nerve
88
The Cranial Nerves
(1 of 2)
• Cranial nerves
– 12 pairs
– Functions:
• Olfactory (I) – smell
• Optic – (II) sight
• Oculomotor (III) – motion of the eyeballs/upper lid
• Trochlear (IV) – downward gaze
• Trigeminal (V) – sensation to scalp, face, and lower jaw
89
The Cranial Nerves
(2 of 2)
• Functions continued:
– Abducens (VI) – lateral eye movement
– Facial (VII) – facial expression, sense of taste
– Vestibulocochlear (VIII) – hearing, balance
– Glossopharyngeal (IX) – pharyngeal muscles
– Vagus (X) – parasympathetic fibers of thorax/abdominal organs
– Spinal accessory (XI) – soft palate
– Hypoglossal (XII) – tongue, C1-C3
90
The Optic Nerve
91
The Autonomic Nervous System
• ANS
– Operates without conscious control
– Sympathetic and parasympathetic
– Terms: sympathetic pathway and adrenal glands
• Preganglionic and postganglionic neurons
– Separated by ganglionic synapse
– Neuroeffector cells
92
Neurotransmitters and
Receptors
• Sympathetic and parasympathetic
– Secrete one of two neurotransmitters
– Both secrete acetylcholine from preganglionic fibers; diffuse across nicotinic receptors
– Acetylcholine destroyed by acetylcholinesterase
– Muscarinic receptors
– Alpha and beta receptors
93
The Endocrine System
• Endocrine system
– Made of various glands
– Hormones regulate body functions
– Targets tissues
– Endocrine versus exocrine glands
– Prostaglandins
– Steroids and thyroid hormones
– Negative feedback or positive feedback
94
The Pituitary Gland and
Hypothalamus
(1 of 2)
• Pituitary gland
– Known as the the “master gland”
– Located at the base of the brain
• Hypothalamus
– Basal portion of diencephalon
– Regulates function of pituitary gland
95
The Pituitary Gland and
Hypothalamus
(2 of 2)
• Posterior pituitary lobe
– Antidiuretic hormone or vasopressin
• Constricts blood vessels and raises BP
• Target tissue is the kidney
– Oxytocin
• Causes smooth muscles (uterus) to contract
• Lactation
• Anterior pituitary lobe
– Not considered part of the CNS
96
Hormones
• Growth hormone
– Stimulates growth (long bones)
– Produced by hypothalamus
• Thyroid-stimulating hormone
• Adrenocorticotropic hormone
– Corticosteroids stimulated by stress
• Reproduction-regulating hormones
– Regulate production of eggs and sperm
97
The Thyroid Gland
• Thyroid
– Large gland at the base of the neck
– Two lobes connected by the isthmus
– Contains follicles filled with thyroglobulin
– Between the follicles are parafollicular cells
• Produce calcitonin
– Thyroid gland produces triiodothyronine and tetraiodothyronine
98
The Parathyroid Glands
• Usually four in number
• Produce and secrete parathyroid hormone
– Maintains normal levels of calcium in the blood and normal neuromuscular function
99
The Pancreas
• Pancreas
– Belongs to both endocrine and digestive systems
– Retroperitoneum
– Produces insulin and glucagon
– Islet of Langerhans
• Alpha and beta cells
– Glycogen
100
The Adrenal Glands
(1 of 2)
• Adrenal glands
– Supra-renal glands
– Manufacture and secrete certain sex hormones
– Medulla
• Epinephrine and norepinephrine
– Adrenal cortex
• Divided into three zones
• Aldosterone
101
The Adrenal Glands
(2 of 2)
• Zona fasiculata
– Glucocorticoids
• Cortisol: regulates blood glucose, metabolizes fat tissue, inhibits inflammation
– Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
• Regulates secretion of corticosteroids
• Zona reticularis
– Androgens
• Androstendedione
102
The Reproductive Glands and
Hormones
• Gonads
– Testes
• Testosterone
– Ovaries
• Estrogen
• Progesterone
• Human chorionic gonadatropin (hCG)
103
Blood and Its Components
• Blood
– Substance consists of plasma and formed elements
• Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
– Adult male contains about 5 liters of blood
– Plasma
• Watery, straw-colored fluid
• Accounts for >50% of total blood volume
• Made of 92% water and 8% other substances
104
Red and White Blood Cells
• RBCs
– Disc-shaped
– Most numerous of the formed elements
– Contain hemoglobin
– Erythropoiesis
• WBCs
– Called leukocytes
– Fight infection
– Granulocytes and agranulocytes
105
Platelets and Blood Clotting
• Platelets
– Necessary in clot formation
– Hemostasis
– Chemicals are released, activation of platelets
– Formation of thrombin
– Conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin
– Binds to platelet plug forming a clot
– Activation of t-PA
106
The Heart
(1 of 2)
• Location and major structures of the heart
– Located behind the sternum
– About the size of the closed fist of the person it belongs to
• Mediastinum
• Myocardium
107
The Heart
(2 of 2)
• The pericardium surrounds the heart
– Visceral and parietal layer
– Pericardial fluid
108
Blood Flow Within the Heart
(1 of 2)
• Superior and inferior vena cava
– Return deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium
• Blood passes into the right ventricle
• Blood is pumped through the pulmonic valve into the pulmonary artery and to the lungs
109
Blood Flow Within the Heart
(2 of 2)
• Freshly oxygenated blood is returned to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins
• Blood flows through the mitral valve into the left ventricle, which pumps the oxygenated blood through the aortic valve into the aorta and then the entire body
110
111
Electrical Properties of the Heart and Conduction System
• Electrical stimulus
– Caused by a set of chemical changes within the myocardial cells
– “Automaticity”
• Conduction system
– Six parts: SA node, AV node, bundle of His, right and left bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers
112
The Cardiac Conduction System
Valves of the Heart
• Atrioventricular valves
– Tricuspid valve
– Mitral valve
• Cusps
• Papillary muscles
• Chordae tendineae cordis
– Semilunar valves
• Pulmonic valve
• Aortic valve
113
Regulation of Heart Function
• Chronotropic state
– Contraction
• Dromotropic state
– Rate of conduction
• Inotropic state
– Strength of contraction
• Baroreceptors and chemoreceptors
• Alpha and beta effects
114
The Cardiac Cycle
• Cardiac cycle
– Contraction results in pressure changes in the chambers
– Systole
– Cardiac output
– Circulatory system
– Ejection fraction: CO = SV x HR
– Starling’s Law of the Heart
– Preload and afterload
115
The Vascular System
• The general scheme of blood circulation
– Transported through arteries and veins
– Arterioles, capillaries, and venules
• Circulation to the heart
– Coronary arteries
– LAD
– Circumflex coronary arteries
116
The Scheme of Circulation
117
Pulmonary and Systemic
Arterial Circulation
• Pulmonary circulation
– Carries blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs and back
• Systemic arterial circulation
– head and neck
– upper extremity
– thoracic aorta
– abdominal aorta
– pelvis and lower extremity
118
Systemic Venous Circulation
• Head and neck
• Upper extremity
• Thorax
• Abdomen and pelvis
– Hepatic portal system
• Lower extremity
– Femoral, popliteal, dorsalis pedis, and posterior tibial arteries
119
Arteries of the Head and Neck
120
Physiology of the Circulatory
System
• Terms:
– Pulse, radial artery, blood pressure, diastole
• Normal circulation in adults
– Vessels adjust to hold 100% of the blood volume
– Perfusion: meets the cell needs
• Inadequate circulation in adults
– Automatic adjustment during blood loss to maintain adequate pressure
121
The Lymphatic System
• Lymphatic vessels
– Diffuse lymphatic tissue and lymph nodules
– Axillary nodes, cervical nodes, and inguinal nodes
• Lymph organs
– Tonsils
– Spleen
– Thymus
122
The Respiratory System
• Respiratory system
– Breathing, gas exchange, and entrance of air
• Upper airway
– Mouth, nasal cavity, and oral cavity
– Uvula, epiglottis, nares, conchae, and turbinates
• Lower airway
– Larynx, vocal cords, glottis, bronchi, alveoli, lungs, pleura, and bronchial arteries and veins
123
Respiratory Physiology
• Physiology
– Primary function to exchange gases at the alveolocapillary membrane
– 21% oxygen in the air
– Pulmonary function tests and spirometry
– Tidal volume, residual volume, vital capacity, and
FEVI
• Respiratory center
– Located in the medulla oblongata
124
The Digestive System
(1 of 2)
• How digestion works
– Complex chemical process
• Anatomy of the digestive system
– Mouth
– Salivary glands
– Oropharynx
– Esophagus
– Stomach
– Pancreas
125
The Digestive System
(2 of 2)
• More anatomy of the digestive system
– Liver
– Bile ducts
– Small intestine
– Large intestine
– Appendix
– Rectum
126
The Urinary System
• Urinary system
– Controls the discharge of waste materials filtered from the blood by the kidneys
– Kidneys
– Ureter
– Urinary bladder
– Urethra
127
The Urinary System
128
The Genital System
• Genital system
– Controls reproductive processes
• Male reproductive system and organs
– Testicles, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, urethra, and penis
• Female reproductive system and organs
– Ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina
129
Fluids and Electrolytes
(1 of 2)
• Body fluid balance
– Total body water averages 50-70% of total body weight
– Intracellular and extracellular fluid
– Intravascular fluid and interstitial fluid
– Fluid balance is the process of maintaining homeostasis through equal intake and output
– ADH, thirst, kidneys, and water shifts
130
Fluids and Electrolytes
(2 of 2)
• Acid-base balance
– Acids and bases
– Alkalotic versus acidotic
– pH range 0-14 with 7.0 being neutral
• Buffer systems
– Act as fast defenses for acid-base challenges
– Absorb hydrogen ions when they are in excess
131