Ch 4
advertisement
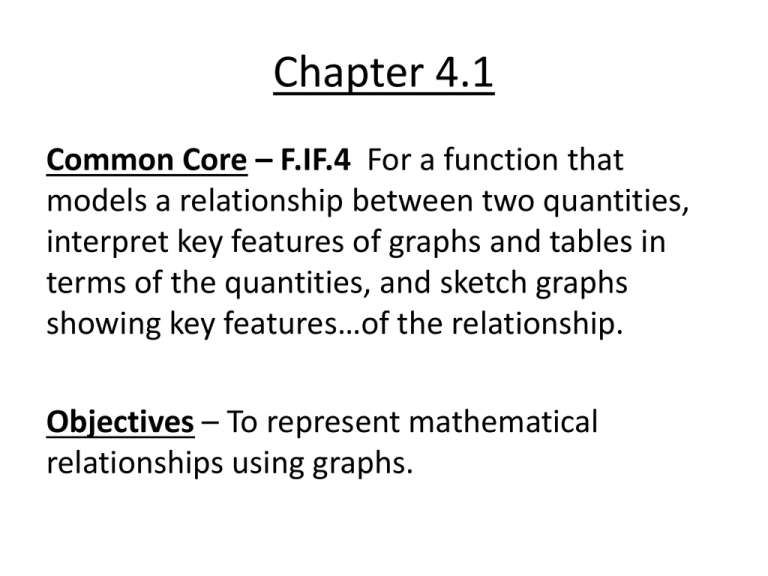
Chapter 4.1 Common Core – F.IF.4 For a function that models a relationship between two quantities, interpret key features of graphs and tables in terms of the quantities, and sketch graphs showing key features…of the relationship. Objectives – To represent mathematical relationships using graphs. Chapter 4.2 Common Core – A.REI.10 & F.IF.4 Understand that the graph of an equation in two variables is the set of al its solutions plotted in the coordinate plane, often forming a curve. Objectives – To identify and represent patterns that describe patterns that describe linear functions. Chapter 4.3 Common Core – A.REI.10 & F.IF.4 Understand that the graph of an equation in two variables is the set of al its solutions plotted in the coordinate plane, often forming a curve. Objectives – To identify and represent patterns that describe nonlinear functions. Chapter 4.4 Common Core – F.IF.5, N.Q.1, & A.REI.10 Relate the domain of a function to its graph and, where applicable, to the quantitative relationship it describes. Objectives – To graph equations that represent functions. Chapter 4.5 Common Core –N.Q.2, A.SSE.1a, & A.CED.2 Define appropriate quantities for the purpose of descriptive modeling. Objectives – To write equations that represent functions. Chapter 4.6 Common Core –F.IF.1 Understand that a function from one set (called the domain) to another set (called the range) assigns to each element of the domain exactly one element of the range. Objectives – To determine whether a relation is a function. To find domain and range and use function notation. Chapter 4.7 Common Core –F.IF.3, A.SSE.1a, A.SSE.1.b, F.BF.1.a, F.BF.2, & F.LE.2 Recognize that sequences are functions, sometimes defined recursively, whose domain is a subset of the integers. Objectives – To identify and extend patterns in sequences. To represent arithmetic sequences using function notation.