Algebra 1 Mathematics Curriculum Northview High School Common
advertisement

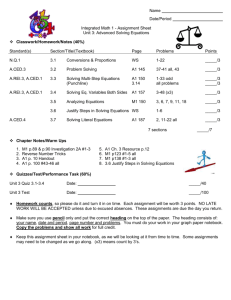
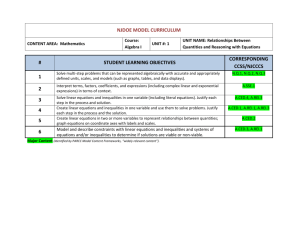
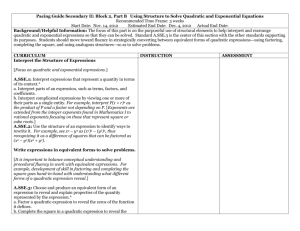
Algebra 1 Mathematics Curriculum Northview High School Common Core State Standards Mathematics Curriculum Description of Standards The high school standards specify the mathematics that all students should study in order to be college and career ready. Additional mathematics that students should learn in fourth credit courses or advanced courses such as calculus, advanced statistics, or discrete mathematics is indicated by (+). All standards without a (+) symbol should be in the common mathematics curriculum for all college and career ready students. Standards with a (+) symbol may also appear in courses intended for all students. The high school standards are listed in conceptual categories including Number and Quantity, Algebra, Functions, Modeling, Geometry, and Statistics and Probability, and Contemporary Mathematics. Conceptual categories portray a coherent view of high school mathematics; a student’s work with functions, for example, crosses a number of traditional course boundaries, potentially up through and including calculus. Modeling is best interpreted not as a collection of isolated topics but in relation to other standards. Number and Quantity • The Real Number System (N-RN) • Quantities (N-Q) • The Complex Number System (N-CN) • Vector and Matrix Quantities (N-VM) Algebra • Seeing Structure in Expressions (A-SSE) • Arithmetic with Polynomials and Rational Expressions (A-APR) • Creating Equations (A-CED) • Reasoning with Equations and Inequalities (A-REI) Functions • Interpreting Functions (F-IF) • Building Functions (F-BF) • Linear, Quadratic, and Exponential Models (F-LE) • Trigonometric Functions (F-TF Geometry • Congruence (G-CO) • Similarity, Right Triangles, and Trigonometry (G-SRT) • Circles (G-C) • Expressing Geometric Properties with Equations (G-GPE) • Geometric Measurement and Dimension (G-GMD) • Modeling with Geometry (G-MG) Modeling Statistics and Probability • Interpreting Categorical and Quantitative Data (S-ID) • Making Inferences and Justifying Conclusions (S-IC) • Conditional Probability and the Rules of Probability (S-CP) • Using Probability to Make Decisions (S-MD) Contemporary Mathematics • Discrete Mathematics (CM-DM) MONTH August - Quarter 1 Unit 1 Relationship Between Quantities and Reasoning with Equations CURRICULUM TOPICS • Reason quantitatively and use units to solve problems (N.Q.1, N.Q.2, N.Q.3) • Create equations that describe numbers or relationships (A.CED.1, A.CED.2, A.CED.3, A.CED.4) • Interpret the structure of expressions (A.SSE.1.a, A.SSE.2.b) • Solve equations and inequalities in one variable (A.REI.3) • Understand solving equations as a process of reasoning and explain the reasoning (A.REI.1) September Unit 4 Expressions and Equations October(Quarter 2) • Write expressions in equivalent forms to solve problems (A.SSE.3.a, A.SSE.3.b, A.SSE.3.c) • Interpret the structure of expressions (A.SSE.1.a, A.SSE.2.b, A.SSE.2) • Perform arithmetic operations on polynomials (A.APR.1) • Create equations that describe numbers or relationships (A.CED.1, A.CED.2, A.CED.4) • Solve equations and inequalities in one variable (A.REI.4.a, A.REI.4.b) • Solve systems of equations (A.REI.7) November Unit 2 Linear and Exponential Relationships December (Quarter 3) • Represent and solve equations and inequalities graphically (A.REI.10, A.REI.11, A.REI.12) • Solve systems of equations (A.REI.5, A.REI.6) • Understand the concept of a function and use function notation (F.IF.1, F.IF.2, F.IF.3) • Interpret functions that arise in applications in terms of a context (F.IF.4, F.IF.5, F.IF.6) • Build a function that models a relationship between two quantities (F.BF.1, F.BF.2) • Analyze functions using different representations (F.IF.7.a, F.IF.7.e, F.IF.9) • Build new functions from existing functions (F.BF.3) MONTH CURRICULUM TOPICS • Construct and compare linear, quadratic, and exponential models and solve problems (F.LE.1.a, F.LE.1.b, F.LE.1.c, F.LE.2, F.LE.3) • Extend the properties of exponents to rational exponents (N.RN.1, N.RN.2) • Interpret expressions for functions in terms of the situation the model (F.LE.5) January February Unit 5 Quadratic Functions and Modeling March (Quarter 4) • Use properties of rational and irrational numbers (N.RN.3) • Interpret functions that arise in applications in terms of a context (F.IF.4, F.IF.5, F.IF.6) • Analyze functions using different representations (F.IF.7.a, F.IF.7.b, F.IF.8.a, F.IF.8.b, F.IF.9) • Build a function that models a relationship between two quantities (F.BF.1.a, F.BF.1.b) • Build new functions from existing functions (F.BF.3, F.BF.4.a) • Construct and compare linear, quadratic, and exponential models and solve problems (F.LE.3) May Unit 3 Descriptive Statistics June • Summarize, represent, and interpret data on a single count or measurement variable (S.ID.1, S.ID.2, S.ID.3) • Summarize, represent, and interpret data on two categorical and quantitative variables (S.ID.5, S.ID.6.a, S.ID.6.b, S.ID.6.c) • Interpret linear models (S.ID.7, S.ID.8, S.ID.9)