intro_to_plant_names_tanner
advertisement

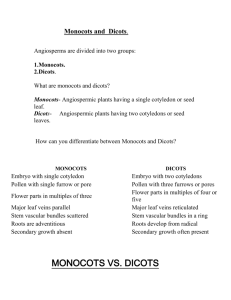
Cory Tanner or Tannerius coryi Consumer Horticulture Agent/Master Gardener Coordinator Terminology Botany: the science of plants Taxonomy: the classification of plants Vascular Plants Ferns Cone Bearing Plants Flowering Plants Dicots Monocots Terminology Gymnosperm – “naked seed” Has no flower or ovary (fruit); only cones All conifers (pines, cedars, arborvitae) Angiosperm – “vessel seeded” Has a flower with an ovary (fruit) All flowering plants Divided into Monocots and Dicots Terminology Dicotyledons (Dicots): - flowering plants that contain two seed leaves Monocotyledons (Monocots): - flowering plants that possess one seed leaf Monocot Dicot Botanical Names What’s Wrong with Common Names? Catesby’s Trillium or Rosey Wake-robin or Bashful Wake-robin Trillium catesbaei Plant Classification Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Cultivar Scientific Plant Names Binomial Nomenclature – 2-name system Genus species Developed by Carolus Linnaeus (1753) Always Latinized and italicized Usually very descriptive of the plant Scientific Plant Names (cont.) Genus – a noun identifies a particular group of related plants First letter always capitalized species – typically an adjective identifies a distinct subset of the Genus all lowercase Let’s try some! White Oak Quercus alba Canadian Hemlock Tsuga canadensis Acer rubrum Red Maple Osmanthus fragrans Fragrant Tea Olive Scientific Plant Names (cont.) When two names aren’t enough… variety – has traits that separate it from the species, but not enough to be a new species Designated by var. Cercis canadensis var. alba cultivar – “cultivated variety” A variety that arose in garden/nursery culture. Designated in single quotes with the first letter of each word capitalized. Not italicized. Magnolia grandiflora ‘Little Gem’ Scientific Plant Names (cont.) What about hybrids? Hybrid – results from cross-pollination between two different species. Designated by an “x” between Genus and species. Osmanthus x fortunei – Fortune’s Tea Olive Hybrid between O. heterophyllus and O. fragrans The Ultimate… Acer palmatum var. dissectum ‘Atropurpureum’ Maple Palmate leaves Leaves are highly dissected (threadleaf) Leaves are dark red/purple AKA: Purple-leaved Threadleaf Japanese Maple Plant Identification It’s all in the details!!! Gather Information 1. Evergreen or Deciduous? 2. Tree, shrub, vine or herbaceous? 3. Leaf Arrangement 4. Leaf Morphology 5. Flower Arrangement and Morphology Leaf Arrangement The various ways leaves are arranged along the stem is used to identify plants. Leaf Morphology • Venation refers to the pattern in which the veins are distributed in the leaf blade • Parallel or Net-veined • Net-veined can be either pinnate or palmate Acute - ending in an acute angle Acuminate tapering to a long, narrow point Obtuse - tapering to a round edge Truncate - having a relatively square base Leaf Morphology Shape of the leaf blade and the type of margin are important in plant identification. Entire - smooth edge Dentate teeth pointed outward Serrate - having small teeth pointed toward the apex Lobed - incisions extending less than 1/2 way to midrib More to come… Next Week – The wonderful world of soils!!!