Nation-State
advertisement

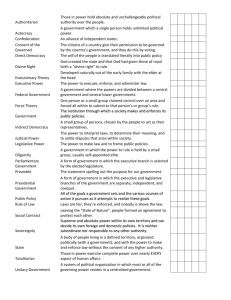
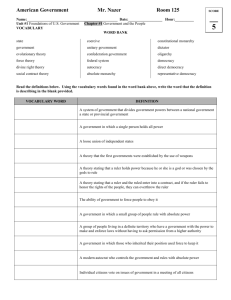
Political Geography What is Political Geography? Study of governmental systems Study of nation-states Nations, States, and Nation States? Nation – a people with common culture, usually in a specific territory + State – sovereign government, located in specific territory = Nation-State – nation and state in same territory Types of Borders Natural Borders – created by physical features Example: Rio Grande River (Mexico and US) Political Borders –artificial, set by govt. (imaginary lines) Example: North and South Korea Major Functions of Governments Different government systems divide powers and responsibilities differently. Separation of powers, distribution of powers vary by country. Executive – authority for the dayto-day operation of the government Legislative – decision-making assembly or other body Judicial – law and justice issues Major Types of Political Systems We will discuss good things and bad things about each one. Democracy or Republic citizens hold political power 2 main kinds – “direct” democracy, “representative” democracy Example: USA, most modern nations “Monarchy” Who has power? King or Queen What else should you know? Usually shares power with other groups, typically a legislature – making them a “constitutional monarchy” Example? Great Britain, Jordan Communism “Authoritarian” Who has power? Government has all political power (not the people) What else should you know? One ruler – “Dictatorship” Group – “Oligarchy” Total control of all aspects of a citizen’s life – “Totalitarianism” Examples? Nazi Germany, Soviet Union Cuba, North Korea, Syria People’s Republic of China “Anarchy” or “Failed State” Who has power? •Nobody, or gangs and warlords… violence = political power in a failed state. There often is a government, but it has no control over its territory. What else should you know? •The instability is often fueled by illegal drugs or resources, because of external interference. Examples: •See map Human Interactions What is an Ethnic Group? A group of people who share language, customs and a common heritage. What is Race? Race A group of human beings distinguished by physical traits, blood types, genetic code patterns or genetically inherited characteristics. Ethnocentrism Believing that one’s own culture is best or better than others. Why people move. Push – means leaving an area because of what is happening in the area you are leaving. Ex. Political unrest, no jobs, natural disaster Pull – means leaving an area because of what is happening in the area you are going to. Ex. Good jobs, stable government, weather What happens when people move? Do you become like them?? Assimilation –the minority is absorbed by the majority. What happens when you move? Do they become a little like you? Cultural Diffusion – The spread of ideas, inventions or patterns of behavior to different societies. What happens when you move? Acculturation – Cultural change that occurs when individuals in a society accept or adopt an innovation.