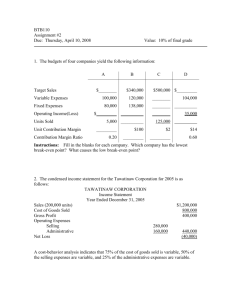
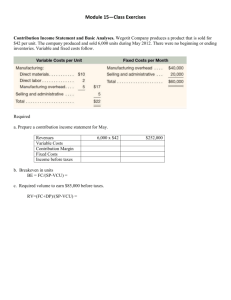
Which of the following refers to the relationship between cost and
advertisement

Which of the following refers to the relationship between cost and activity? A)Cost prediction B)Cost behavior C)Cost estimation D)Cost prevention E)None of the above This refers to the relationship between cost and activity, and is relevant to the management functions of planning, control, and decision making. Which describes the flow of the linear relationship between cost behavior, cost prediction, and cost estimation? A)Cost behavior → Cost prediction → Cost estimation B)Cost prediction → Cost behavior → Cost estimation C)Cost estimation → Cost prediction → Cost behavior D)Cost estimation → Cost behavior → Cost prediction E)Cost behavior → Cost estimation → Cost prediction The correct flow of the linear relationship between cost behavior, cost prediction, and cost estimation is: Cost estimation → Cost behavior → Cost prediction. In other words, (1) determine how a cost behaves, (2) determine the relationship between the cost and activity, and (3) forecast the cost at a particular level of activity.= The managerial accountant will use the visual-fit method as a tool to accomplish which of the following? A)Cost prediction B)Cost behavior C)Cost estimation D)Cost prevention E)None of the above Cost estimation is the process of determining how a particular cost behaves. Different techniques can be used by the managerial accountant including the visual fit method. Yummy Donuts uses flour when producing both its yeast and cake donut varieties. Select the answer below that best explains how Yummy's flour cost will change as a result of an increase in production volume. A) B) C) ---------- This one (C) D) E) Flour would be considered a variable cost by Yummy. Variable costs change in total in direct proportion to a change in production. As more donuts are produced more flour is used in total. The flour per individual donut (i.e. per unit) does not increase and instead stays constant. Consider the following schedule of activities, unit cost, and total costs: Which of the following is correct with respect to each activity and the cost classification of that activity? 7 A)Activity A: Fixed cost. Activity B: Variable cost. Activity C: Semivariable cost B)Activity A: Variable cost. Activity B: Fixed. Activity C: Semivariable cost C)Activity A: Fixed cost. Activity B: Semivariable cost. Activity C: Variable cost D)Activity A: Semivariable cost. Activity B: Fixed cost. Activity C: Variable cost E)Activity A: Semivariable cost. Activity B: Variable cost. Activity C: Fixed cost Activity A is a fixed cost, which is a cost that remains unchanged in total as the activity level varies. The fixed cost per unit will decrease or increase inversely to increases or decreases in changes in levels of activity. A variable cost increases in direct proportion to changes in levels of activity and is constant on a per unit basis. A semivariable cost increases with increases in level of activity, but not proportionately. Consider the following schedule of activities, unit cost, and total costs: Which of the Activities is most likely a semivariable cost? A)Activity A B)Activity B C)Activity C D)All of the above E)None of the above This is a cost that will vary with activity, but not in direct proportion to activity levels, and does not remain unchanged per unit. Semivariable costs have both a fixed and variable component. When using a semivariable cost behavior pattern to approximate a curvilinear cost, the approximation should be limited to which of the following? 8 A)Determining only the variable portion of the cost B)The curvilinear costs within the relevant range of activity C)All activity above the relevant range of activity D)The approximate fixed cost portion E)All of the above Usually, the approximation is quite accurate for activity levels within the relevant range. Outside of the relevant range, the curvilinear cost line is not a straight line, but the regression line that depicts both variable and fixed costs would be. Yummy Donuts uses flour when producing both its yeast and cake donut varieties. Select the answer below that best explains how Yummy's flour cost would be classified. A)an engineered cost B)a committed cost C)a discretionary cost D)a guaranteed cost E)none of the above An engineered cost bears a definitive physical relationship to the activity measure. Flour, is a significant direct material and it is impossible to produce more donuts without using more flour. Consider the following costs incurred by a small state university and identify the cost which would be an example of a committed cost? A)Salaries paid to tenured faculty in the Engineering school B)Advertising and promotion Salaries paid to non-tenured faculty teaching under an annual contract 11 C) D)Contributions to charities E)Training programs for graduate teaching assistants A committed cost results from an organization's ownership or use of facilities and its basic organizational structure. Salaries of tenured faculty would be considered a committed fixed cost. These costs can be changed but it is a major decision and is not easy to do. Faculty working under a one year contract would be discretionary as the school can simply choose to not renew for the upcoming year. Sales personnel are paid a fixed, monthly salary and a commission of 5 percent of net sales. Cost estimation of the Sales Salaries Expense account might be accomplished most easily by which of the following methods? A)Multiple regression B)Account-classification C)Visual-fit D)High-low E)Least-squares regression The account-classification method of cost estimation, also called account-analysis,involves a careful examination of the organization's ledger accounts. Consider the following: Use the high-low method of cost estimation to solve for the fixed and variable cost portions of this cost and select the appropriate answer. A)Fixed cost: $ 6,000; variable cost: $1.20 per unit. B)Fixed cost: $22,000; variable cost: $2.20 per unit. 12 C)Fixed cost: $10,000; variable cost: $1.20 per unit. D)Fixed cost: $ 4,000; variable cost: $1.20 per unit. E)Fixed cost: $ 6,000; variable cost: $2.20 per unit The variable cost per unit (b) is $1.20 (= $6,000/5,000). Substituting known values, the total cost = (a) + $1.20(15,000), or $28,000 = (a) + $1.20(15,000). The fixed cost (a) = $10,000 (= $28,000 – ($1.20 x 15,000)). Consider the following cost for the first and second quarters of the fiscal year: Use the high-low method of cost estimation and determine the estimated total cost for July, which is budgeted for 9,000 units of activity. A)$23,750 B)$21,500 C)$23,150 D)$22,550 E)$26,200 Using the high-low method of cost estimation, the variable cost per unit (b) is $1.50 (= ($27,500 – $20,000)/(13,000 – 8,000)). Applying the equation of Y = a + bX, the fixed cost (a) is $8,000 (= $27,500 – ($1.50 x 13,000)). To solve for total costs when two or more independent variables exist, you should use which of the following for cost estimation? A)A simple regression equation B)The high-low method A multiple regression equation 15 C) D)A goodness of fit E)Visual-fit method Multiple regression is a cost estimation method thatuses an equation that includes the multiple independent variables. The phenomenon of labor time and labor cost declining as output increases is known as which of the following? A)Experience curve B)Learning curve C)Variable cost curve D)Multiple regression E)Simple regression The learning curve is the term given to phenomenon of labor time and labor cost declining as output increases. When the learning-curve concept is applied to a broader set of costs than just labor costs, it is referred to as an experience curve. Which of the following frequently is a problem that complicates the process of data collection? A)Missing data B)Outliers C)Mismatched time periods D)Inflation E)All of the above In addition to those items listed (A, B, C, and D), trade-offs in choosing the time period and allocated and discretionary costs are also problems that frequently complicate the process of data collection 1 Total contribution margin can be defined as which of the following? A Total sales revenue minus total fixed expenses ) B Total sales revenue minus the total of fixed and variable expenses ) C Total sales revenue minus total variable expenses ) D Total sales revenue minus profit ) E Total fixed expenses minus total variable costs ) Total contribution margin is defined as total sales revenues minus total variable expenses. It is the amount of revenue that is available to contribute to covering fixed expenses after all variable expenses have been covered. 2 If fixed expenses are $54,000, break-even sales units are 15,000, and the contribution margin ratio is .60, what is the unit contribution margin? A $2.40 ) B $3.60 ) C $6.00 ) D $5.40 ) E $4.50 ) The break-even point in sales dollars is equal to total fixed expenses divided by the contribution margin ratio. In this case, the break-even point is sales dollars is $90,000 ($54,000/0.60). The unit sale price is $6 ($90,000/15,000). The unit contribution margin is $3.60 ($6 x 0.60). 3 If fixed expenses are $38,000, break-even sales units are 9,500, and the contribution margin ratio is .40, what is the unit selling price? A $4.00 ) B $6.00 ) C $10.00 ) D $2.00 ) E None of the above ) Solve for the unit contribution margin. The break-even point in units (9,500) is equal to total fixed expenses ($38,000) divided by the unit contribution margin (unknown). Solve the problem as follows: $38,000/X = 9,500 X = $4 The contribution margin ratio is the unit contribution margin (found in step 1) divided by the unit sales price. Use the contribution margin ratio (.4) and contribution margin ($4) to solve for the unit sales price 4 Fixed expenses are $75,000. The unit sales price is $25. The contribution margin ratio is .60. What are the break-even sales units? A 10,000 ) 5,000 B ) C 7,500 ) D 125,000 ) E None of the above ) Using the contribution-margin approach, the break-even point in units is equal to the fixed expenses divided by the unit contribution margin. The break-even point in units is 5,000 (= $75,000/($25 x 0.60)). 5 Consider the following: In constructing a cost-volume-profit (CVP) graph, at what level on the vertical axis will the total expenses line begin? A $120,000 ) B $80,000 ) C $240,000 ) D $40,000 ) E $200,000 ) The total cost line will begin on the vertical axis at the dollar amount of total fixed expenses. 6 Consider the following: At what sales volume was the above data derived? A 12,500 units ) B 7,500 units ) C 15,000 units ) D 10,000 units ) E 5,000 units ) The sales volume can be calculated by dividing total variable expenses by the unit variable cost. The unit variable cost can be calculated by subtracting the unit contribution margin from the unit sales price. $24- $8 = $16 of variable cost per unit $120,000 total variable expense/ $16 = 7,500 units. LO 3 7 An increase in a company's variable cost per unit will: A decrease the number of units which must be sold to break even. ) B decrease the fixed costs on a per unit basis. ) increase the number of units that must be sold to cover variable and fixed C costs. ) D increase net income ) make it impossible for the company to break-even. If variable cost per unit increases, more units will need to be sold in order to break-even. This can be seen mathematically using the Contribution Margin Approach and noting that the unit contribution margin is smaller, making the break-even point in units larger. 8 Consider the following: How many sales units are required to earn the target profit? A 15,000 units ) B 12,000 units ) C 6,400 units ) D 12,800 units ) E 10,000 units ) The number of units required to earn the target profit is equal to fixed expenses plus the target profit, divided by the unit contribution margin. The number of units required to earn the target profit is 10,000 (= ($78,000 + $42,000)/$12)). 9 Consider the following: Use the equation method and compute the units of sales required to earn a target profit of $12,000. A 3,220 ) 4,440 B C 3,840 ) D 4,267 ) E 4,560 ) : The equation is: $38X – $18X – $76,800 = $12,000. Solve for X (X = the units required to earn the target profit). X = $88,800/$20X; X = 4,440 units. 10 Consider the following: What is the weighted-average unit contribution margin for the sales mix? A $12.00 ) B $17.33 ) C $26.00 ) D $16.00 ) E $15.00 ) The weighted-average unit contribution margin is the average of the unit contribution margins weighted by the relative sales proportion of each product: ($4 x 4/8) + ($16 x 3/8) + ($32 x 1/8), or $2 + $6 + $4, or $12. (Alternative: [(($4 x 4) + ($16 x 3) + ($32 x 1)) / 8]. LO 5 11 Consider the following: Fixed expenses are $32,000. What is the number of units of Product A sold at the break-even point? A 6,000 ) B 4,000 ) C 1,500 ) D 1,000 ) E 2,500 ) The weighted-average unit contribution margin is $6.40, or ($4 x 4/5) + ($16 x 1/5). Fixed expenses divided by the weighted-average unit contribution margin determines total units sold at break even: $32,000/$6.40= 5,000. Units of Product A break-even: 5,000 x 4/5 = 4,000. Proof: (4,000 x $4) + (1,000 x $16) = $32,000. 12 Consider the following: Sales revenues were $300,000. There was no beginning or ending inventory. Which of the following statements is false? A Income in a traditional income statement is $75,000. ) Income in a contribution income statement is $80,000. C The contribution margin is $190,000. ) D A contribution income statement is an internal document (report). ) E traditional income statement would include gross margin. A ) Income in a traditional income statement: $300,000 – $110,000 – ($70,000 + $45,000) = $75,000. The contribution margin is $190,000 ($300,000 – ($60,000 + $10,000 + $40,000)). Income in a contribution income statement is $75,000 (=$190,000 – ($50,000 + $60,000 + $5,000)), which is the contribution margin minus all fixed expenses. Income computed under either method equals $75,000 because there was no beginning or ending inventories. 13 Consider the following: Which of the following statements about the companies is false? A operating leverage for Company A is 6. The ) B operating leverage for Company B is more than that of Company C. The ) C The break-even point in sales dollars for Company C is $360,000. ) D The operating leverage for Company B is 5. ) The operating leverage for Company B is 7. E Operating leverage is determined by dividing total contribution margin by income. The operating leverage for Company A is 6 (= $360,000/$60,000). The operating leverage for Company B is 5 (= $200,000/$40,000); the operating leverage for Company C is 2 (= $360,000/$180,000). The break even point for Company C (in sales dollars) is $180,000/50% = $360,000. Consider the following: Management is considering installing a new, automated manufacturing process that will increase fixed costs by $50,000, and reduce variable manufacturing costs by $3 per unit. Assume that management desires to achieve a target profit of $70,000 with or without the acquisition of the automated machine. If the automated machine is installed, what will be the change in the number of units required to achieve the target profit? A 6,667 unit increase ) B 5,667 unit decrease ) C 3,000 unit decrease ) D 2,000 unit increase ) E 3,333 unit decrease ) Currently, the number of units required to earn the target profit is 30,000 (($200,000 + $70,000)/$9). If the automated machine is placed into service, the number of units required to earn the target profit will be 26,667 (= ($250,000 + $70,000)/$12). Change in units: 30,000 – 26,667 = 3,333 decrease in sales units. Consider the following: What will be (1) the increase or decrease in break-even units, and (2) the increase or decrease in units necessary to achieve a target income of $45,000 when changing from current conditions to advanced technology in machinery and JIT implementation? A change in break-even point; increase in sales volume to achieve target income No ) B Increase in break-even point; increase in sales volume to achieve target income ) No C change in break-even point; decrease in sales volume to achieve target income ) D Decrease in break-event point; decrease in sales volume to achieve target income ) None of the above the break-even point is 10,000 units ($130,000/$13); and the sales volume to achieve a target income of $45,000 is 13,462 units (= ($130,000 + $45,000) / $13).