Profit Center Analysis
advertisement

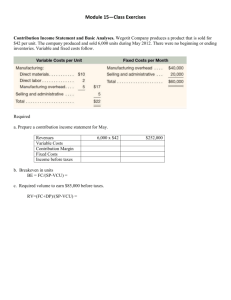
Profit Center Analysis Jack Davis, CPA, MBA SDSU-CES, Area Management Specialist Profits squeezed? • Everyone knows their costs, don’t they? • Do you know how these costs behave? Word List • Cost Behavior • Variable Costs. – Variable Costs per unit are constant. • Fixed Costs. – Fixed costs per unit vary with production level. • Mixed Costs. – Semi-variable costs change in total with changes in production level, but not proportionately. Terms to Recognize • Cost volume profit analysis – Profit = Sales (S) – Variable Costs (VC) – Fixed Costs (FC) • Contribution Margin – Sales -- Variable Costs – Contribution Margin Ratio • (Sales – Variable Costs)÷ Sales Breakeven Point • Sales (in dollars) = Fixed Costs / Contribution margin ratio • Sales (units) = Fixed Costs / Contribution margin per unit Cost or Revenue ($) Quantity Produced Break-Even Diagram Cost or Revenue ($) Quantity Produced Break-Even Diagram Break Even Quantity Break Even Quantity Profit / Loss Corridor Variable Costs Cost or Revenue ($) Fixed Cost Quantity Produced Break-Even Diagram Fixed Cost Break Even Quantity Increased Fixed Costs Break Even Quantity Break-Even Diagram Profit / Loss Corridor Variable Costs Cost or Revenue ($) Fixed Cost Quantity Produced Management Hubs • Profit Centers. – Subunit that has responsibility for generating revenue as well as for controlling costs. • Cost Centers. – Subunit that has responsibility for controlling costs but does not sell product. i.e. service departments. Cost Allocation Cost Objective Cost Pools Allocation base Relates the cost pool to the cost objective Profit Center Analysis • Organize business into subunits, profit center & cost centers. • Track variable costs to profit centers. – Control escalators • Allocate asset use to subunits. • Evaluate on contribution margin and amount of capital invested. Cost-Volume-Profit Diagnostics Differential Analysis • Decision method to chose among alternative courses of action. – Additional Processing – Make or buy – Drop enterprise • Outsourcing • Core competencies Vocabulary • Differential costs and revenue – The additional cost or revenue incurred when one alternative is chosen over another. • Sunk cost. – Costs that are already incurred & not reversible. • Opportunity Costs. – The benefit given up by selecting one alternative over another. i.e. Interest on stored grain. Process or Sell Sell Revenue Less: Prior Costs Add. Costs Gain (loss) Additional Processing Differential Rev. & Costs Produce or Purchase Make Cost to Buy Variable Costs Fixed Costs Total Buy Savings (Costs) ( ) Differential Analysis Discontinued Operations • Cost allocation death spiral. – What will happen to common costs if enterprise is dropped? – They are allocated over remaining enterprises. Which may make those enterprises seem unprofitable.