The cell
advertisement

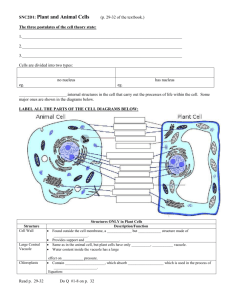
The cell Learning objectives To identify the function and structure of the cell. To describe the movement of molecule across cell membranes. The cell All living organisms are composed of cells All new cells are derived from other cells Cells contain hereditary material All metabolic process take place within cells PLANT CELL VS ANIMAL CELL Plant cell ~ Cellulose cell wall ~ Present of chloroplast ~ Central vacuole ~ Nucleus at the edge ~ No lysosome ~Starch for storage only meristematic cells can divide ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ Animal cell No cell wall No chloroplast Small & scattering vacuoles Nucleus in the central Lysosomes present Glycogen for storage All cells can divide CELL MEMBRANE Separation of internal & external environment Control the exchange of substances Form separate compartments inside cells As receptor sites ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM內質網 Network of double membrane-bounded sacs Rough ER Vs Smooth ER Functions: biosynthesis, transportation, support, storage, detoxification, increase surface area GOLGI APPARATUS A stack of membrane bounded sacs Functions: packaging, glycosylation, concentration, transportation, lysosome formation, membrane differentiation, enzyme production LYSOSOMES Simple spherical sac Functions: endocytosis, exocytosis, autolysis, autophage Functions of lysosome Vacuoles Fluid-filled sac containing cell sap Functions: Support & cell growth, store pigments, as lysosome, temporary stores for wastes & food Mitochondria Surrounded by an envelope of 2 membranes, the inner being folded to form cristae Functions: energy metabolism & respiration, heat production NUCLEUS Largest cell organelle Mono- nucleate, Bi- nucleate & polynucleate Functions: contains genetic materials, control centre, presence of DNA, production of ribosomes & RNA, cell division Cellulose cell wall Only in plant cell Functions: support, mechanical strength, permit movement of water, give shape of cell Chloroplast Only in plant cell Functions: photosynthesis Movement in & out of the cell Semi-permeable cell membrane: the plasma membrane only allow some substances to pass through but not others Factors affecting permeability of cell membrane Chemical natures of molecules ~ water ~ water soluble neutral substances ~ Fat soluble neutral substances ~ Electrolytes Size of molecules ~ small enough molecules Diffusion Diffusion: a process, the substance moves from a region of high concentration of that substance to a region of low concentration of the same substance Factors affecting the rate of diffusion: the concentration gradient, the distance, the area. The nature of the membrane,the size & nature if the molecules Process of diffusion Osmosis The movement of water molecules from high water potential to a region with lower water potential through a semipermeable membrane Water potential Osmotic potential Pressure potential Process of osmosis Plasmolysis Outward diffusion of water Reduction of turgor pressure Separation of cell wall & plasma membrane Decrease in size of vacuole & cytoplasm Decrease in water potential Active transport An energy consuming transport of molecules across a membrane against a concentration gradient. Factors affecting active transport concentration, electrical charge & energy available Features of cells with active transport: many mitochondria, ATP & a high respiratory rate THE END A typical animal cell Cell wall nucleus Endoplasmic reticulum Vacuole Golgi apparatus A typical Plant cell