The Earth in Space
advertisement
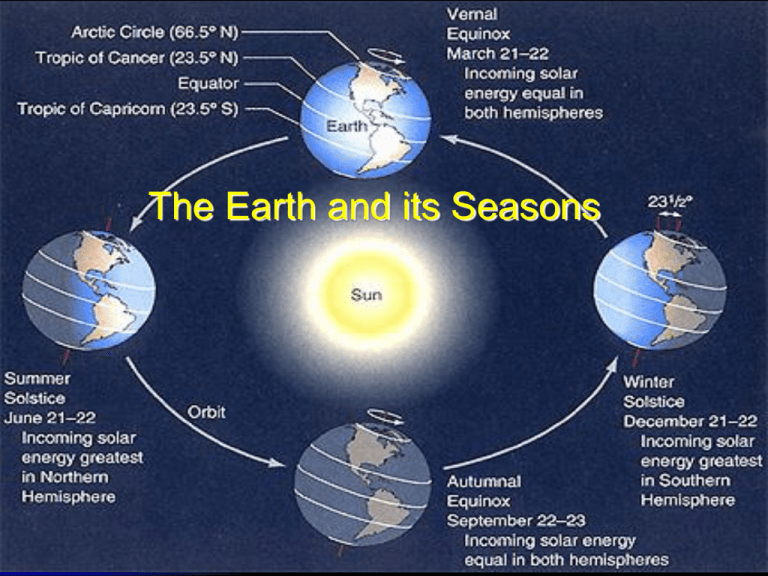
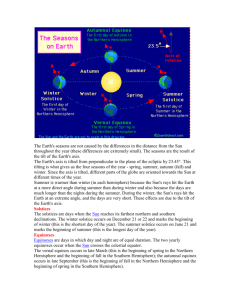
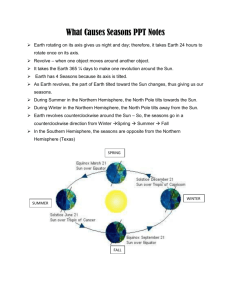
The Earth and its Seasons Taking Cornell NOtes Let’s set up our notes … Reasons for the Seasons Notes Keywords/ Questions Does the distance between Earth and the Sun change? Rotation: Revolution: Tilt: Notes Does the distance between Earth and the Sun change? Earth’s orbit is elliptical, but never “super skinny” The distance between Earth and Sun never changes significantly We are actually closer to the sun in January than any other time of the year Earth’s Orbit Around the Sun Rotation: the spinning of Earth on its axis Its rotation on its axis causes day and night It takes 24 hours to rotate once on its axis Earth rotates counterclockwise Rotation Animation Day and Night Song Revolution: the movement of one object around another object Earth travels around the sun counter-clockwise One complete revolution around the sun is a year The path is called its orbit Earth’s revolution along with its tilted axis cause our seasons Revolution Animation Revolution Words to Know Orbit : a curved path followed by Earth as it moves around the Sun Now You Try! Stand in place, and make one complete turn You Take a trip around your chair You have just rotated have just revolved Do you think you can rotate and revolve at the same time? Think about what a spinning top, a race car on an oval track, and a globe have in common. Think – Pair - Share 1. 2. 3. What is a spinning top doing? What is a race car on an oval track doing? How does that relate to the movement of Earth? Turn to your neighbor and explain… What is the difference between Earth’s rotation and Earth’s revolution? Earth in Space Earth rotates On its axis causing Day and night revolves Around the sun causing Years Earth’s Tilted Axis Earth is tilted toward the North Star (Polaris) 23.5º Earth has seasons because its axis is tilted as it revolves around the sun If Earth’s axis were straight up and down temperatures would remain constant year round Direct vs. Indirect Sunlight Direct vs. Indirect Light Why is it warmer near the equator than near the poles? At the equator - sunlight hits Earth’s surface more directly Closer to the poles, sunlight hits Earth’s surface at an angle Near the poles, energy from the sun is spread out over a greater area Predict the Season Write “What Season?” Write “Why? Draw a Diagram What Season in the Northern Summer Hemisphere? Explain why What Season in the Northern Winter Hemisphere? Explain why As the Earth moves around the Sun, this axis always stays pointing in the same direction. WHY DO WE HAVE SEASONS? So, seasons are caused by the tilt of the Earth’s axis as it revolves around the sun. Because of this, hemispheres receive different amounts of direct/indirect sunlight throughout the year, causing seasons. Seasons and Earth The Seasons of Earth Solstice and Equinox Solstice • Longest and shortest day of the year • Winter Solstice – the Northern Hemisphere is pointed furthest away from sun (December 21) • Summer Solstice – the Northern Hemisphere is pointed furthest toward the sun (June 21) Winter Solstice Summer Solstice Equinox • Day and night are equal length • Sun is directly over the equator, causing equal hours of day and night • Spring Equinox (March 21) • Fall Equinox (September 23) Equinox The Earth's seasons are NOT caused by the differences in the distance from the Sun throughout the year. Section 1 Review Question 1 Explain the process that causes day and night. Answer: Earth rotates on its axis once per day. As Earth rotates, half its surface is facing the sun (day) and half is facing away from the sun (night). Question 2 What two factors cause the cycle of the seasons? Answer: The cycle of the seasons is caused by Earth’s revolution around the sun and the tilt of Earth’s axis. Question 3 Compare rotation and revolution. Answer: Rotation is turning around a point or an axis; revolution is movement around another object. Question 4 What do the words solstice and equinox mean? How are they related to the position of the earth’s axis? Answer: A solstice is a day when the noon sun is overhead at 23.5° S or 23.5° N. This occurs when one end of Earth’s axis is tilted most directly toward the sun. Equinox means “equal night”, and occurs when neither pole of Earth’s axis is tilted toward the sun. Question 5 Are changes in the distance between the Earth and the sun important in causing the cycle of the seasons? Explain. Answer: The tilt of Earth’s axis, not its distance from the sun, is the cause of the cycle of seasons. During the summer months in the Northern Hemisphere, Earth is actually at its farthest point from the sun. During winter in the Northern Hemisphere, Earth is at its closest point to the sun.