Double Replacement Reactions
advertisement

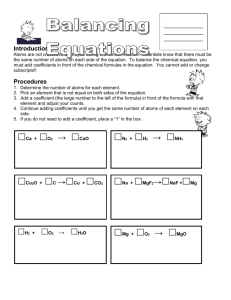
Determining if a compound is soluble (aq) or NOT • LOOK AT TABLE F – LiOH – Cu(NO3)2 – AgCl2 – MgS – NaS2 – KOH – aq – aq – insoluble = precipitate = s – insoluble = precipitate = s – aq – aq Double Replacement Reactions Double Replacement Format: AX + BY AY + BX DR rns occur in aqueous solutions • So, what exactly happens to a substance when we put it in water? – depends if ionic or covalent Dissolving Covalent substance – ex: sugar (C6H12O6) C6H12O6(s) C6H12O6(aq) • sugar molecules spread out among water molecules Dissolving • Ionic substance – • ex: table salt (NaCl) • NaCl(s) Na+1(aq) + Cl-1(aq) •ions spread out among water molecules Double Replacement Reactions occur with 2 ionic compound solutions • Products can be: - liquid (H2O) - - gas - - solid Reactions producing solids Precipitation: solid is formed opposite of dissolving! MOVIE EX: Reactions producing Solids 2 NaOH(aq) + CuCl2(aq) 2 NaCl(aq) + Cu(OH)2(s) This is the Chemical Equation but it’s not the whole story… 2 NaOH(aq) + CuCl2(aq) 2 NaCl(aq) + Cu(OH)2(s) In solution it’s not NaOH and CuCl2 You actually have ions floating around in water Cu2+ Cu2+ Na+1 Na+1 Cu2+ Cl+1 Cu Na+1 Cu2+ Cl+1 Cu Cl-1 ions in solution are written as aqueous • Reactants: 2Na+1(aq) + 2OH-1(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2Cl-1(aq) • Products: 2Na+1(aq) + 2Cl-1(aq) + Cu(OH)2(s) 2 NaOH(aq) + CuCl2(aq) 2 NaCl(aq) + Cu(OH)2(s) Net Ionic Equations 2Na+1(aq) + 2OH-1(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2Cl-1(aq) 2Na+1(aq) + 2Cl-1(aq) + Cu(OH)2(s) •Notice some ions do not participate in reaction • = spectator ions • cross out spectator ions to get net ionic equation Here’s what is really involved in the reaction… 2OH-1(aq) + Cu2+(aq) Cu(OH)2(s) Double Replacement Reactions occur with 2 ionic compound solutions • Products can be: - liquid (H2O) - - gas - - solid Reactions that form Water HBr(aq) + NaOH(aq) H2O(l) + NaBr(aq) H+1(aq) + Br-1(aq) + Na+1(aq) + OH-1(aq) H2O(l) + Na+1(aq) + Br-1(aq) H+1(aq) + OH-1(aq) H2O(l) Reactions that form Gases HCl(aq) + NaHCO3(aq) H2CO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) H2O(l) + CO2(g) Reactions that form Gases HCl(aq) + NaHCO3(aq) H2O(l) + CO2(g) + NaCl(aq) H+1(aq) + Cl-1(aq) + Na+1(aq) + HCO3-1(aq) H2O(l) + CO2(g) + Na+1(aq) + Cl-1(aq) H+1(aq) + HCO3-1(aq) H2O(l) + CO2(g) Conservation of Charge total charge (reactant side) must equal total charge on product side • 2OH-1(aq) + Cu2+(aq) Cu(OH)2(s) • -1 x 2 + +2 = 0 • H+1(aq) + OH-1(aq) H2O(l) • H+1(aq) + HCO3-1(aq) H2O(l) + CO2(g)