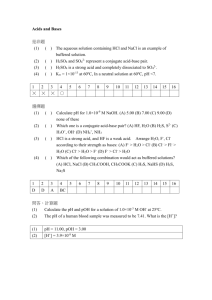
Acid-Base Neutralization Reactions
advertisement

Acid-Base Neutralization Reactions Chem 12 Acid + Base Salt + Water • Orange juice + milk bad taste • Evergreen shrub + concrete dead bush • Under a pine tree + fertilizer white powder • HCl + NaOH NaCl + HOH salt water Acid-Base Neutralization Reactions HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) • The products of an acid-base neutralization reaction are a salt made up of the positive ion of the base (Na+) and the negative ion (Cl-) of the acid, and water. • Remember, in writing the correct formula for the salt, the total positive charge of the ions in the salt must equal the total negative charge of the ions in the salt. • Make sure you write the correct formula for the products, salt and water first, then balancing the equation. • The particles present in the HCl(aq) solution due to ionization are HCl(g) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + Cl-(aq) Or HCl(g) H+(aq) + Cl-(aq) • The particles present in the NaOH(aq) solution due to dissociation are NaOH(aq) Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) • Therefore, the ionic equation for the reaction is H3O+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + 2H2O(l) or H+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + H2O(l) • If we remove the spectator ions, Na+(aq) and Cl-(aq), we are left with the net ionic equation for the acid-base neutralization reaction: H3O+(aq) + OH-(aq) 2H2O(l) H+(aq) + Or OH-(aq) H2O(l) • Therefore, in an acid-base neutralization reaction we can see that it is the hydronium ion from the acid that reacts with the hydroxide ion from the base to produce neutral water. • Since the hydronium ion gives the acid its properties and the hydroxide ion gives the base its properties, the acid-base reaction has resulted in the neutralization of the properties of both the acid and the base. SAMPLE PROBLEM 1 For the acid-base neutralization of nitric acid, HNO3(aq) and calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2(aq), write the balanced: a) complete equation b) ionic equation c) net ionic equation a) The complete balanced equation for the reaction is Ca(OH)2(aq) + 2HNO3(aq) Ca(NO3)2(aq) + 2H2O(l) b) The ionic equation is Ca2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) Ca2+ (aq) + 2NO3-(aq) + 2H2O(l) c) The net ionic equation is 2OH-(aq) + 2H+(aq) 2H2O(l) SAMPLE PROBLEM 2 For the acid-base neutralization of perchloric acid, HClO4(aq), and potassium hydroxide, KOH(aq), write the balanced: a) complete equation b) ionic equation c) net ionic equation a) The complete balanced equation for the reaction is HClO4(aq) + KOH(aq) KClO4(aq) + H2O(l) b) The ionic equation is H+(aq) + ClO4-(aq) + K+(aq) + OH-(aq) K+(aq) + ClO4-(aq) + H2O(l) c) The net ionic equation is OH-(aq) + H+(aq) H2O(l)