Earth in Space
advertisement

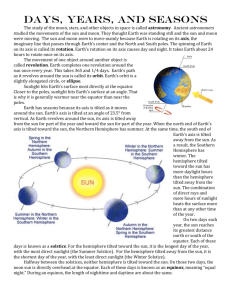
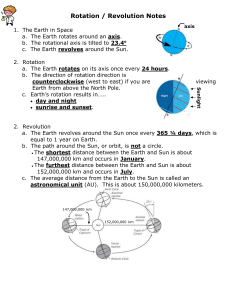
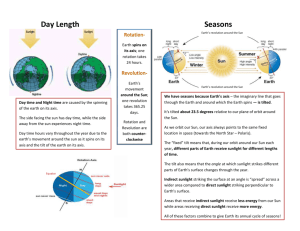
Earth in Space How Earth Moves • Earth moves through space in two major ways: rotation and revolution. How Earth Moves - Rotation • The spinning of Earth on its axis is called rotation. The axis is an imaginary line that passes through Earth’s center and the North and South poles. • Earth’s rotation causes day and night. As the Earth rotates eastward, the sun appears to move westward across the sky. It is day on the side of the Earth facing the sun and night on the side facing away from the sun. • It takes Earth about 24 hours to rotate once. Each 24-hour cycle is called a day How Earth Moves - Revolution • Revolution is the movement of one object around another. The Earth revolves around the sun while it rotates on its axis. • One complete revolution around the sun is called a year. • The path that Earth follows around the sun is its orbit. Earth’s orbit is elliptical. Calendar • The rotation and revolution of the Earth is the basis of our calendar. Ancient Egyptians created one of the first calendars by counting the days between the first appearance of the star Sirius in the morning. They found there were about 365 days in a year. • Early people used the moon cycle to divide the year into 12 “moonths”. Calendar • In reality the Earth orbits the sun about 365 ¼ days. The Romans adjusted the Egyptian calendar by adding one day every four years. This is known as “leap year” and the extra day is added to February. This helped annual events like the beginning of summer to occur on the same date every year. • Every so often adjustments still need to be made by adding a “leap second” to adjust for irregularities in Earth’s rotation. The Seasons on Earth • Most places outside the tropics and polar regions have four distinct seasons: winter, spring, summer, autumn. But there are great differences in temperature from place to place. How Sunlight Hits Earth • Sunlight hits Earth most directly near the equator. More direct = more intense light and heat. • Sunlight hits the poles at a steep angle, which makes it spread over a greater area. Less direct = less intense light and heat. How Sunlight Hits Earth Less direct sunlight. Spread across a greater area. Most direct sunlight. Intense, concentrated in smaller area. Less direct sunlight. Spread across a greater area. Earth’s Tilted Axis • Earth has seasons because its axis is tilted as it moves around the sun. If it wasn’t tilted, temperatures would remain fairly constant year round and there would be no seasons. • Earth’s axis is tilted at an angle of 23.5° from vertical. As Earth revolves around the sun, the north end of its axis is tilted away from the sun for part of the year and toward the sun for the other part of the year. Earth’s Tilted Axis • When the north end of the axis is tilted toward the sun, the Northern Hemisphere has summer. The hemisphere tilted toward the sun has more daylight hours than the hemisphere tilted away from the sun. The combination of direct rays and more hours of sunlight heats the surface more than at any other time of the year. Earth’s Tilted Axis • At the same time, the south end of the axis is tilted away from the sun and the Southern Hemisphere has winter. The sun’s energy is spread over a larger area and the days are shorter than nights. The combination of less direct rays and fewer hours of sunlight heats Earth’s surface less than at any other time of the year. Solstices • Twice a year, the sun reaches its greatest distance from the equator. This is known as a solstice. • The summer solstice happens around June 21st every year. This is when the sun is farthest north of the equator. It is the longest day of the year. • The winter solstice happens around December 21st every year. This is when the sun is farthest south of the equator. It is the shortest day of the year. Equinoxes • Halfway between the solstices, neither hemisphere is tilted away or towards the sun. • Equinox means “equal night”. During an equinox, day and night are about 12 hours long all over the world. • The vernal (spring) equinox is around March 21st and is the beginning of spring. • The autumnal (fall) equinox is around September 22nd and is the beginning of fall.