Chapter 22 Section 3 Review

Chapter 22 Section 3
Review
Page 564 #’s 1-6
1
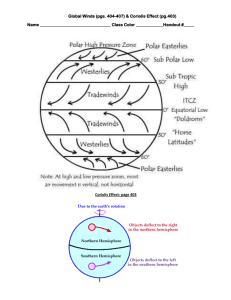
• Describe the pattern of air circulation between an area of low pressure and an area of high pressure.
– Air moves from regions of high pressure toward regions of low pressure.
High pressure and low pressure
2
• Explain how the Coriolis effect affects wind flow.
– In the Northern hemisphere, winds curve to the right; in the southern hemisphere, they curve to the left.
Coriolis effect on winds
3
• Name and describe Earth’s three global wind belts.
– Polar easterlies are prevailing winds that blow from east to west between 60 o and 90 o latitude in both hemispheres.
– The westerlies are winds that blow from the southwest in the Northern Hemisphere and from the northwest in the southern
Hemisphere in the belts between 30 o and 60 o latitude.
3 continued
• Name and describe Earth’s three global wind belts.
– The trade winds are prevailing winds that blow from the northeast from 30 o N to the equator and from the southeast from 30 o S to the equator.
Earth’s three global wind belts
4
• Summarize the importance of the jet streams.
– Jet streams are narrow bands of high-speed winds that blow in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere.
– They are important because they can affect the paths of storms and airline routes.
5
• Identify two factors that create local wind patterns.
– Temperature differences between land and sea and between mountains and valleys influence local wind patterns.
Temperature differences between land and sea
6
• Determine whether wind moving south form the equator will curve eastward or westward because of the Coriolis effect.
– Wind moving southward from the equator will curve to the east because of the Coriolis effect.