Elements, Compounds, Mixtures
advertisement

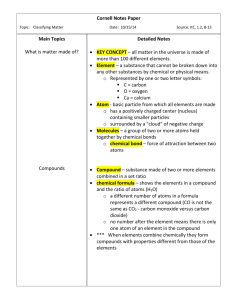
Classification of Matter Elements, Compounds, Mixtures Lesson Objective • • • • Physical and Chemical Changes. Elements Compounds Mixtures Physical and Chemical Changes • All reaction in Chemistry can be divided into two types of changes: Physical or Chemical. • Physical Change: • • NO new substance is formed. These changes are easily reversible or temporary. An example is dissolving salt in water. Other examples of physical change include: melting, boiling, mixing 2 solids or liquids. • • Physical and Chemical Changes • Chemical Change: • A NEW substance is formed. • These changes are irreversible or permanent. • The new substance formed will have different properties compared to its original elements. (E.g. different melting and different chemical reactions from the original substance.) Physical and Chemical Changes • One can recognize a chemical change from 2 observations: • The new substance has a different appearance, such as different color or different physical state. • An example is the electrolysis of water. • Reason: Electrolysis of water produces two new substances, Hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. Hydrogen and oxygen are both gases but water is a liquid. • A lot of heat is given out in a chemical changes. • Chemical changes are called chemical reactions. Illustration of chemical changes An Overview Elements, Compounds and Mixtures “ single, attached, play play…” Introducing Little Miss “Element” Hi! I am Little Miss “Element” I am PURE SUBSTANCE I cannot be broken down into any simpler substance by means of a chemical reaction* or electricity**! *Chemical process refers to chemical reaction or heat **Electricity refers to electrolysis Elements Definition of an element: An element is a pure substance which cannot be split up into two or more simpler substances by chemical means. Sugar is not an element as it can be broken down into carbon and water. Elements Note that an element: • Consists of only one kind of atom, • Cannot be broken down into a simpler type of matter by either physical or chemical means • Can exist as either atoms (e.g. argon) or molecules (e.g., nitrogen). Examples of elements Elements are made up of tiny particles Elements can be further classified into two groups: Is the smallest particle of an element and has the same chemical properties of the element Hi, I am from the “Noble gas” family and I work alone Is made up of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded together (note: these atoms are of the SAME element!!) We same same!! These are elements! Atoms of same element Cu copper element Na sodium element He Molecules of same element H H Hydrogen gas element helium element O O ozone O Atoms An element is made of tiny particles called atoms. The atoms of an element is different from that of another element. ElementsAtoms Consists of only one kind of atom Microscopic view of the atoms of the element argon (gas phase). What is an atom? Examples of models of atoms: H Hydrogen atom Na Sodium atom Cl Chlorine atom Molecules Very few elements exists as atoms besides elements such For example, hydrogen is H2. as helium and neon. Most elements exist as molecules. Ozone is O3. Hydrogen (H2) is a diatomic molecule. Molecules consisting of a few atoms are called polyatomic molecules. Ozone (O3) is a triatomic molecule. ElementsMolecules Consists of only one kind of atom Microscopic view of the molecules of the element nitrogen (gas phase). Examples of molecules (elements) O H H O O O S O S S S S S N N S S Allotropes of Carbon molecule (element) • Carbon is an element but made up of a very large molecule (also known as MACROMOLECULE) • There are 3 types of carbon molecular structures – C60 – Diamond – Graphite Chemical Symbols of Elements Chemists use symbols to represent elements. For example, O represents oxygen while Fe represents iron. Element Symbol Element Symbol Calcium Ca Mercury Hg Carbon C Neon Ne Hydrogen H Silicon Si Iron Fe Sodium Na Classification of Elements – Metals and Non-metals There are two major groups of elements – metals and non-metals. Iron is a metal. Oxygen is a non-metal. Metals and non-metals are grouped separately on the Periodic Table. There are some elements called metalloids which behave like both metals and non-metals. What is an element? An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into two or more simpler substances by any chemical means. - They are arranged in the Periodic Table, classified as metals and non-metals. - They may consist of atoms of same element or molecules of Non-metals (including the same element. Metals (excluding hydrogen) hydrogen) Physical Properties metals and non-metals Metals Non-metals Shiny appearance Dull appearance Solids at r.t.p (except mercury) Gases, liquids or solids at r.t.p (room temp & pressure) Malleable, Ductile, Sonorous Brittle if solid (general) High melting and boiling points Good conductors of heat Low melting and boiling points Good conductors of electricity Poor conductors of electricity (expect carbon and graphite) Poor conductors of heat Summarising Elements Non Metals Metals Atoms Atoms Molecules Introducing Little Miss “Compounds” Harlow! Hehee!!! *giggles* I am also a PURE SUBSTANCE I am made up of a fixed number of two or more elements chemically combined. Compounds Note that a compound: • can be broken down into a simpler type of matter (elements) by chemical means (but not by physical means), • has properties that are different from its component elements, and • always contains the same ratio of its component atoms. What is a compound? A compound is a substance which is made up of two or more elements chemically combined together. - Chemical reactions taking place. Qn: Is this a compound? It only contains one type Cu of element. Qn: Is this a compound? Qn: Is this a compound? H H It only contains one type of element. O O It is not chemically H combined. H O So, what is a compound then? H H H O H Water N H Ammonia gas Consists of two or more elements And They are chemically combined together! Compounds Microscopic view of the molecules of the compound water (gas phase). Oxygen atoms are red and hydrogen atoms are white. Making compounds from their elements Example: Making water (picture) lighted splint ELEMENTS hydrogen oxygen (colourless gas) (colourless gas) COMPOUND heat, light and explosion water (colourless liquid) Example: Making water (models) mixture of hydrogen heat, and oxygen light and water explosion Hydrogen molecule Oxygen molecule Water molecule Making compounds from their elements Example: Making iron sulphide compound compound elements heat Iron + sulphur iron sulphide heat + yellow grey black Little Miss “Compound” Property #1 I can be represented as a “chemical formula” The different elements present in a compound are combined in a fixed ratio General Rules: - Only write the name of the metallic element first - Write the number of atoms of any element in the compound in subscript (applies to only 2 or more atoms) - “ide” will always be written at the end of the non metal element Special Rules: • Does not apply to organic compounds (chapter 18 onwards) Little Miss “Compound” Property #2 I am formed by atoms of different elements. However, I do not have the properties as them. Examples • Na + Cl2 NaCl (s) (g) (s) • H2 + O2 H2O (g) (g) (l) Little Miss “Compound” Property #3 Electrolysis (breaking down of compound by electricity) 2MgCl(s) Mg(s) +Cl2(g) Thermal Decomposition (breaking down of compound by heat) HgO(s) Hg(s) + O2(g) Because of my chemical bonds, I cannot be broken down by physical means. I can only be broken down by chemical reaction or electricity. How do we name compounds? Rule 1 A compound made up of two elements has a name that ends in -ide. • Sodium chloride — made up of the elements sodium and chlorine • Zinc oxide — made up of the elements zinc and oxygen • Carbon dioxide — made up of the elements carbon and oxygen How do we name compounds? Rule 2 A compound that contains hydroxide ions , OH– (a negatively charged ion made up of oxygen and hydrogen) is named a hydroxide. • Potassium hydroxide — contains potassium ions and hydroxide ions How do we name compounds? Rule 3 A compound that contains a negatively charged polyatomic ion containing oxygen usually has a name ending in –ate. • Copper(II) sulphate — contains oxygen atoms in the sulphate ion • Sodium nitrate — contains oxygen atoms in the nitrate ion Fixed Composition of Compounds A compound is made up of different elements chemically combined in a fixed ratio. For example, water (H2O) is a compound made only by joining together two atoms of hydrogen to one atom of oxygen. That is, the ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms in water is always 2 : 1. Chemical Formula of a Compound A compound can be represented by a chemical formula. The chemical formula states • the types of atoms (i.e. elements) in the compound, • the ratio of the different atoms in the compound. Types of atoms: hydrogen, oxygen Ratio of H to O = 2:1 Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International How do we write chemical formula? Rule 1 For many compounds that contain both metallic and non-metallic elements, the symbol of the metallic element is written first. • calcium oxide (CaO) • sodium chloride (NaCl) • magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) How do we write chemical formula? Rule 2 The number of atoms is written as a subscript, to the right of the atom’s symbol. • water (H2O, not H2O or 2HO) • magnesium carbonate (MgCO3, not MgCO3 or MgC3O) How do we write chemical formula? Rule 3 It is not necessary to write the subscript ‘1’. • water (H2O, not H2O1) • calcium oxide (CaO, not Ca1O1) How do we write chemical formula? Rule 4 The oxygen atom is usually written at the end of the formula. • water (H2O, not OH2) • carbon dioxide (CO2, not O2C) • nitric acid (HNO3, not O3NH) How do we calculate the number of atoms in a formula? Number of lead (Pb) atoms = 1 Number of nitrogen (N) atoms =1x2=2 Pb(NO3)2 Number of oxygen (O) atoms =3x2=6 Compounds can be Decomposed Heat can be used to break down compounds into elements or simpler compounds. Such a chemical reaction is called thermal decomposition. Oxygen Mercury(II) oxide Summarizing • A compound is made up of two or more elements chemically joined together • A compound has a fixed composition • Every compound has a unique chemical formula • A compound has a completely different properties from its elements • A chemical reaction (decomposition or electrolysis) is needed to separate the elements in the compound Molecules- Elements or compounds? • A molecule consists of two or more atoms of the same element, or different elements, that are chemically bound together. • It can be a molecule of an element S S S S N N O O S • E.g. N2, O2, S8 S SS • It can be molecule of a compound. • H2O, CO2, NH3 O H O O H N H C H H Think about this… ROJAK!! Introducing Little Mr. “Mixture” Burp!!!! I am messy! I am formed when two or more substances joined together physically (without chemical bonds) I have the same properties as all the substances I am his best friend! AIR Mixtures Definition of a mixture: A mixture is not a pure substance as it contains a mixture of atoms of molecules which are not chemically combined together. Mixtures • Note that a mixture: • consists of two or more different elements and/or compounds NOT chemically combined. • Can be homogeneous or non-homogeneous • can be separated into its components by physical means, and • often retains many of the properties of its components. Mixtures Microscopic view of a gaseous mixture containing two elements (argon and nitrogen) and a compound (water). Mixtures • Examples of mixtures include muddy water and air. Air is made up of gases such as nitrogen and oxygen mixed together. Little Mr “Mixture” I do not have a fixed composition of the substances. A Mixture can be: • element + element • element + compound • compound + compound (Refer to page 59, Fig 4.7) He is a “boo-boo!” He can be separated to its substances by physical methods A mixture of 2 elements A mixture of two elements, e.g. neon (Ne) and hydrogen (H2) A mixture of 1 element and 1 compound A mixture of one element and one compound, e.g. hydrogen (H2) and ammonia (NH3) A mixture of 2 compounds A mixture of two compounds, e.g. water vapour (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2) Alloy: What is it?? Mr Alloy Yup! That’s ME! • It is a mixture of metals with other elements • Alloy metals are generally stronger and better in physical properties • Examples – Steel (Iron + Carbon) – Stainless Steel (Nickel + Iron + Chromium + carbon) – Brass (Copper + Zinc) Can you differentiate? Mixture of 2 elements-Alloy Compound Mixture of element & compound Molecules of an element Mixture of 2 elements Conclusion An element is a pure substance which cannot be split up into two or more simpler substances by chemical means. A compound consist of a fixed number of different kinds of atoms chemically combined together. A mixture is not a pure substance as it contains a mixture of atoms of molecules which are not chemically combined together. Difference between mixtures and compounds. Compounds E.g. Water H2O Separation Cannot be separated into its Mixtures E.g. Salt solution Can be easily separated into constituents by physical its constituents by physical methods. Separation can only methods. be done by chemical methods e.g. Salt can be obtained or by electricity. from its solution by e.g. Water can only be evaporation. Water can be separated into Hydrogen and obtained by simple Oxygen by Electrolysis. distillation. Difference between mixtures and compounds. Compounds E.g. Water H2O Mixtures E.g. Salt solution Composition The composition is fixed. The Has no fixed constituents (elements) in the composition. The compound are combined in amount of constituents definite amount. in a mixture can vary. e.g. To form one molecule of water, two atoms of Hydrogen and one atom of Oxygen is needed. e.g. The amount of salt added into the water to make salt solution can vary and vice versa. Difference between mixtures and compounds. Compounds E.g. Water H2O Mixtures E.g. Salt solution Properties The physical and chemical The mixture does not have its properties of the compound is different from the properties of its constituents. own properties. It has the average physical and chemical properties of the constituents that made it up. (Each constituents still retain its own properties) e.g. Hydrogen and Oxygen are gases while water is a e.g. The salt solution still retains liquid at room temperature its salt taste. and pressure. e.g. Salt solution does not have a e.g. Water has a fixed fixed melting or boiling point, but melting and boiling point. rather over a range of temperature. Difference between mixtures and compounds. Energy Change Compounds E.g. Water H2O Mixtures E.g. Salt solution Energy is usually given out or occasionally taken in when a compound is formed. Normally little or no energy is given out or taken in when a mixture is formed. Differences between mixtures and compounds Laugh what? I know I am a little “bushy and hairy” than you… Mr Messy *giggles * HeE stupid… Little Miss Compound Comparison between mixtures and compounds Mixture Compound Components can be separated by physical methods Same properties as its components Elements in a compound Cannot be separated by physical methods Properties are unique and different from its elements Mp / Bp No chemical change takes place when a mixture in formed Variable A chemical reaction takes place when a compound is formed Fixed Compositio n Does not have a fixed composition Has a fixed composition Separation /breakdown Properties (chemical / physical) Energy Change Challenge Time • Is mineral water an element, mixture or compound? Challenge Time • Are YOU an element, mixture or compound? EXTRA! • Human body is made up of 28 elements? • About 99% our mass is made up of the 6 main elements – Oxygen (65%) – Carbon (18%) – Hydrogen (10%) – Nitrogen (3%) – Calcium (1.5%) – Phosphorus (1.5%) The End……