Biology Unit 3 summary posters
advertisement

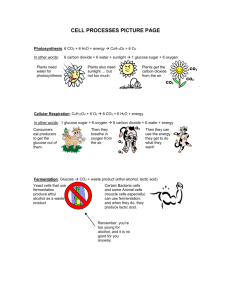
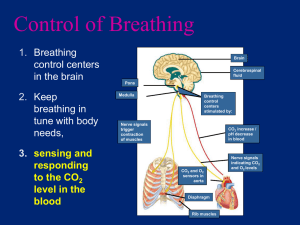
Water moves from the roots to E.g. Eat Quorn (mycoprotein) and Stopping over fishing (conserve stocks, change fishing methods, set catch quotas) water and minerals a plant will need. Grow your mycroprotein – Fungus Fusarium Aerobic respiration Waxy cuticle – water and gas proof. Stops too much water loss. (only one cell between blood and air in lungs) •Good blood supply Short food chains are better then long ones! Energy and biomass is own lost at every stage. Using a fermenter by root hair cells) as they absorb most of the Reduce food miles (how far food travels) •Large surface area = Less fuel used and less pollution •Short diffusion pathway (to take absorbed products of digestion – using diffusion and active transport to get it from the intestine to the blood) Energy lost as movement Energy lost as heat It’s a living thing! Keeps everything evenly mixed Lots of chloroplast for photosynthesis. The way we use the earth resources can have long and short term effects on the environment Poor cows and chickens Data we use to make conclusions about the Intensive Farming: environment must be checked to ensure it is valid (has Stop energy loss by been collected correctly), is reproducible (similar limiting movement experiments can be done to check the results). (keep in small enclosed space) This is much easier said then done! Grow in sugar syrup Adaptations for gaseous exchange (in your lungs) Thorax If more water is lost then can be replaced the plant will WILT. Leaves are thin and flat giving them a large surface area for diffusion of gases (CO2 in and oxygen out). Guard cells around stomata can open and close to let CO2 in but stop too much water being lost! OK sometimes its placed in the trachea Artificial breathing Positive pressure – pushing the air in. Benefits: Not invasive (just a mask), can aid the paralysed for years and can be used during surgery. Can be used at home! Negative pressure – a vacuum is created outside the body moving the chest up and causing air to be drawn in. The Iron Lung Benefits: Will keep you alive. Drawbacks: Very restricting and out dated. Must stay in hospital. (not really used anymore) •Large surface area •Short diffusion pathway Ribs All your chest space Water leaves leaf by evaporation and keeping animals warm (keeping them inside). Is this ethically OK? Monitor pH and temperature careful Trachea (windpipe) CO2 enters leaf by diffusion Villi/villus Creased up surface of intestine for really large surface area. (protect your lungs) Energy Drinks - For when your DEHYDRATED Contain: Water, sugar and mineral ions. Water – to rehydrate Sugar – for energy Minerals – to replace those lost during sweating. (only one cell between blood and air in lungs) •Steep concentration gradient. Remember: a substance will move from where there's a lot to where there's a little. This is helped with good blood supply and Breathing (to take absorbed oxygen away-bring CO2 to lungs / to replace the oxygen as its absorbed and remove CO2) Osmosis Diaphragm Breathing in (inhalation) Active Transport Diaphragm contracts flattens Intercostal muscles (Muscles around the ribs) contract – moving ribs up and out This is when some thing moves against the concentration gradient. Low to High! Volume of lungs increases – air moves in WATER diffusing from where it is a lot of it to where there is less of it. Water moved up a plant stem from cell to cell by osmosis. Lots of water keeps the cell rigid. Breathing in (exhalation) Diaphragm relaxes coming up Intercostal muscles (Muscles around the ribs) relax – moving ribs down and in Volume of lungs decreases – air moves out It needs energy to happen! But means ions can be absorbed from soil and sugars and salts can move into cells. Water moves in and out of cell depending on the concentration of the solution surrounding them. Through a partially permeable membrane. Remember: A concentrated substance actually contains less water. Transport in Plants The phloem the leaves, up the xylem via the The xylem transports TRANSPIRATION STREAM transports water dissolved and minerals up the sugars to the plant from roots to rest of the leaves. plant from the leaves. Roots also have a large surface area (provided Biogas (mainly methane) – gas you can burn for energy It’s uses living bacteria so needs food and warmth Organic waste including carbohydrates Comes in family and city size! Biofuels Coronary arteries supply the heart with blood – blockages can lead to heart attack! - Fuels made by using yeast or bacteria to ferment organic material Your Heart – The Pump! (keeping your blood moving) Vena cava Pulmonary The ethanol is then distilled out to use in cars. Anaerobic decay = no oxygen Pulmonary (that’s your right not my right) CO2 absorbed in photosynthesis is equal to CO2 released during burning. No extra CO2 is added to the atmosphere. Pesticides (to kill pests) and Herbicides (to kill weeds) can pollute land. They can also enter food chains and dangerous levels of toxins build up on top producers. Veins go away from your heart Remember: You have a double circulatory system. Blood goes through your heart twice during one circuit. Don’t forget! Cows and rice fields have increased the levels of methane (a greenhouse gas). (as ice caps melt) •Changes in migration and distribution of organisms. The air becomes polluted as un-burnt fuels are released causing global dimming. The Main Three Blood Vessels Fixing leaky valves The removal and destruction of woods and forests… • Increase CO2 • Reduces CO2 removed by photosynthesis Also reduces biodiversity! – the variety of different organisms in an area. Destroying habitats for farming and quarrying. Ecology into rivers and lakes polluting it. Recent years have seen massive population growth More food and better healthcare Fertilisers, chemicals and untreated waste Stents can open up narrow or blocked arteries. Under high pressure valves can become damage allowing blood to flow backwards. (as wood is burnt and decays) Eutrophication – Fertilisers are washed Arteries go toward your heart We can replace valves with biological animals valves but these only last about 15 years. Deforestation: Sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide pollution from factories forms acid rain. This damages tress and makes lakes to acidic for life. Blockages in blood vessels can stop oxygen reaching the heart. This can happen due to age or a bad diet. Step 1: Find a doctor! Step 2: Get a STENT! The blood coming from the lungs and going to the body is oxygenated. Increasing amounts of greenhouse gases make it harder for the heat to escape the atmosphere. Increasing the temperature of the planet. This could lead to: •Changes in weather and flooding •Rising in sea levels How to remove a blockage… Capillaries link arteries and veins. The have thin walls so oxygen and glucose can diffuse out to cells and waste and CO2 can diffuse back from cells. Blood plasma (liquid) carries dissolved food, CO2 and urea. White Blood cells Help defend the body against disease Red Blood cells carry oxygen Platelets help with clotting (think scabs) Remember: Red blood cells are biconcave discs giving them a bigger surface area and have no nucleus to fit in more haemoglobin. This lets them carry more oxygen as oxyhaemoglobin. Or Use Mechanical valves made form plastics and metals but you will need lifelong medicine to stop blood clotting problems. Artificial Hearts Sometimes the heart is so damaged it needs replacing. This can mean waiting for a heart donor. We can use temporary heart replacements but have nothing permanent so far. Advantages: You don’t Disadvantages: They're big! have to wait for a donor Blood clotting problems and there is no chance of mean lifelong drugs, organ rejection. normally mean staying in hospital and they’re THEY KEEP YOU ALIVE!!! If you suffer blood loss you will need a transfusion – Real blood needs to be matched from donors. expensive. Artificial Blood: Plasma & Saline, PFCs and Haemoglobin-based products Advantages: Readily available, doesn’t have to be stored in a fridge, will work with any blood type. Disadvantages: Expensive! Doesn’t carry oxygen as well as real blood, doesn’t always mix with real blood, is broken down quickly by the body and can cause side effects. Things that unbalance your bodies internal environment: Movement Carbon dioxide is produced when your cells respire. A build up would be dangerous so CO2 is removed by your lungs when you breath out. When its cold! Blood vessels contract When its hot! so heat can isn't lost by When we sweat and pee our bodies lose water Blood vessels dilate so radiation. heat can be lost by and ions. These need to be replaced so water You don’t sweat so radiation. doesn’t move in or out of cells (by osmosis) and heat can’t be lost by You sweat so heat can damage them. evaporation. be lost by evaporation. It also helps us regulate temperature. Hairs on the skin (sweating is less effective in Excess protein (amino acids) is broken down by the liver. Why bother? become erect to trap humid conditions) Kidneys If you get too hot your air for insulation. Hairs on the skin also Making Making sure you enzymes will denature and (this doesn’t work well in humans) This creates UREA which passes into the blood. have enough water lie flat. Urine stop working. You shiver which (urea is poisonous) and getting rid of Too cold and they will work Selective the waste. means your muscles too slowly. Reabsorption are contracting and The kidneys filter out the urea and some water and salts. Healthy kidneys: relaxing. This required respiration that Filter your blood (removing stuff) This creates URINE which is stored in the bladder. Type 2 Diabetes produces heat. And then reabsorb Type 1 Diabetes Cells stop • ALL of the glucose Server temperatures can - Blood glucose can get responding to insulin lead to really problems. • Some of the water and ions fatally high as no insulin is even when the Very cold conditions can (depending on what’s needed) released by the pancreas. cause hypothermia where pancreas is making it. •None of the urea The pancreas the core body temperature Before meals insulin is Eating a healthy diet (remember we want to get rid of this – as monitors the has fallen below 35oC. well as extra water and ions we don’t need) injected so that glucose low in carbohydrates, amount of glucose Very hot conditions can can be converted to losing weight and lead to heat stroke. This And if your kidneys stop working… in your blood. It glycogen if it is not needed. can also be caused by exercise can help can produce two You need this overheating during High carbohydrate diets are frequently and have to hormones ISULIN control this type. stay in hospital while it happens. and GLUCAGON. Insulin lowers blood sugar. Glucagon raises blood sugar. Removes urea As blood passes through the dialysis Damaged or diseases machine waste and excess water The recipients kidneys can be and ions pass through the semiimmune system might replaced by a healthy permeable membrane into the try to reject the new kidney from a donor. dialysis fluid. kidney. (down the concentration gradients as there To avoid this we is none in the fluid to begin with) match donors and But recipients as closely as The dialysis fluid contains the same possible. concentration of glucose ions the Immunosuppressant blood should have so none moves drugs are taken. out of the blood by diffusion. avoided but type 1 diabetics must eat regularly. There is no cure. (other than a panaceas transplant. Stem cells might be the answer) Disadvantage for dialysis Frequent long sessions in hospital Expensive over a long time Big effect on diet and lifestyle Can become difficult after many years Disadvantage for transplant Possible rejection Lifelong immunosuppressant drugs Donor kidneys don’t last forever NEVER ENOUGH KIDNEYS FOR EVERYONE! This tends to affect older people. If lifestyle changes don’t work drugs maybe needed. exercise. Congratulations! Here’s the instructions to make a balloon to celebrate…