Plant test study guide answers
advertisement

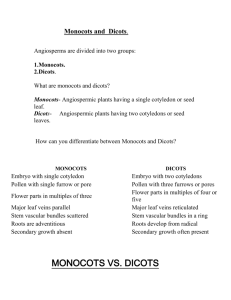
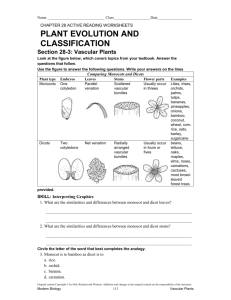
Name _______________________________ Study Guide on Plants/Insects Label each part of the flower. Tell whether the part is female or male. A. Filament - male B. Anther - male C. Stigma - female D. style - Female E. ovary - female Label each part of the leaf and tell what it is or its job/function. C. cuticle – waterproof covering D. chloroplast - photosynthesis E. xylem (transports water) and phloem (transports food) F. stomata – oxygen and carbon dioxide exchanged here Letter B is an insect. Label the 3 parts of an insect on letter B. Head thorax abdomen How is an insect able to obtain food (mouth)? Specialized mouth structures – specific to its food Insects: 1. What is the difference between gradual metamorphosis and complete metamorphosis? Gradual metamorphosis – no distinct larvae stage Complete metamorphosis – goes through all 4 stages 2. What are the 4 stages of the butterfly and what happens during each stage? Eggs – hatch into larva, larvae – eat and grow, pupa – protective covering, adult (can fly) 3. Insects belong to the phylum Arthropods. Plants: 1. The ancestors of today’s plants were most likely green algae. 2. What are the parts of the seed and what does each part do? Endosperm – food, seed coat – protective covering, embryo – future plant 3. List 5 characteristics of plants. Multicellular, autotroph, eukaryotic, cuticle, photosynthesis, cell wall with cellulose 4. What is the major difference between vascular plants and nonvascular plants? Vascular plants have vascular tissues, nonvascular plants do not 5. There are 2 main vascular tissues: xylem and phloem. What does xylem do? Transports water from the roots to the top of the plant 6. What does phloem do? Transports food from the leaves down 7. What are the 2 different types of vascular plants? Angiosperms and gymnosperms 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. What is an example of a vascular plant? Tree, etc What is an example of a nonvascular plant? Moss, liverwort, hornwort The supportive structure that holds the plant up is the stem. The organ responsible for absorbing water and minerals and anchoring the plant is the root. Does the root do photosynthesis (make food)? no The main place photosynthesis occurs is in the leaves Gases pass in and out of the leaves through the stomata. The stomata are at the top of the leaf or the bottom? bottom The cuticle is a waxy waterproof coating on the leaf. Water evaporation from leaves is known as transpiration Germination is when embryo sprouts from the seed. Photoperiodism is period of light and dark a plant needs If a plant is dormant, what does this mean? A period of inactivity/rest If a plant is a deciduous plant, what does that mean? Plant that loses it leaves in the fall If a plant is an evergreen, what does that mean? Leaves that stay green year round What are the 2 types of stems? What is the difference? Herbaceous – green/photosynthesis, woody – brown, trees and shrubs 24. (cram session notes) A plant’s response to a stimulus is known as a tropisms. 25. Tropisms: Light phototropism, gravity gravitropism and touch thigmostropism 26. Plant hormones include: chemicals that control the growth in the plant ex. auxin Gymnosperms vs. Angiosperms or Both 27. Which contains cones? g 28. What protects the seeds in fruit? a 29. Which has flowers? a 30. Which can live far from water? both 31. Which contains vascular tissues? both 32. Which contains seeds? both 33. Which has monocots and dicots? a 34. Which is a tree like a pine tree? g 35. Angiosperms List the steps that happens after pollen falls on the stigma? 1. Fertilizes the eggs 2. Petals fall off 3. Ovaries will develop into fruit Parts of the flower: 36. The sperm cell is in the pollen. 37. The egg cell is in the ovule. 38. The ovules are contained within the ovary. 39. petals are used to attract pollinators. 40. The stigma is sticky and is used to catch pollen. 41. The style is used to hold the sticky part up. 42. The anther contains the pollen in the flower. 43. The filament’s job is to hold the anther up 44. What will eventually become a fruit? ovary 45. Once a zygote forms, what will soon follow? Fruit forms Monocots vs. Dicots 46. The seed leaves are known as a cotyledons. Monocots have 1and Dicots have2 47. The radicle will eventually become the root. 48. m have petals in 3’s 49. dhave petals in 4’s or 5’s 50. d have taproots 51. mhave fibrous roots 52. 53. 54. 55. dhave net-like leaf veins mhave parallel leaf veins Name 3 examples of monocots: corn, wheat, grasses, rice, lilies Name 3 examples of dicots: magnolias, maples, oaks, beans