BIOS 1300 SI WORKSHEET – Exam 2 prep SI Leader: Merrin

BIOS 1300
SI WORKSHEET – Exam 2 prep
SI Leader: Merrin Jeffries (email: mj983011@ohio.edu
)
02 October 2014
1. Cells that secrete the organic components of the bone matrix are called: a. osteocytes b. osteoprogenitor cells c. osteoblasts d. osteoclasts e. chondrocytes
2. The central canal of an osteon contains: a. bone marrow b. osteocytes c. concentric lamallae d. blood vessels e. lacunae
3. The lining of the medullary cavity is called the: a. endosteum b. periosteum c. epimysium d. perimysium e. perichondrium
4. What structures allows a bone to grow in length? a. lacunae b. epiphyseal c. periosteal bud d. metaphysis e. trabeculae
5. Secondary ossification centers occur a. in the diaphysis b. at the periosteum c. in the epiphysis d. in the metaphyses e. in dermal bones
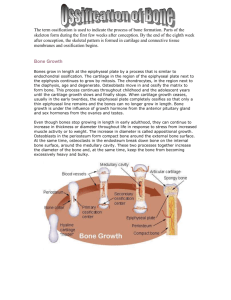
6. The following are important steps in the process of endochondral ossification
1. Enlarged chondrocytes die
2. Osteoblasts replace calcified cartilage with spongy bone
3. Chondrocytes enlarge and the surrounding matrix begins to calcify
4. Blood vessels invade the perichondrium
5. Perichondrial cells become osteoblasts and produce a thin shell of bone
The correct order for these events is: a. 3,1,5,4,2 b. 1,3,5,4,2 c. 1,5,3,4,2 d. 2,3,1,5,4
e. 3,1,4,5,2
7. The following are stages in the regeneration of skin following an injury:
1. blood clot/scab formation
2. cellular migration
3. epidermis covers granulation tissue
4. epidermis covers scar tissue
The correct order of these events is: a. 1,2,3,4 b. 4,3,2,1 c. 4,3,1,2 d. 3,4,1,2 e. 2,4,1,3
8. Of the following selections, the one that correctly identifies a long bone is: a. rib b. sternum c. humerus d. scapula e. patella
9. The process of replacing other tissues with bone is called: a. calcification b. ossification c. chondrification d. remodeling e. osteoprogenesis
10. One of the basic histological differences between compact bone and spongy bone is that in compact bone: a. the basic functional unit is the osteon b. there is a lamellar arrangement c. there are plates or struts called trabeculae d. osteons are not present e. there are no blood vessels
11. Endosteum is in all these places, EXCEPT: a. around the exterior of the femur b. on the trabeculae of spongy bone c. lining the central canal of an osteon d. lines the medullary cavity
12. Dead skin cells are shed in thin sheets because they are held together by “spots” of proteoglycan reinforced by intermediate filaments. Such strong intercellular connections are called: a. gap junctions b. intermediate junctions c. tight junctions d. desmosomes e. junctional complexes
13. In stratified epithelia adapted to resist mechanical forces, which of the following types of cell-to-cell junctions are especially abundant?
a. tight junctions b. basolateral junctions c. gap junctions d. hemidesmosomes e. desmosomes
14. Which of the following is a type of secretion in which some cytoplasm is lost with the product? a. holocrine b. merocrine c. apocrine d. mucus e. serous
15. Examination of a tissue sample reveals groups of cells united by junctional complexes and interlocking membranes. The cells have one free surface and lack blood vessels. The tissue is most likely _______________ tissue. a. muscle b. neural c. epithelial d. connective e. adipose
16. Storage of lipids that represent an important energy reserve in bone occur in areas of: a. red marrow b. ground substances c. bone matrix d. yellow marrow
17. Appositional bone growth at the outer surface results in: a. an increase in the diameter of growing bone b. an increase in the overall length of bone c. a thickening of the cartilages that support bones d. an increased hardening of the periosteum
18. Giant cells, called osteoclasts, with 50 or more nuclei serve to: a. synthesize the organic components of the bone matrix b. form the trabecular framework which protects cells of the bone marrow c. line the inner surfaces of the central canals d. secrete acids which dissolve the bony matrix and release stored minerals
19. The epiphysis of long bone is primarily filled with: a. spongy bone b. yellow bone marrow c. compact bone d. hyaline cartilage
20. The vitamins essential for normal adult bone maintenance and repair are a. A and E b. C and D c. B and E d. B complex and K
21. The presence of an epiphyseal line indicates a. epiphyseal growth has ended b. epiphyseal growth is just beginning c. growth of bone diameter is just beginning d. the bone is fractured at the location e. no particular event
22. The process of bone growth at the epiphyseal cartilage is similar to: a. intramembranous ossification b. endochondral ossification c. the process of osteopenia d. the process of healing a fracture e. the process of calcification
23. Which of the following conditions would you possibly observe in a child who is suffering from rickets? a. abnormally short limbs b. abnormally long limbs c. oversized facial bones d. bowed legs e. weak, brittle bones
24. Dermal bones, such as the mandible, are a result of ________________________ ossification.
25. The basic function unit of compact bone is the _______________________.
26. In adults, the cells responsible for maintaining the matrix in osseous tissue are the ______________________.
27. The condition in which an individual develops a bow-legged appearance as the leg bones bend under the weight of the body is _____________________.
28. The fibrous protein that is responsible for the strength and water resistance of the skin surface is: a. collagen b. eleiden c. keratin d. elastin e. keratohyalin
29. The cells that tear down and remodel bone are the _____________________ a. osteoblasts b. osteocytes c. osteoclasts d. macrophages
30. The medullary cavity in the diaphysis of an adult bone would contain: a. compact bone mainly b. spongy bone mainly c. red bone marrow
d. yellow bone marrow
31. The part of bone that the articular cartilage covers directly is the: a. diaphysis b. endosteum c. epiphysis d. periosteum
32. The junction between the diaphysis and epiphysis in a growing bone is called the: a. endosteum b. periosteum c. epiphyseal disk d. articular cartilage
33. Connective tissue is complex because it has a variety of cells and a noncellular background called a ______________ surrounding them. a. collagen b. elastin c. mucous secretion d. matrix
34. Which of these is not a connective tissue? a. blood b. bone c. muscle d. cartilage
35. The strength of the dermis would mainly be due to ____________ a. the amount of blood vessels b. the distribution c. the presence of collagen fibers d. the thickness of the layers
36. The yellowish color of some person’s skin is due to __________ a. lack of blood supply b. low melanin levels c. carotene d. hemoglobin
37.Modified sweat glands, called ________________ glands, secrete wax in the ear canal. a. sebaceous b. eccrine c. apocrine d. ceruminous
38. Melanocytes lie within the _________________ of the skin. a. stratum corneum and top layers b. deepest dermis c. stratum spinosum and stratum lucidum d. stratum basale and upper dermis
39. Choosing from the following list of connective tissues, which one consists of cells in a fluid matrix? a. loose connective tissue
b. adipose tissue c. bone d. blood
40. Which muscle tissue is multinucleate, voluntary, and bears striations? a. skeletal muscle b. smooth muscle c. multiunit smooth muscle d. cardiac muscle
41. An exocrine gland that loses small parts of its cell bodies during secretion, as is the case for the mammary gland is further classified as a(n) __________________ gland. a. merocrine b. apocrine c. holocrine d. endocrine
42. Microvilli, which function to increase surface area, are more likely to be found in
__________________ epithelium. a. simple cuboidal b. simple squamous c. transitional d. simple columnar
43. Which of the following is not a compatible base pairing DNA? a. adenine-uracil b. adenine-thymine c. cytosine-guanine d. guanine-cytosine
44. The production of mRNA from a DNA template is termed: a. transcription b. translation c. replication d. mutation
45. The base sequence termed the anticodon is found on molecules of: a. DNA b. tRNA c. mRNA d. rRNA
46. Enzymes function in chemical reactions to a. lower the energy of activation needed to start the reaction b. act as substrate molecules c. prevent the development of metabolic pathways d. keep reactions from interacting
47. A flagellum is found only on which of the following a. a sperm b. a cardiac muscle cell c. a skin cell d. an intestinal cell
48. In the liver, the _________________ may play a role in producing the enzymes that help detoxify drugs a. mitochondria b. RER c. SER d. golgi apparatus
49. The term _________ can be used to imply all of the chemical reactions within a cell. a. metabolism b. respiration c. anabolism d. catabolism
50. Chromosomes align midway between centrioles during what phase of mitosis? a. prophase b. metaphase c. anaphase d. telophase
51. During what phase of the cell cycle does DNA replication occur? a. mitosis b. prophase of mitosis c. G2 phase d. S phase
52. Cells use up to 40% of their daily energy expenditure engaged in what important process? a. active transport b. endocytosis c. exocytosis d. facilitated diffusion
53. Choose the organelle that consists of microtubules and functions both in distributing chromosomes during cell division and in forming portions of cilia and flagella. a. lysosome b. mitochondria c. vesicle d. centrosome
54. Molecules that are soluble in _______________ can pass through the fatty acid portion of the cell membrane unassisted. a. water b. cholesterol c. gases d. lipids
55. The ____________ of a cell is the most critical factor in determining its function. a. size b. shape c. age d. chromosome number
56. Label all of the sections on the long bone:
57. List the six major steps in bone development for both intramembranous and endochondral ossification:
INTRAMEMBRANOUS OSSIFICATION
1. Sheets of relatively undifferentiated connective tissue appear at sites of future bones
ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION
1. Masses of hyaline cartilage form models of future bones
2.
3. 3.
2.
4.
5.
6.
5.
4.
6.
58. Label each of the solutions (Hypotonic, Hypertonic, Isotonic)