2.1 Properties of Matter
advertisement

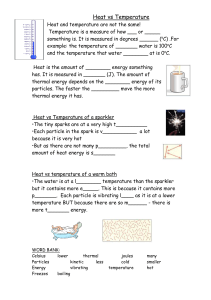
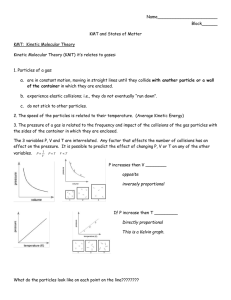
2.1 Properties of Matter • Classifying Material Properties • Physical Properties versus Chemical Properties • Particle Relationships • Thermal Energy, Temperature, and Heat • States of Matter & Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) • Some Thermal Properties of Matter 2.1 Properties of Matter Classifying Material Properties Extensive properties are qualities that are or depend upon the amount of the material. Intensive properties are qualities that do not depend upon the amount of the material. Every material possesses a unique set of intensive properties that can be used to identify it. 2.1 Properties of Matter Physical Properties versus Chemical Properties Physical properties describe physical changes. Most physical properties describe relationships or interactions between matter and energy. Chemical properties describe chemical changes or interactions between different forms of matter. 2.1 Properties of Matter Particle Relationships New properties emerge at and describe each level of organization. Particle Properties e.g. water molecule Material Properties e.g. water Object Properties e.g. water droplet 2.1 Properties of Matter Thermal Energy, Temperature, and Heat Thermal Energy is the total mechanical energy of an object’s particles. Temperature is the average mechanical energy of the particles that compose an object. Heat is the energy transferred from one object to another because of a difference in temperature. 2.1 Properties of Matter States of Matter & Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) Kinetic Molecular Theory states that matter is composed of tiny moving particles. The more energy particles have, the faster they move and therefore the harder they strike each other and the farther they bounce apart from each other. 2.1 Properties of Matter Some Thermal Properties of Matter Physical: Melting Point and Heat of Fusion Boiling Point and Heat of Vaporization Chemical: Heat of Formation Heat of Combustion