Do Now:
advertisement

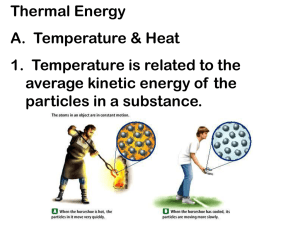
Do Now (2/15/12): Define the following items as “hot” or “cold.” Describe your reasoning for each. 1. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Hot tea Iced tea Ice Steam Water The sun 2. What does the word temperature mean to you? What would/could you measure it in? Temperature and Thermal Energy 2/16/11 Intro to Thermodynamics Thermodynamics – the study of the movement of heat Kinetic Molecular Theory Matter is made up of tiny molecules that are always in motion. In a hot body the particles move faster and have a greater kinetic energy than particles in a cooler body. Energy Temperature –measure of average KE of particles in a system. Thermal energy – overall energy of motion of particles in an object Measures of Temperature Farenheit (˚F) Celsius (˚C) Kelvin (K) 9(C ) F 32 5 K C 273 5( F 32) C 9 Example: Convert the following temperatures: 1. 12˚F=____˚C 2.0˚C=____˚F 3.10˚C=____K Conversion Practice Convert the following temperatures: 1. 12˚F=____˚C 2. 0˚C=____˚F 3. 10˚C=____K 4. 12K =____˚C 5. 72 K=____˚F 6. -200˚F=____K 7. 455˚F=____˚C 8. 388K=____˚C Absolute Zero 0 K – the temperature at which all motion theoretically stops (hasn’t been reached or found yet) Heat Transfer: Types of Heat Transfer Radiation – transfer in the form of waves Conduction – transfer by direct contact Convection – transfer through fluids HEAT WILL ALWAYS FLOW FROM A HOTTER OBJECT TO A COOLER ONE!!! Practice: Work with your partner to answer the questions on the classwork. We will go over it 10 minutes before the end of class. Questions: Why would a balloon get larger in the sun than if you put it in the refrigerator? Use what you know about temperature and thermal energy in your answer. Questions Do solid objects still have thermal energy even though they don’t move? Explain. Questions Can heat flow from a cold object to a hot one? Why or why not? Questions Can an object have a temperature below 0K? Why or why not? What happens at 0k?