Leg Muscles Handout
advertisement

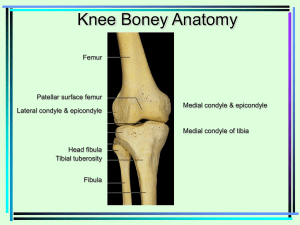
Rectus Femoris Vastus Intermedius Vastus Medialis Vastus Lateralis O Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine [A.I.I.S.]; Upper Margin of Acetabulum I Patella; Tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament; Sesamoid Bone A Extension of knee; Assists flexion of femur at hip N Only quad muscle crossing both hip and knee joints; combined action in walking O Anterior & Lateral femur I Patella; Tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament A Extension of knee N Deepest quad; deep to rectus femoris; may try to palpate underneath by pushing rectus femoris medially in active knee extension O Linea Aspera (posterior femur) I Patella; Tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament A Extension of knee N Anterior, medial surface of lower third of thigh, medial to rectus femoris in active knee extension; sartorius overlaps vastus medialis O Linea Aspera; Greater Trochanter I Patella; Tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament A Extension of knee N Lateral surface of anterior thigh; lateral to rectus femoris in active knee extension Tibialis Anterior Ext. Hallucis Longus Ext. Digitor. Longus O Lateral Condyle & Lateral shaft of tibia I Base of 1st Metatarsal (plantar surface); First (medial) cuneiform (plantar surface) A Dorsiflexion of Ankle; Inversion of Foot N Area of “shin splints”; Paralysis of this muscle causes “foot drop” O Anterior Shaft of fibula I Base of distal phalanx of great toe (Hallucis) A Extension of great toe; assists dorsiflexion of ankle N Comparable to Extensor Pollicis Longus in the hand O Lateral condyle of tibia; anterior shaft of fibula I Middle and distal phalanges of 4 lateral toes A Extension of 4 lateral toes; assists dorsiflexion of ankle N Comparable to Extensor Digitorum in the hand Key O = Origin I = Insertion A = Action N = Notes 7 June 2008 Muscles of the Shin Quadriceps Femoris Group Anterior Leg Muscles Healing Hands Institute 1 Biceps Femoris Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Hamstrings Notes O Ischial Tuberosity I Head of Fibula (inserts laterally at the knee) A Flexion of Knee; (to a lesser degree, Extension of Hip) N Most lateral of the hamstrings; “biceps” indicates “2 heads” O Ischial Tuberosity I Anterior proximal tibial shaft (inserts medially at the knee, at “Pes Anserinus”) A Flexion of Knee; (to a lesser degree, Extension of Hip); Medial rotation of flexed knee N Central hamstring; tendon is deep, and difficult to palpate O Ischial Tuberosity I Posterior medial tibial condyle A Flexion of Knee; (to a lesser degree, Extension of Hip); Medial rotation of flexed knee N Most medial of the hamstrings; adjacent to Gracilis All three of the Hamstrings cross both the hip and knee joints from lateral to medial (BTM): Gastrocnemius Soleus Tibialis Posterior O Medial Head: medial epicondyle of femur Lateral Head: lateral epicondyle of femur I Calcaneus via Achilles Tendon A Plantarflexion of ankle; assists flexion of knee N “Gastro” (Greek = belly); Can act on the knee or the ankle separately, but not simultaneously; raises heel during running & jumping O Soleal line of tibia; posterior head & upper shaft of fibula I Calcaneus via Achilles Tendon A Plantarflexion of ankle (stronger than gastroc.) N “Soleus” (Latin = sole, a flat fish); deep to gastrocnemius; together, gastroc and soleus are often referred to as the “Triceps Surae” O Posterior tibia & posterior fibula I Navicular; adjacent tarsals & metatarsals on plantar surface of foot A Inversion of foot; assists plantarflexion of ankle N Belly of muscle deep to Triceps Surae, cannot be palpated Key O = Origin I = Insertion A = Action N = Notes 7 June 2008 Muscles of the Calf Hamstrings Posterior Leg Muscles Healing Hands Institute Biceps Femoris SemiTendinosus SemiMembranosus An inability to touch your toes while keeping your knees extended is largely due to shortened hamstrings. 2 Gluteals Muscles of the Gluteal Region Gluteus Maximus Gluteus Medius Gluteus Minimus Tensor Fasciae Latae O Posterior sacrum; Ilium; superior gluteal line of ilium I Gluteal Tuberosity of femur; I.T. Tract A Extension of femur at hip; lateral rotation of extended hip N “Gluteus” (Greek = Rump); Maximus used mostly for power, as in climbing stairs, running, rising from sitting position O Iliac Crest I Greater Trochanter of Femur A Abduction N When standing on one foot, Medius contracts on that side to stabilize pelvis and prevent tilting to unsupported side; alternate contraction of these muscles occurs in walking O Posterior Ilium I Anterior surface of Greater Trochanter A Abduction N Gluteus Minimus works with anterior portion of Gluteus Medius O Iliac Crest (posterior to A.S.I.S.) I Iliotibial Tract (I.T. Band) A Stabilizes knee; prevents collapse of extended knee during walking N Braces the knee while walking Key O = Origin I = Insertion A = Action N = Notes 7 June 2008 Deep Lateral Hip Rotator Piriformis O Anterior sacrum I Greater Trochanter A Lateral rotation of femur at hip N (Sciatic Nerve); attempt to palpate just posterior to greater trochanter during active lateral rotation of hip; difficult to differentiate from gluteus medius Healing Hands Institute 3 Pectineus Adductor Longus Adductor Brevis Adductor Magnus O Anterior Pubis I Linea Aspera A Flexion of femur at hip; assists adduction of femur at hip N Uppermost of the medial thigh muscles; only adductor that flexes hip O Anterior Pubis I Linea Aspera A Adduction of femur at hip; assists flexion of femur at hip; medial rotation of femur at hip N Forms medial border of femoral triangle O Anterior Pubis I Linea Aspera A Adduction of femur at hip; assists flexion of femur at hip; medial rotation of femur at hip N Not present in all individuals; if present, lies deep to adductor longus O Inferior Pubic Ramus, Ischial tuberosity & ramus of ischium I Linea Aspera A Adduction of femur at hip; assists flexion & extension of femur at hip N Largest and deepest adductor PES ANSERINUS Gracilis Three thigh muscles insert at the Superior (proximal) Medial Tibia forming the shape of a “duck foot”: O Anterior Pubis I Medial proximal tibia (“Pes Anserinus”) A Adduction of femur at hip; assists flexion & medial rotation of flexed knee N Most superficial and medial of adductor group; only adductor that crosses the knee joint; Femur and Gracilis form the shape of the letter “V” Sartorius Gracilis Semitendinosus Key O = Origin I = Insertion A = Action N = Notes 7 June 2008 The initial letters of these muscles form the mnemonic expression “Silly Goose Steps”. Sartorius Healing Hands Institute Muscle of Anterior Thigh Adductors Muscles of the Medial Thigh O Anterior Superior Iliac Spine (A.S.I.S.) I Upper medial shaft of tibia (“Pes Anserinus”) A Assists flexion, abduction, lateral rotation of femur at hip; assists flexion, medial rotation of knee N Longest muscle in the body; most superficial thigh muscle; not an adductor 4 Peroneals Muscles of the Lateral Lower Leg Peroneus Longus Peroneus Brevis Peroneus Tertius Peroneals Notes O Head & lateral shaft of fibula I Base of first metatarsal; 1st (medial) cuneiform (plantar surface of foot) A Eversion of foot; assists plantar flexion of ankle N Traverses the sole of the foot to meet the tibialis anterior tendon to form a stirrup for the foot (wraps under the foot); a.k.a. Fibularis Longus O Lateral shaft of fibula I Base of 5th metatarsal A Eversion of foot; assists plantar flexion of ankle N Helps when walking or running on uneven surfaces; a.k.a. Fibularis Brevis O Anterior distal fibula I Base of 5th metatarsal A Eversion of foot; assists dorsiflexion (lifts little toe) N Functions to place the foot flat on the ground by raising its lateral border Peroneus = Greek for “fibula” These muscles would be involved in the case of a lateral ankle sprain. “Eversion” occurs when the foot is turned or rotated outward; i.e., while standing, lifting the lateral edges of the feet while ‘collapsing’ toward the inner arches. Key O = Origin I = Insertion A = Action N = Notes 7 June 2008 Healing Hands Institute 5