Epithelial Tissues Lab
advertisement

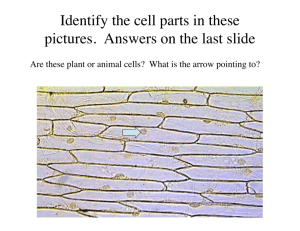
Epithelial Tissues Laboratory Exercise 7 Background Epithelial tissues are tightly packed single (simple) to multiple (stratified) layers of cells that provide protective barriers. The underside of this tissue layer contains a basement membrane layer to which the epithelial cells anchor. Epithelial cells always have a free surface that is exposed to the outside or to an open space internally. Many shapes of the cells exist that are used to name and identify the variations. Many of the prepared slides contain more than the tissue to be studied, so be certain that your view matches the correct tissue. Also be aware that stained colors of all tissues might vary. Materials Needed Textbook Compound light microscope Prepared slides of the following: Simple squamous epithelium Simple cuboidal epithelium Simple columnar epithelium Pseudostratified columnar epithelium Stratified squamous epithelium Transitional epithelium Purpose of the Exercise Review the characteristics of epithelial tissues and observe examples of each type. Procedure 1. Complete Part A . 2. Use the microscope to observe the prepared slides of the types of epithelial tissues. View under high power (400x). Compare your prepared slides to the micrographs at the front of the room. Note that some of the tissue colors may vary with the stain. 3. Complete Part B. Make a sketch of each tissue and label the following: basement membrane, nucleus, and any other distinguishing characteristic (goblet cell, cilia, microvilli). Part A Match the tissue type with the characteristics. Place the letter of your choice in the space provided. (Some answers will be used more than once.) ___ 1. Consists of several layers of cube-shaped, elongated, and irregular cells. ___ 2. Commonly possesses cilia that move sex cells and mucus. ___ 3. Single layer of flattened cells. ___ 4. Nuclei located at different levels within cells. ___ 5. Forms walls of capillaries and air sacs (alveoli) of lungs. ___ 6. Forms linings of trachea and bronchi. ___ 7. Younger cells are cuboidal and older cells are flattened. ___ 8. Forms inner lining of urinary bladder. ___ 9. Lines kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands. ___10. Forms lining of stomach and intestines. ___11. Nuclei located near basement membrane. ___12. Forms lining of oral cavity, anal canal, and vagina. a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium e. Stratified squamous epithelium f. Transitional epithelium Part B Sketch each type of epithelial tissue in the spaces provided. Indicate their function and their location within the body. Simple squamous epithelium (400x) Location _______________ Function _______________ Simple columnar epithelium (400x) Location _______________ Function _______________ Simple cuboidal epithelium (400x) Location _______________ Function _______________ Pseudostratified columnar epithelium (400x) Location _______________ Function _______________ Stratified squamous epithelium (400x) Location _______________ Function _______________ Transitional epithelium (400x) Location _______________ Function _______________ Critical Thinking Application As a result of your observations of epithelial tissues, which one(s) provide(s) the best protection? Explain your answer.