Electronegativity and Polarity
advertisement

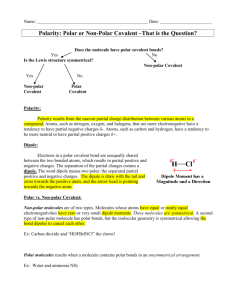
Electronegativity and Polarity Elecronegativity • Relative ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond • Fluorine has the highest electronegativity value • Trend: – Increases across (left to right) a period – Decreases down a group Types of covalent bonds –Non-polar covalent: equal sharing of electrons –Polar covalent: unequal sharing of electrons Non-polar covalent • Sharing of electrons equally • Usually occurs when two identical atoms are bonded together. • Examples: H2, O2, N2, Cl2, Br2, I2, F2 Polar covalent • Unequal sharing of electrons • Unequal sharing caused by 2 elements with different electronegativities (different abilities to attract electrons). • The bond is called a dipole (two poles) • Creates molecule with partial charges • Partial charges symbolized by (delta) + and • The more electronegative atom is located at the partially negative end • Example: + H-Cl and H-Cl Polar molecule or not? • The shape of a molecule usually tells if a molecule is polar or not • If the VSEPR shape is symmetric it is usually non-polar • If the molecule is asymmetric it is polar Name Linear Polar example HCl Non-polar example CO2 Trigonal Planar CH2O AlH3 Tetrahedral CH3OH CH4 Trigonal pyramidal always Bent always Youtube polar vs nonpolar Intermolecular Forces • The force that exists between separate molecules. • This force attracts molecules to each other. • 3 Types – London Dispersion force or induced dipole moment between molecules; only force in non-polar molecules; weakest force (caused by the motion of electrons) (ex: CH4) Induced dipole moment – Dipole-dipole the force between two polar molecules; stronger force (ex: HCl) – Hydrogen bond forms between the hydrogen end of one dipole and fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen (that have at least one lone pair) end of another dipole; strongest force (ex: H2O) Hydrogen bond IMF’s • ALL molecules have dispersion forces • All polar molecules have dipole-dipole forces and dispersion forces • Molecules that hydrogen bond have all 3 Solubility of polar molecules • Properties are due to intermolecular forces • Like dissolves like – Polar substances will dissolve polar molecules (and ionic compounds) – Non-polar substances will dissolve non-polar molecules