About test, questions something you knew you did not do well on
advertisement

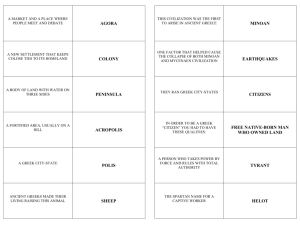
Read 10 min Finished Chinese handout (Dorian, Confucianism, Legalism) Get to know Greece activity 6 groups/no more than 6 people Each person will read one sheet to their group to discuss, then put in their LL Glue/Label Map - Mediterranean Aegean sea, Sparta, Greece 300 years of conflict/confusion – Dorian Period, greatest loss was the ability to write/trade. TPS Why is the ability to write so key to a great civilization? Lacking writing, learned about their history through the spoken word. Tradition states the greatest storyteller was a blind man named Homer, little is known about him. Trojan War forms the backdrop for one of his great epic poems, the Iliad Partner read from Odyssey by Homer 800 BC new society emerged through stability. Centered on Polis-ancient Greek city-state How do we see the word Polis affect us today? TPS Appears in cities such as Annapolis, Indianapolis, Minneapolis Greece rugged/travel & communication difficult, each Polis developed separately and independent of the other. What are the problems with this? Each developed own gov’t, laws, customs Greek City-States Polis center of life/culture for ancient Greeks….One philosopher defined a person as one who lived in a polis. We can see how central the Polis is to there lives & their identity. LL What happens when you dedicate yourselves to something i.e. Sports team/church/club LL You become fiercely loyal willing to do anything to protect People did not think themselves as Greeks but members of a polis instead. - Athenians -Corinthians -Spartans Acropolis-citadel or highly fortified area of an ancient Greek city. Most famous located in Athens Polis Life Housed temples to the gods/public ceremonies. Below was other public spaces/ Agoras - marketplaces. Did business, gossiped, politics Outside of the Agora, homes, shops, more temples Other areas of polis gymnasiums for athletes, training grounds, public bath for athletes Sturdy wall for defense around entire polis. Few scattered homes/markets/fields for all of food was grown outside of polis. What is the problem?? TPS – what is the solution to the problem? Cartoon Quick Draw of what an acropolis would look like include…. Agora, walled areas, homes, gymnasium, public bath, fields, temples on top. Features of the Acropolis Read 10 Min What roles did the acropolis and the agora play in a typical Greek polis? Bell Ringer Each Polis had a separate political system. LL why? Mostly due to geography of Greek, mountains divided polis’ with few roads, if there was a road we would call it a dirt path Trading Polis of Corinth ran an oligarchy (city-state ran by few individuals) Athens (birthplace of democracy) Sparta……. Major Polis’ in Greece Located in Peloponnesus(large peninsula of S. Greece) Surrounded by smaller towns seized control of towns including Messenia. Made Messenians Into helots-state slaves, Helots given Spartan cit. to labor. LL WHY? Enables Spartans to Spend free time training for war, motivation to do good work Believed that only way to keep order was to fight The Mighty Spartans! Helots outnumbered Spartans 7:1. Ready to rebel at all times/had to keep strong army to keep helots in check Men/Women trained top physical shape. Men to serve in army/Women to bear strong, healthy children All babies/boys and girls/ examined for strength after birth. If found unhealthy left in wild to die. Healthy ones trained for soldiers from young age. Boys taught physical/mental toughness from young age by mother until 7. Entered special school system designed to train them for combat created by legendary king Lycrurgus. Spartans continued.. Spartan Video View and write as a Historian documenting this time frame. Complete a few paragraph write up of the Spartan training system for young boys. To help guide you Who, What, When, where, Why Partner Read - What have historians said As you are reading compare and contrast with a chart, summarize each piece (2)! what are the main differences between the two pieces, what type of pieces are they, are they accurate/reliable?, What is each pieces purpose, what do they say about the same topic? -Xenophon, The Polity of the Spartans, c. 375 BC “Instead of softening their feet with shoe or sandal, his rule was to make them hardy through going barefoot. This habit, if practiced, would, as he believed, enable them to scale heights more easily and clamber down precipices with less danger. In fact, with his feet so trained the young Spartan would leap and spring and run faster unshod than another in the ordinary way. Instead of making them effeminate with a variety of clothes, his rule was to habituate them to a single garment the whole year through, thinking that so they would be better prepared to withstand the variations of heat and cold.” Training continued…. Training boys sent into wilderness with no food/tools expected to survive Age 20 became hoplites – foot soldiers. 10 years, then took place as citizens The Man It was unusual that woman played important role in society. Why do you think? TPS Trained in gymnastics for fitness/thought they had to be fit to bear strong children Had right to own property, forbidden throughout rest of Greece Sparta led by two kings/served as military commanders Over time elected council of elders took over decision making responsibilities Honor to take a seat on council and run the city. Spartan Women/Commanders Spartan Debate Was the Spartan way of life good for it’s citizens? 6 groups/3 debates. Half will support the Spartan system, against Spartan system. Prepare and write statements that support your point of view. Write a brief persuasive essay explaining your position on the topic. Exit ticket 3-2-1 Write down….. 3 things I learned today 2 questions I still have/muddy topics 1 connection to something we have previously learned about READ 10 MIN GRADE LL Grade TEST Bell Ringer Was King Lycrurgus’ training system for boys fair? Was it effective? Would other training methods have worked for the Spartans, back up your reasoning. Last stand handout Finish section on training center with partner Bell Ringer Explain the significance of a Polis, Acropolis, Democracy & Helot. Which is the first campaign of the Persians and which is the second, how are they identified? What do the numbers in parentheses represent? By what routes did the Persians choose to attack Greece? Explain why? Where did most of the battles of the Persian Wars occur? How might their citizens have been affected? Map p. 132 – answer in your LL Persian War Chart Name of Battle Winner Persian Leader Greek Leader Key events/ Information LL Summarize what we already know about the Persian empire especially King Cyrus & Darius. Shortly after democracy aboutreligion/gov’t 400 BC, all of Initially Persian rule very soft est. allowing Greece brought into war with Persian Empire , to stay the same league of Greeks called Delian League. Ionians rebel TPS If you were a leader of a small Greek city Persian army too strong asked fellow help state, would you have joined theGreeks Delianfor League? including Athens-supplied ships to Ionian rebels Persian could not put down revolt, Ionians burn Persian Temples, emperor Darius furious & sought revenge Planned to punish Ionian allies, especially Athens/Greek mainland Causes of the conflict 1st Persian Invasion/handout 490 BC Persian fleet tens of thousands of men set out to fulfill Darius’ plan. Came ashore near Marathon Athenians warned ahead of time met them at the beach while the Persian’s were unloading. Charged in a Phalanx – tight rectangle formation in which soldiers held long spears out ahead of a wall of shields Persians counter attacked while Greeks closed in from sides. Greeks highly outnumbered (25,000 10,000) but Persians retreat, casualties 6,000 Persians , less than 200 Greeks Battle of Marathon Athenian messenger, Pheidippides (fy-DIP-uhDEEZ) ran from marathon to Athens after the battle to announce the Greek’s victory. Run was 26 miles Now we run “marathons”; 26 mile races to commemorate the messenger’s dedication and athleticism. What happened to him after the run??? Died from exhaustion. What famous phrase did he yell? Why? TPS Also a warning sign to defend city for the Persians Battle of Marathon continued… Partner Read History of Herodotus – Battle of Marathon Greek victory shocked both sides/Persians humiliated Darius wanting revenge more than ever planned a second invasion but dies in 486, son Xerxes takes over and plans attack for his father 10 years after initial invasion 100’s of thousands of Persians set out for Greece Greek legend states that army so big took a week to cross manmade bridge they built Athenians called on other Greek city-states for help – bitter rival Sparta responded. Greece very split at this time, some help, some fight for Persia, some sit still thinking Athens should be taken and then the Persians will leave LL What would you have done, why. Why are they not unified? Athens with Navy agreed to take charge of ships while Sparta took charge of Greek’s armies 2nd Persian Invasion Persians marching quickly/Greeks afraid not enough time, Spartans gathered at mtn pass in Thermopylae (Persians had to pass through) to slow them down 300 Spartans held off entire Persian army for several days in tiny pass @ a chokehold area Local resident in end show Persians an alternate path through the mountains, eventually surrounded and killed the Spartans. Gave Greeks enough time to set up defense Themistocles convinces Greeks abandon Athens , Persians burned it to the ground Waited for fleet to bring more supplies Continued… Athenian navy commander lured Persian fleet into the narrow strait of Salamis near Athens(same strategy as Spartans). Persian ships too large to maneuver, smaller quicker Greek fleet sank Persian fleet TPS List 3 downfalls of the Persians loosing their fleet. How did it change the war? With your partner in your LL, list the 3 major battles of the Xerxes brought a throne to watch the battle from shore Persian different leaders for both Greece/Sparta watched Wars, his fleetthe be sunk by smaller Greeks and the main facts about each battle 479 BC full Greek/Sparta army destroyed Persians near Plataea Continued… Warring City-States activity – groups of 4 Last Stand of 300 Fill out accompanying worksheet with video Create a map in your group that must show events contributing to the Persian wars Must portray 10 events within a larger historical time period Include: Where they took place Routes traveled Groups involved Chronologically numbered Provide a legend/key Must include an annotation explaining why each individual event is important and/or significant to the historical time period News Report Activity Ionian Rebellion Battle of Marathon Battle of Thermopylae Battle of Salamis Choose either Greek or Persian side Use books/all in group must play a part Exit Ticket Draw a quick Diagram (graphic organizer) that shows your perspective on today’s lesson combining the chart we made and the map. Below the diagram summarize in 2-3 sentences what was learned/covered today.