MEDIEVAL EUROPE FROM THE 11thCENTURY TO THE 15th
advertisement

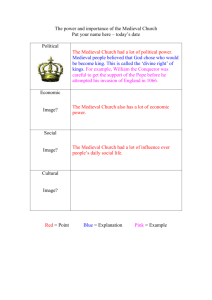
MEDIEVAL EUROPE FROM THE 11thCENTURY TO THE 15th CENTURY Culture and society The Middle Ages are known as the Dark Ages because of wars, violence and epidemics. But It was also a very religious period and the Church was to give people hope and really guided people’s life. Today in our secular societies, such devotion is surprising. This is why it is very interesting to focus on medieval Christianity First, let’s show the features of this medieval Christianity to describe in a second part the organisation of rural societies. I/ Features of medieval Christianity A/ People’s faith Most people either secular (95%) or clergymen believed in the Christian dogma through the Bible. They believed in the beyond and searched salvation during the final judgement. They were scared of Hell and hoped to go to Heaven. However, in the countryside, popular believes remained and sometimes they criticised the Catholic Church. They were called the HERETICS. The most famous example in southern France were the CATHARS ( also in northern Italy and in the Rhineland) who searched for a purer faith, advocating a poor Church far from ostentation, aimed at helping people get out from temptation of Hell. In 1231, the Inquisition was created by the Catholic Church and crusades were launched against the so-called heretics: Jews, Cathars, Basques… A pyre by the Inquisition Cathars being expelled from Carcassonne in 1209.a miniature from the Grand Chronicles of France around 1415. The British Library B/ A tight control of the Church Faithful got organised around a priest in a parish. Most people were baptised, married and attended massed. Priests’ looks were typical: tonsure, frock. They were to stay single ( celibacy), and were the only ones to read and write. They preached and were seen as guides and role models. At this time the Church was wealthy and most priests were land-owners and raised taxes ( Dime). They could also be lords and have vassals In some parishes, faithful worshipped remains of saints and participated to pilgrimages. For instance the CONQUES( midi-Pyrenees/ Aveyron) abbey-Church on the route to Santiago de Compostela.( Saint Jack- one of Jesus ‘ first apostles) In Conques there are the remains/ relics of Sainte FOY. There, one can see the very famous gold and jewel-encrusted reliquary statue of St. Foy. She was a martyred young woman from the 4th century. Another very special pilgrimage : The crusades: they were an armed pilgrimage to set Palestine free from Muslim domination. The Pope called on the first crusade in 1099 Pope Urban II calls for the crusade in 1095 in the Council of Clermont in France “For you must haste to exterminate and carry aid to our brethren dwelling in the East who need your help (…) The Turks a Persian people have attacked them and have advanced into Roman territory, seizing more and more of the lands of the Christians, have defeated them already in many battles, have destroyed churches and have devastated the Kingdom of God.(…) Wherefore, I, not I but God, exhorts you as heralds of Christ to urge men of all ranks to hasten to exterminate this vile race. (…) For those going there, there will be remission of sins if they come to the end of their fettered life… this I grant to all who go by the power vested in me by God. Let those who liked waging war against other faithful, now march upon the infidels, let those who have been robbers now be soldiers of Christ and those who’ve been hireling for a few pieces of silver now attain an eternal reward (…) On the one hand will be the enemies of the Lord and there his friends. 1-what did the Pope ask? 2-what did crusaders have to do once in Jerusalem? 3-What did they get in return? C/ Monasticism Monasticism is a religious way of life characterized by the practice of getting fully devoted to spiritual work. It’s an extreme way of practising religion. 4 MENDICANT ORDERS to remember : The Benedictines . developed from the 10th century to the 12th century. The Cistercians,It developed from the 11th century with an abbaye-Church founded by Bernard de Fontaines in Clairvaux in 1115. It’s based on poverty and austerity. Dominicans, founded in 1215 Franciscans, founded in 1209 by St. Francis of Assisi Monks and nuns had a huge influence on people particularly in the countryside: they were seen as role models. But very soon, those orders are going to get richer ( lands, taxes ) and get closer to political power. II/ Life in the countryside A/ Peasants’ way of life Subsistence agriculture was the main economic activity at this time. However, very few peasants owned lands: they got their land from lords , they were tenant farmers and held tenures. In return they worked on the lord’s lands ( corvée ) and paid taxes to the Lord to use his tools ( oven, mill …) ( les banalités) Their life was harsh and precarious because it depended on seasons and crops. Productions were not very high due to poor techniques like the three field-crop rotation B/ Feudalism Feudalism is a hierarchy between lords and vassals. Vassals paid/pledged homage to lords : lords lend them a feud and protected them. In return they had to work on the lord’s land and give a part of their crop. 13th century archives départementales Perpignan It was possible to pay homage to many lords. There was a hierarchy such as/ CONCLUSION Medieval Christianity had specific features. First of all it was very closely linked with religion, far more than today. At this time, religion and the Clergy had a huge power over men who feared Hell and divine punishment. Pilgrimages, monasticism, the Inquisition all reflect the power of the Church at this time. Moreover, medieval men and women were mostly farmers and made a living from subsistence agriculture into a feudal system. At the end of the Middle-Ages, Christianity will evolve thanks to humanism but the Church will keep a great power.