Cell Cycle and Cell Division
advertisement
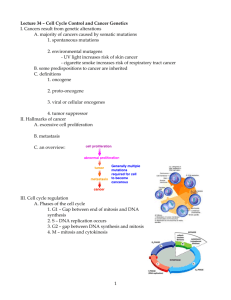
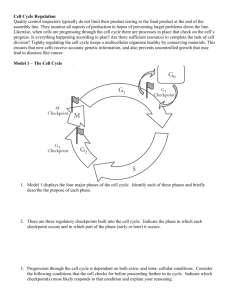
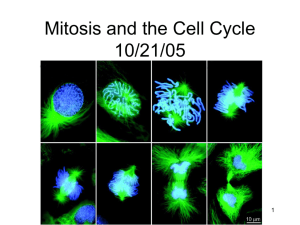
Cell Division Cell divides into two daughter cells Revised 10-09-2006 Cell Cycle G1 phase •Cellular Growth •Development S phase •DNA Replication •Protein synthesis G2 phase •Synthesis of organelles •Materials for cell division M Phase •Mitosis Length of the Cell Cycle • Intestine •24-48 hours • Frog embryo •1 hour Control of the Cell Cycle • Cyclins • Cyclin Dependent Kinases Cell Cycle Regulation The cyclins are named “cyclins” because their appearance during the cell cycle is cyclical Cyclins/Kinases Complexes G1 phase Cellular Growth and Development Cyclin D CDK4 CDK6 Cyclin E CDK 2 Checkpoint 1 •Cell size? •DNA? Cyclin D cyclin D-dependent kinase Cdk6 S phase DNA Replication and Protein synthesis Cyclin A CDK 2 Cyclin A • Residues 173432 • 2 similar domains • Cyclin fold –5 α-helices CDK 2 • Domain 1 –85 residues –1 α-helix –5 stranded βsheet • Domain 2 –213 residues –α-helices Cyclin A/CDK 2 Complex Cyclin A/CDK 2 Complex Inactive Active G2 Checkpoint 2 •All DNA Duplicated? •Cell size? •All DNA Intact? •Repair DNA • Cyclin B Cell Cycle Regulation M-phase promoting Factor MPF Checkpoint 3 •Chromosomes attached to spindle fibers? Mitosis • Process by which the nucleus of . the cell is divided into two nuclei, each with the same number and kinds of chromosomes as the parent cell. • Cytokinesis is the process by which the cytoplasm is divided. Chromosomes Prophase Longest (50 - 60%) • • • • Appearance of chromosomes Nucleolus disappears Nuclear membrane breaks down Centrioles separate and migrate to opposite poles of cell Metaphase Shortest • Chromosomes line up across center of cell • Spindle fibers form from centrioles to centromere Anaphase • Sister Chromatids split at Centromere • Individual Chromosomes move toward poles Telophase Final Phase • • • • Spindle fibers breakdown Chromosomes uncoil into Chromatin Nuclear envelope reforms Nucleolus becomes visible Mitosis in Whitefish and Onion Cytokinesis The process by which the cytoplasm divides, forming two new cells. Cytokinesis The process by which the cytoplasm divides, forming two new cells. • Animals •Cell membrane •pinches inward • Plants •Cell plate Result of Cell Division Two cells that are identical to each other.