86 - Metamorphic Rock Notes
advertisement

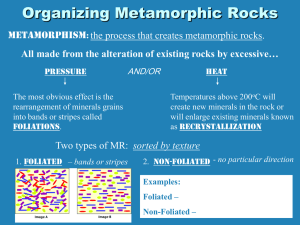
Doc ____ METAMORPHIC ROCK NOTES Name is from the Greek meaning to change form Are called “daughter rocks” because they are created from existing rocks, called “parent rocks” – the original rock that the metamorphic rock is made from Can be from igneous, sedimentary or metamorphic rocks Created by heat, pressure or chemical change 12-16 km below earth’s surface Fossils present are distorted or deformed Some are easy to cut and polish so used for buildings, statues, monuments, etc. Dynamic Metamorphism o o o o o Forms most metamorphic rocks Occurs during mountain building and some other movements of tectonic plates Occurs in large areas so also called regional metamorphism Existing rocks are subjected to high heat and pressure Mineral crystals of existing rocks are squeezed together, making the new rock more dense and less porous o Produces foliated rocks in which mineral grains are arranged in parallel layers or bands; o Splits along these layers into thin sheets o Examples – slate, schist, gneiss Contact Metamorphism o Magma forces its way into a layer of rock and heats it. It is also called thermal metamorphism o Hot liquids and gases from magma react with surrounding rock causing structural and chemical changes o Occurs in small areas so also called local metamorphism o Produces non foliated rocks in which mineral grains are arranged randomly o Does not split into layers o Examples – marble, quartzite Sedimentary Igneous Metamorphic Parent Rock → Metamorphic Rock limestone → marble Sandstone → quartzite Shale → slate Bituminous coal → anthracite coal Conglomerate → metaconglomerate granite → gneiss Basalt → metabasalt, amphibolite phyllite → schist Slate → phyllite Slate → hornfels Doc ____ METAMORPHIC ROCK NOTES Name is from the Greek meaning to ______________________ Are called “___________________rocks” because they are created from existing rocks, called “____________________rocks” – the original rock that the metamorphic rock is made from Can be from ___________________, ___________________or ___________________rocks Created by ___________________, ___________________or ___________________change ___________________below earth’s surface ___________________present are distorted or deformed Some are easy to ___________________and ___________________so used for buildings, statues, monuments, etc. Dynamic Metamorphism o Forms ___________________metamorphic rocks o Occurs during ___________________building and some other movements of ______________________________________ o Occurs in ________________areas so also called __________________ metamorphism o Existing rocks are subjected to high ___________________and ___________________ o Mineral crystals of existing rocks are squeezed together, making the new rock more ___________________and less ___________________ o Produces ___________________rocks in which mineral grains are arranged in ___________________layers or ___________________; o Splits along these layers into ___________________sheets o Examples – ___________________, ___________________, ___________________ Contact Metamorphism o ___________________forces its way into a layer of rock and ___________________it. It is also called ___________________metamorphism o Hot liquids and gases from magma react with surrounding rock causing ___________________and ___________________changes o Occurs in _________________areas so also called _________________metamorphism o Produces ___________________rocks in which mineral grains are arranged ___________________ o Does ___________________split into layers o Examples – ___________________, ___________________ Sedimentary Igneous Metamorphic Parent Rock → Metamorphic Rock limestone → marble Sandstone → quartzite Shale → slate Bituminous coal → anthracite coal Conglomerate → metaconglomerate granite → gneiss Basalt → metabasalt, amphibolite phyllite → schist Slate → phyllite Slate → hornfels