Unit 12 Classification and Kingdoms notes 2016

Name: ______________________________
Unit 12- Classification & Kingdoms
Per. ________
I.
What is Classification: (pg. 484-489)
Classification is the grouping of items (living or non-living) based on similarities
The branch of biology concerned with the grouping and naming of organisms is known as Taxonomy
II.
History of Classification
A.
Aristotle (384-322 bc) – a.
First to develop a classification system based on either animals or plants: i.
Animal- then further classified as red blood or bloodless, then based on their habitats and morphology. ii.
Plants- by size and structure as trees, shrubs or herbs.
B.
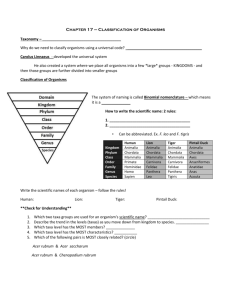
Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778)- a.
Broadened Aristotle’s classification. b.
First formal system of taxonomic organization. c.
groups are formed according to physical characteristics d.
Developed Binomial Nomenclature (Scientific Name) i.
the 2-words naming system for classification- Scientific Name ii.
The scientific name is the Genus and species
1.
The genus and species names are always italicized or underlined
2.
Genus is capitalized, species is not
3.
Once the scientific name has been used the Genus can be abbreviated by just using the first letter and then the full species. Ex:
Cardinalis cardinalis can be written as C. cardinalis (Cardinal)
4.
The scientific name for humans is Homo sapiens
C.
Modern Classification:
The study of evolution in the 1800s has added to Linnaeus’s classification system. (the use of
DNA) a.
Morphological Characters-
Organisms are classified by their similarity in form and structure. b.
Biochemical Characters-
Scientists use amino acids and nucleotides to help determine evolutionary relationships among species.
Chromosome structure and number is also used
1. Who’s more closely related to the Humans?
2. How can you tell?
3. Who is the least related to the human? Why?
Define
Classification:
When would you use it?
Who was Carolus
Linnaeus?
What does Binomial
Nomenclature mean?
How do you write a scientific name?
What is our scientific name?
Group the following
& say what morphological characteristics are shared:
Dog, cat, wolf, lion, snake, lizard, tiger, coyote, chameleon
III.
Taxonomic Categories
1.
Domain- Three groups made up of kingdoms
2.
Kingdom – broadest category, groups of closely related _phyla
3.
Phylum – groups of closely related _classes
4.
Class – groups of closely related _orders
5.
Order - groups of closely related _families
6.
Family - groups of closely related _genera
7.
Genus - groups of closely related _species
8.
Species – _Smallest and most _closely-related group; organisms that share specific
characteristics and can interbreed
Name: Plains Zebra Okapi Nubian Giraffe South African giraffe (or Cape giraffe)
Lion
K ANIMALIA
P CHORDATA
C MAMMALIA MAMMALIA MAMMALIA MAMMALIA MAMMALIA
O PERISSODACTYLA ARTIODACTLYA ARTIODACTLYA ARTIODACTLYA CARNIVORA
F EQUIDAE
G Equus
ANIMALIA
CHORDATA
GIRAFFIDAE
Okapia
ANIMALIA
CHORDATA
GIRAFFIDAE
Giraffa
ANIMALIA
CHORDATA
GIRAFFIDAE
Giraffa
ANIMALIA
CHORDATA
FELIDAE
Panthera
S quagga johnstoni
IV.
The Three Domains of Life camelopardalis giraffa leo
Domain Bacteria – Includes all remaining prokaryotes or the _Eubacteria
Domain Archaea – Includes the _Archaebacteria
Domain Eukarya – Includes all eukaryotic kingdoms - _Protista, Fungi, Plantae,
Animalia
V.
THE KINGDOMS OF LIFE (pg. 499-503)
DNA analysis has had a major impact on the classification system, changing the longaccepted system of 5 kingdoms to 6 kingdoms. The two prokaryotic kingdoms,
Archaebacteria and Eubacteria were originally classified together as Kingdom Monera
Write a mnemonic device to help you remember the order of the Taxonomic categories:
O
F
G
S
D
K
P
C
Which two animals are closely related?
________________
How can you tell?
________________
Which animals are the least related to the rest?
_________________
How can you tell?
_________________
Which kingdom(s) would be found in
Domain Bacteria?
________________
Which kingdom(s) would be found in
Domain Archeaea?
________________
Which kingdom(s) would be found in
Domain Eukarya?
_________________
_________________
_________________
Prokaryote
Non-Motile
Identify the kingdoms that fit into each
Eukaryote Multicellular Unicellular
Motile Cell Wall Absent Cell Wall Present
No Chloroplast Chloroplast Heterotrophic Autotrophic
VI.
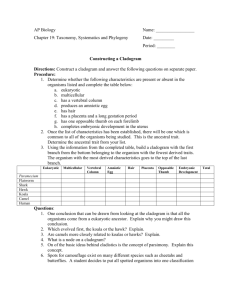
Cladograms
The cladogram is a branching diagram that depicts species divergence from common ancestors.
Similar to a pedigree, whose branches show direct ancestry, a cladogram’s branches indicate phylogeny.
They show the distribution and origins of shared characteristics.
Cladograms are testable hypotheses of phylogenetic relationships.
The groups used in cladograms are called clades. i.
A clade is one branch of the cladogram
Look at the cladogram to the right: i.
Bears & Chimpanzees have 4 derived characters in common and are presumed to share a more recent common ancestor than Chimpanzees and Lizards, which only share 3 characteristics
In the past, biologists would group organisms based solely on their physical appearance. Today, with the advances in genetics and biochemistry, biologists can look more closely at individuals to discover their pattern of evolution, and group them accordingly - this strategy is called EVOLUTIONARY CLASSIFICATION
CLADISTICS is form of analysis that looks at features of organisms that are considered "innovations", or newer features that serve some kind of purpose. (Think about what the word "innovation" means in regular language.) These characteristics appear in later organisms but not earlier ones and are called DERIVED CHARACTERS.
PART I - Analyze the Cladogram
Examine the sample cladogram, each letter on the diagram points to a derived character, or something different (or newer) than what was seen in previous groups. Match the letter to its character. Note: this cladogram was created for
simplicity and understanding, it does not represent the established phylogeny for insects and their relatives.
Identify which letter represents:
1. ______ Wings
2. ______ 6 Legs
3. ______ Segmented Body
4. ______ Double set of wings
5. ______ Cerci (abdomenal appendages)
6. ______ Crushing mouthparts
7. ______ Legs
8. ______ Curly Antennae
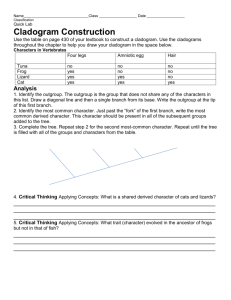
PART II - Create Your Own Cladogram
To make a cladogram, you must first look at the animals you are studying and establish characteristics that they share and ones that are unique to each group. For the animals on the table, indicate whether the characteristic is present or not. Based on that chart, create a cladogram like the one pictured above.
Cells Backbone Legs Hair Opposable Thumbs
Slug
Catfish
Frog
Tiger
Human
DRAWING OF YOUR CLADOGRAM
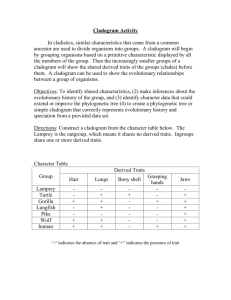
Sets
1
2
Traits
Dorsal nerve cord Notochord
Paired appendages
Vertebral Col
Paired Legs
Kangaroo Lamprey Rhesus
Monkey
X X X
X X
Bullfrog Human
X
X
X
X
Snapping
Turtle
X
X
Tuna
X
X
3
4 Aminiotic sac
X
X
X
X
X X
X
X
X
5
6
7
Mammary glands
Placenta
X X
X
X
X
Canine teeth
Foramen
Magnum
Total # of X’s
X
5 1 6 3 7 4 2
Make a Cladogram with the information above & Place the Traits, from the chart, in the appropriate location
1.
Which 2 organisms on the cladogram are more closely related?
2.
How can you tell?
3.
Which 2 organisms on the cladogram are the farthest from relation?
4.
How can you tell?