Histology and Physiology of Bone
advertisement

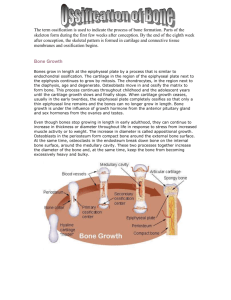
Histology and Physiology of Bone Part 2 Bone Growth 1 Bone Development • Bones develop in the fetus by 2 • Intramembranous Ossification– Form within sheet-like layers of connective tissue. – Primitive connective tissue cells enlarge and differentiate into osteoblasts (bone forming cells) – Osteoblasts deposit bone matrix on collagen fibers of tissue forming trabeculae of woven bone. – Osteoblasts continue to lay down matrix on the surface forming cancellous (spongy) bone. – Red bone marrow develops within the spaces and cells surrounding this developing bone specializes to form periosteium – Osteoblasts from periosteium lay down bone matrix to form an outer surface of compact bone. 3 • Centers of ossification– These centers expand to form a bone by gradually ossifying the membrane. – So, the centers of ossification have the oldest bone while the expanding edges the youngest. 4 • Endochondral Ossification– Remember…bone starts as a hyaline cartilage model! 5 • Steps of endochondral ossification… 6 7 8 • Primary ossification centers appear early in fetal development (~8 or 9 weeks) and secondary ossification centers appear about 1 month before birth. 9 10 11 12 13 Bone Growth 14 • Growth in Bone Length: – Long bones and bony projections increase in length because of growth at the epiphyseal plate. – Growth at the epiphyseal plate involves formation of new cartilage by interstitial cartilage growth followed by appositional bone growth on the surface of the cartilage. 15 – The hypertrophied chondrocytes die and are replaced by osteoblasts from the endosteum. – Through appositional bone growth…osteoblasts deposit new bone matrix on the calcified cartilage matrix. 16 • Growth in Bone Width… – Fast bone growth= • Osteoblasts from periosteum lay down bone to form series of ridges with grooves between them. • Periosteum covers bone ridges and extend to bottom of grooves and 1 or more BVs from periosteum lie in each groove. • Osteoblasts continue to produce bone, ridges grow and extend toward each other till they meet…forming a tunnel that contains BVs. • Osteoblasts in the periosteum lining the tunnel (endosteum) continue to lay down bone to form concentric lamella, which eventually forms osteons. 17 Factors that affect bone growth: 18 • Nutrition… • Vitamin D 19 • Hormones… – Hormones are important for bone growth. – Growth hormone: – Sex Hormones: 20 Bone Remodeling 21 Bone Repair Step 1- Hematoma formation • When a bone is injured/fractured, the BVs in the bone and surrounding periosteum are damaged = hematoma formed. 22 Step 2- Callus formation • A callus • The callus forms as the clot dissolves. 23 Step 3- Callus Ossification 24 Step 4- Bone remodeling 25