Stoechiometry Unit Jeopardy ppt
advertisement

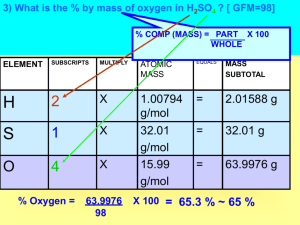
By: Hilary Megeney & Kristen Jorgensen Chemistry 11 adv Mole conversions volume STP: 22.4 L NTP: 24.4 L SATP: 24.8 L moles 6.02 x 10²³ g/mol mass atoms/molecules Pv = nRT P - pressure in kPa v - volume in liters (L) n - number of moles R - the universal constant of gases (8.31) T - temperature in K Empirical/Molecular Formula An empirical formula give the lowest whole number ratio of the elements in a compound. Take the percentage composition given of each element and then divide by their atomic mass. This gives you the number of moles. Divide all the numbers by the lowest number of moles. This gives you the amount of element in the compound. Coefficients N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3 The number in front is called the coefficient; it gives us the mole ratio. The example above has a 1:3:2 ratio. Anhydrated and Hydrated Compounds An anhydrated compound does not have any water in it. It is dry. A hydrated compound has water added to it. Stoichiometry Grams to Moles 1. Write down the balanced equation of the reaction. 2. Then use the given number of grams to calculate moles, using the factor label. Grams to Grams 1. Write down the balanced equation of the reaction. 2. Use the given number of grams as the starting value for factor label. 3. Then convert to the number of moles of that element. 4. Use the mole to mole ratio to convert in terms of the element you are solving for. 5. Convert the moles into grams by multiplying by atomic mass. Limited and Excessive Reactant When you’re given a balanced equation a precise amount of each reactant is needed, similar to a recipe. When you do an experiment you only have a limited supply of each compound. Your limited reactant is the compound that you run out of first. You excessive reactant is the compound you have left over. Defining the mole Gases Factor Label Limited and Excessive Percentages 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 400 400 400 400 400 600 600 600 600 600 800 800 800 800 800 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 What is Avogadro’s number? 6.02 x 1023 particles How many atoms are present in 1.75 mole of calcium? 1.0535 x 1024 1 mole = ? in grams (Hint: It’s unit is g/mol) 1 mole = molar mass in grams What’s the cookie analogy? 3F + 2S = 12C What is the molar mass in a compound? The molar mass in a compound is the sum of all the masses of all the elements. What is the molar mass of an element? The molar mass of an element is the number of grams of the element that is equivalent to it’s atomic mass. What is the volume of gases measured at standard ambient temperature and pressure? 24.8 L What is the volume of 0.505 mole NH3 gas at SATP? 12.524 L What are the units for Pv=nRT? • • • • Pressure – kPa Volume – L Constant – 8.31 Temperature – K What is the volume of 2.8 grams of CO2 (g) at SATP 1.578 L What is the formula for the ideal gas law? *(in words)* Pressure · volume = number of moles · constant · temperature How many litres of CO2 are produced? If 20 L of O2 are consumed at NTP, using the equation below. C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O 12 L of CO2 How many moles H2 of are produced, given the balanced equation: N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3 1.71 mol of H2 3.45g H2 x 1 mol H2 = 1.71 mol of H2 2.02g H2 How many steps are in a mass to mass problem? (factor label) 3 How many grams of NH3 are produced, given the balanced equation: N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3 19.4 g NH3 3.45g H2 x 1 mol H2 x 2 mol NH3 x 17.04gNH3 = 19.4g NH3 2.02g H2 3 mol H2 1 mol NH3 How many grams of H2(g) will be needed to react with 50.0g of N2(g) in the following reaction? N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3 10.82 grams H2 50 g H2 x 1 mol N2 x 3 mol H2 x 2.02 g H2 = 10.82 g H2 28 g N2 1 mol N2 1 mol H2 What is the mass of potassium chloride formed when 24.5 g of potassium chlorate decompose. Use the balanced equation: 2KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2 14.9 g KCl 14 g H2 x 1 mol KClO3 x 2 mol KCl x 74.55 g KCl = 14.9 g KCl 122.55 g KClO3 1 mol KClO3 1 mol KCl Potassium reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and dihydrogen. Determine the mass of water decomposed during this reaction, if there is 14 g of H2. 249.5 g H2O 2K + 2H2O → 2KOH + H2 14 g H2 x 1 mol H2 x 2 mol H2O x 18 g H2O = 249.5 g H2O 2.02 g H2 1 mol H2 1 mol H2O Define the limiting reactant? The element that is used up first Define the excessive reactant? The element that is left over after the reaction. 0.486g of magnesium react with 0.1 moles of dioxygen to form magnesium oxide. 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO Magnesium: Limited Oxygen: Excessive 0.486gMg = 0.0101 48g limited 0.1mol02 = 0.1 1mol excessive Identify the limited and excessive reactant if 1g of NH3 is mixed with 1 g HCl, using the following balanced equation. NH3(g) + HCl(g) → NH4Cl(g) NH3 – excessive HCl - limiting NH3 1 = 0.05868 17.04 HCl 1 = 0.02743 36.46 Chlorine dioxide, ClO2, has been used as a disinfectant in air-conditioning systems. It reacts with water according to the following equation. If 142.0 g of ClO2 is mixed with 38.0 g of H2O, how many grams of which reactant remain if the reaction is complete? 6ClO2 + 3H2O → 5HClO3 + HCl 19.0371 g of H2O in excess 142 g ClO2 404.7108 = 0.35087 (limited) 38 g H2O 54.04584 = 0.78107 (excessive) 142 g ClO2 x 1 mol ClO2 x 3 mol H2O x 18.01528 g H2O = 18.9629 67.4518 g ClO2 6 mol ClO2 1 mol H2O 38 – 18.9629 = 19.0371 Fill in the blanks using this equation: C2H4 + H2O → C2H5OH What happens if we mix three molecules of ethylene with 5 molecule of water? The _______ will be completely used up before all of the _______ is, and the product will contain _______ molecules. In this reaction mixture ethylene is called the ______ reactant, because it ______ the amount of product formed, and water is called the ______ reactant, because there will be _______________ HINT: you can use your textbook. What happens if we mix three molecules of ethylene with 5 molecule of water? The ethylene will be completely used up before all of the water is, and the product will contain 2 unreacted water molecules. In this reaction mixture ethylene is called the limited reactant, because it limits the amount of product formed, and water is called the excessive reactant, because there will be water molecules left over. What is percent composition? The amount of each element by mass that makes up a compound, for a total of 100% What is the percent composition of the compound H2CO3? • % of H = 2.6 % • % of C = 15.4 % • % of O = 82.1% Find the empirical formula of the compound, given the mass in percentage composition: 9.93% of carbon, 58.6 % of chlorine, and 31.4% of fluorine. CCl2F2 C = 9.93 = 0.83 Cl = 58.6 = 1.65 12.01 35.45 0.83/0.83 = 1 1.65/0.83 = 2 F = 31.4 = 1.65 19 1.65/0.83 = 2 If we mix together 28.2 grams of salicylic acid with 15.6 grams of acetic anhydride in this reaction we obtain 30.7 grams of aspirin. What is the percentage yield? In the synthesis of aspirin we react salicylic acid with acetic anhydride. 83.5% yield Salicylic acid: 28.2 = 0.1021 (limited) 276.26 Acetic anhydride: 15.6 = 1.528 (excessive) 10.21 28.2 g SA x 1 mol SA x 2 mol ASA x 180.17 ASA = 36.78 g ASA 138.13 g SA 2 mol SA 1 mol ASA theoretical Actual: Theoretical: 30.7 g = 83.5% 36.78 g Define Percentage Yield The amount of product obtained in a chemical reaction What is the difference between Empirical formula and Molecular formula? Empirical Formula represents the most simple ration between the elements.