First Year Experience
advertisement

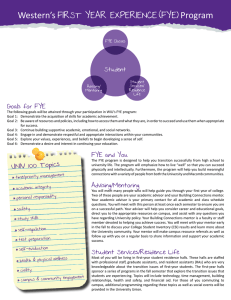
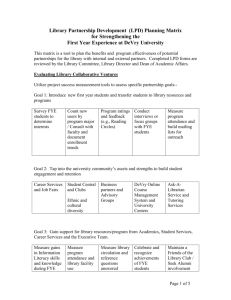
FIRST YEAR EXPERIENCE SAVANNAH HAIG INTRODUCTION • What is FYE? • Why is it important? RESEARCH QUESTIONS • Why should institution implement a Frist-Year Experience program? • In what ways do FYE programs help students make the college transition? • What effects do these programs have on student retention? • How are orientation programs essential to FYE? • What part do convocation ceremonies play in the FYE experience? • In what ways are peer mentors helpful to these programs? LITERATURE REVIEW OUTLINE • Intentions of the program • FYE as a course • Correlation with retention • Orientation • Convocation • Peer mentors PROGRAM INTENTIONS • Varies institution to institution • Connection student to school • Student’s accountability • Engagement • Scholarly curiosity • Connections • Skills for success (Jamelske, 2009) FYE AS A COURSE- OBJECTIVES • Main objective- Transition and integrate • Campus resources and activities • Skills for success • Classroom as encouraging environment • Connections with peers and faculty (Jamelske, 2009) FYE AS A COURSE- RESULTS • In 2006, 85% have a program in place • Further sense of community • Results dependent on variables, with common goals • Students agree that this is the time • Higher GPAs, larger course loads, likelihood to return • 844 -> 696, 2.777 -> 2.657 • 88% of 696 returned vs 81% (Enke, 2011) FYE AS A COURSE- INSTRUCTORS & CURRICULUM • Set of parameters to follow • No system of accountability • Formal application process • Lack of motivation and support of goals • Students respond to engaged faculty • Common Read (Jamelske, 2009) CORRELATION WITH RETENTION • A sense of community • First few weeks and first year are monumental • 2009 study, those required to live on and take course = 88% • Building the precollege experience, strengthen commitment • 2010 study, improving academics is better tool for measuring success (Schrader & Brown, 2008) (Benjamin, 2007) ORIENTATION • Few days to a week long • Front load resources • Campus, connections, academics • Handle administrative matters • Emotionally, socially, spiritually, academically • Separate orientations based on demographics • First-generations • Non-traditional • International, etc (Schrader & Brown, 2008) (Benjamin, 2007) CONVOCATION • Welcome to incoming students • Academic based message about college and mission • Ritual to further sense of community • Set the tone for upcoming year (Benjamin, 2007) PEER MENTORS • Difficult to fully define • Help with the transition • 51% of students feel as though having a PM improved their learning • Assist in teaching class • Improves GPA, lessens anxiety • Extensive hiring and training process (D’Abate, 2009) (Hall, 2011) PEER MENTORS • Advocate for students • Source of encouragement • Give access to resources • Help to figure out goals and values • Serve as guide and role model • Encourage quest for knowledge/challenge thinking • Integration with peers • New opportunities and experiences (D’Abate, 2009) (Hall, 2011) OVERALL EFFECTIVENESS • 75% found information to be helpful • 75% felt prepared for the semester ahead • 91% would recommend future students the part in the program • 77% understood what was expected of them after the fact • 66% had high levels of optimism for their potential • 76% felt part of the community CONCLUSION • Retention hardly effected • Other positive effects apparent • Transition • More involved • Better communication and stronger connections • Skills for success • Part of the community • Some demographics of students get left out CONCLUSION • Important pieces: • Orientation/welcome week • Peer mentors • Credit bearing courses • Convocation • Benefit to any institution and their first-year students REFERENCES Benjamin, M., Earnest, K., Gruenewald, D., & Arthur, G. (2007). The First Weeks of the First Year. New Directions for Student Services, (117), 13-24. D’Abate, C. (2009). Defining mentoring in the First-Year Experience: One institution's approach to clarifying the meaning of mentoring first-year students. Journal of The FirstYear Experience & Students in Transition, 21(1), 65-91. Enke, K. (2011). Lasting Connections: A case study of relationships formed during a first-year seminar course. Journal of The First-Year Experience & Students in Transition, 23(1), 75-102. Hall, R., & Jaugietis, Z. (2011). Developing peer mentoring through evaluation. Innovative Higher Education, 36(1), 41-52. Jamelske, E. (2009). Measuring the impact of a university first-year experience program on student GPA and retention. Higher Education: The International Journal of Higher Education and Educational Planning, 57(3), 373-391. Schrader, P., & Brown, S. (2008). Evaluating the First Year Experience: Students' knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors. Journal of Advanced Academics, 19(2), 310-343.