Unit 3: Microscopes, Structure and Function of Cells
advertisement

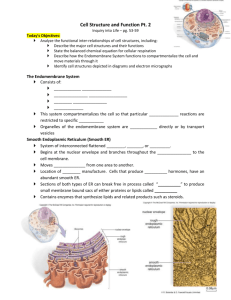
Unit 4: Microscopes, Structure and Function of Cells Endomembrane System (EMS) Monkemeier Which cellular structures are part of the Endomembrane system? Answer Endoplasmic Reticulum (smooth and rough) The Golgi Apparatus Lysosomes (animal cells only) Transport vesicles Contrast the structure and functions of rough endoplasmic reticulum with those of smooth endoplasmic reticulum Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) Contains ribosomes Produces proteins Attaches sugars to proteins Proteins fold into their three dimensional shape Packages proteins in transport vesicles which go to Golgi Apparatus Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) Produces Lipids In testes produces testosterone In liver helps detoxify drugs Describe the relationship between the components of the Endomembrane system Proteins synthesized on ribosomes on RER are via transport vesicles to Golgi Apparatus. The Golgi Apparatus receives the vesicles from the cis side. The Golgi Apparatus modifies the proteins. The modified proteins leave the Golgi Apparatus from the trans side via transport vesicles. The Transport Vesicles then transport the modified proteins either back to RER or to the cell membrane for export. Describe the relationship between the components of the Endomembrane system The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is involved with synthesis of lipids. The lipids (such as testosterone) leave the SER via transport vesicles. The transport vesicles transport the lipids to the Golgi apparatus. The Golgi Apparatus receives the transport vesicles from the cis side and releases the modified lipids from the trans side. The modified lipids within the transport vesicles get transported out of the cell. Describe the relationship between the components of the Endomembrane system The Golgi Apparatus in animal cells makes lysosomes. Lysosomes have a very low pH and are filled with hydrolytic enzymes. The lysosomes fuse with worn out cell parts and with transport vesicles to break down structures. Other Vesicles and Vacuoles Peroxisomes Made by ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Contain enzymes. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a natural by-product of cellular metabolism. Enzymes in peroxisomes break hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen gas. Prevalent in cells that are synthesizing and breaking down lipids. In germinating seeds the peroxisomes break down fatty acids into sugars needed by the growing plant. Other Vesicles and Vacuoles Vacuoles Are larger than vesicles Some are specialized (as in Protists – the contractile vacuole) to perform specific functions. Usually store substances Some animal cells contain vacuoles that store fat. Other Vesicles and Vacuoles – Plant Cell Large Central Vacuole Contains water, salt, sugars and can contain enzymes. The membrane surrounding the large central vacuole is called the tonoplast. The large central vacuole helps plants maintain their tonicity – water balance. Endomembrane System Human Diseases Tay Sachs disease involves enzymes in the lysosomes. Within the lysosome is a faulty enzyme that cannot properly break down a specific lipid. This lipid builds up in the brain and causes nerve degeneration. Children born with Tay Sachs Disease show symptoms at 6 months and usually do not live past four years old. Connections The mutation that causes Tay Sachs disease is the HEXA gene on chromosome number 15. The mutation is a change in the sequence of the DNA nucleotides. This causes a change in the protein. The protein = the enzyme that does not break down lipids properly.